Abstract
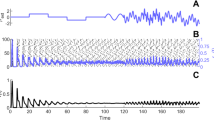
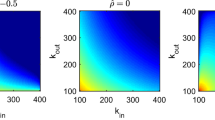
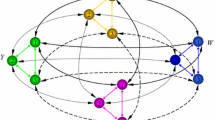
In this paper we present an oscillatory neural network composed of two coupled neural oscillators of the Wilson-Cowan type. Each of the oscillators describes the dynamics of average activities of excitatory and inhibitory populations of neurons. The network serves as a model for several possible network architectures. We study how the type and the strength of the connections between the oscillators affect the dynamics of the neural network. We investigate, separately from each other, four possible connection types (excitatory→excitatory, excitatory→inhibitory, inhibitory→excitatory, and inhibitory→inhibitory) and compute the corresponding bifurcation diagrams. In case of weak connections (small strength), the connection of populations of different types lead to periodicin-phase oscillations, while the connection of populations of the same type lead to periodicanti-phase oscillations. For intermediate connection strengths, the networks can enter quasiperiodic or chaotic regimes, and can also exhibit multistability. More generally, our analysis highlights the great diversity of the response of neural networks to a change of the connection strength, for different connection architectures. In the discussion, we address in particular the problem of information coding in the brain using quasiperiodic and chaotic oscillations. In modeling low levels of information processing, we propose that feature binding should be sought as a temporally coherent phase-locking of neural activity. This phase-locking is provided by one or more interacting convergent zones and does not require a central “top level” subcortical circuit (e.g. the septo-hippocampal system). We build a two layer model to show that although the application of a complex stimulus usually leads to different convergent zones with high frequency oscillations, it is nevertheless possible to synchronize these oscillations at a lower frequency level using envelope oscillations. This is interpreted as a feature binding of a complex stimulus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott, L. F. 1990. A network of oscillators.J. Phys. A: Math. & Gen. 23, 3835–3859.
Arnold, V. I. 1983.Geometric Methods in the Theory of Ordinary Differential Equations. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
Aronson, D., G. B. Ermentrout and N. Kopell. 1990. Amplitude response of coupled oscillators.Physica D 41, 403–449.
Baird, B. 1986. Nonlinear dynamics of pattern formation and pattern recognition in the rabbit olfactory bulb.Physica D 22, 150–175.
Borisyuk, R. M. 1991. Interacting neural oscillators can imitate selective attention. InNeurocomputers and Attention. Neurobiology, Synchronization and Chaos, A. V. Holden and V. I. Kryukov (Eds), pp. 189–200. Manchester: Manchester University Press.
Borisyuk, R. M. and L. M. Urzhumtseva. 1990. Dynamical regimes in a system of interacting neural oscillators. InNeural Networks—Theory and Architecture, A. V. Holden and V. I. Kryukov (Eds), pp. 9–20. Manchester: Manchester University Press.
Borisyuk, R. M. and A. B. Kirillov. 1992. Bifurcation analysis of a neural network model.Biol. Cybern. 66, 319–325.
Borisyuk, R. and G. Borisyuk. 1995. Complex dynamic behavior of oscillatory neural networks: examples and application.Proc. of WCNN'95 (submitted).
Borisyuk, G. N., R. M. Borisyuk, A. B. Kirillov, V. I. Kryukov and W. Singer. 1990. Modelling of oscillatory activity of neuron assemblies of the visual cortex. InProc. of Intern. Joint Conf. on Neural Networks—90,2, San-Diego, 431–434.
Borisyuk, G. N., R. M. Borisyuk, Ya. B. Kazanovich, T. B. Luzyanina, T. S. Turova and G. S. Cymbalyuk. 1992a. Oscillatory neural networks. Mathematics and applications.Math. Modeling 4, 3–43 (in Russian).
Borisyuk, G. N., R. M. Borisyuk and A. I. Khibnik. 1992b. Analysis of oscillatory regimes of a coupled neural oscillator system with application to visual cortex modeling. InNeural Network Dynamics, J. G. Taylor, E. R. Caianiello, R. M. J. Coterill and J. W. Clark (Eds). Springer Series Perspectives in Neural Computing, pp. 208–226. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
Borisyuk, G., R. Borisyuk, Y. Kazanovich and G. Strong. 1994. Modeling the binding problem and attention by synchronization of neural activity. InSPRANN'94 IMACS International Symposium on Signal Processing, Robotics and Neural Networks, Lille, France.
Cymbalyuk, G. S., E. V. Nikolaev and R. M. Borisyuk. 1994. In-phase and antiphase self-oscillations in a model of two electrically coupled pacemakers.Biol. Cybern. 71, 153–160.
Damasio, A. R. 1989. The brain binds entities and events by multiregional activation from converges zones.Neural Comput. 1, 123–132.
Dmitriev, A. S. 1993. Chaos and information processing in nonlinear dynamical systems.Radiophys. Electronics 38, 1–24 (in Russian).
Eckhorn, R., R. Bauer, W. Jordan, M. Brosch, W. Kruse, M. Muk and H. J. Reitboeck. 1988. Coherent oscillations: a mechanism of feature linking in the visual cortex?.Biol. Cybern. 60, 121–130.
Ermentrout, G. B. and J. D. Cowan. 1979. Temporal oscillations in neuronal nets.J. Math. Biol. 7, 265–280.
Ermentrout, G. B. and N. Kopell. 1991. Multiple pulse interactions and averaging in systems of coupled neural oscillators.J. Math. Biol. 29, 195–217.
Fenichel, N. 1971. Persistence and smoothness of invariant manifolds for flows.Indiana Univ. Math. J. 21, 193–226.
Finkel, L. H. and G. M. Edelman. 1989. Integration of distributed cortical systems by reentry: A computer simulation of interactive functionally segregated visual areas.J. Neurosci. 9, 3188–3208.
Freeman, W. J., 1987. Simulation of chaotic EEG patterns with a dynamical model of the olfactory system.Biol. Cybern. 56, 139–150.
Freeman, W. J. 1991. The physiology of perception.Scient. American 2, 34–41.
Freeman, W. J., Y. Yao and B. Burke. 1988. Central pattern generating and recording in olfactory bulb: a correlation learning rule.Neural Networks 1, 277–288.
Gambaudo, J., P. Glendinning and C. Tresser. 1988. The gluing bifurcation I: symbolic dynamics of the closed curves.Nonlinearity 1, 203–214.
Gray, C. M., P. König, A. K. Engel and W. Singer. 1989. Oscillatory responses in cat visual cortex exhibit inter-columnar synchronization which reflects global stimulus properties.Nature 338, 334–337.
Gray, C. M., P. König, A. K. Engel and W. Singer. 1990. Synchronization of oscillatory responses in visual cortex: a plausible mechanism for scene segmentation. InSynergetics of Cognition. H. Haken and M. Stadler (Eds). Springer Series in Synergetics45, pp. 82–98. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
Gray, C. M. and W. Singer. 1989. Stimulus-specific neuronal oscillations in orientation columns of cat visual cortex.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86, 1698–1702.
Guckenheimer, J. and Ph. Holmes. 1983.Nonlinear Oscillations Dynamical Systems, and Bifurcations of Vector Fields. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
Hansel, D., G. Mato and C. Meunier. 1993. Phase dynamics for weakly coupled Hodgkin-Huxley neurons.Europhys. Lett. 23, 367–372.
Hindmarsh, J. L. and R. M. Rose. 1982. A model of the nerve impulse using two first-order differental equations.Nature 296, 162–164.
Kawato, M., M. Sokabe and R. Suzuki. 1979. Synergism and antagonism of neurons caused by an electrical synapse.Biol. Cybern. 34, 81–89.
Kazanovich, Y. B., V. I. Kryukov and T. B. Luzyanina. 1991. Synchronization via phase-locking in oscillatory models of neural networks. InNeurocomputers and Attention. Neurobiology, Synchronization and Chaos, A. V. Holden and V. I. Kryukov (Eds), pp. 269–284. Manchester: Manchester University Press.
Kelso, J. A. S., J. P. Scholz and G. Schöner. 1986. Nonequilibrium phase transitions in coordinated biological motion: critical fluctuations.Phys. Lett. A 118, 279–284.
Khibnik, A. I. 1990.Using TraX: A Tutorial to Accompany TraX, A Program for Simulation and Analysis of Dynamical Systems. Setauket, New York: Exeter Software.
Khibnik, A. I., R. M. Borisyuk and D. Roose. 1992. Numerical bifurcation analysis of a model of coupled neural oscillators. InBifurcation and Symmetry: Cross Influences between Mathematics and Applications, E. L. Allgower, K. Boehmer and M. Golubitsky (Eds), Int. Ser. Numer. Math.104, pp. 215–228. Basel: Birkhauser.
Khibnik, A. I., Yu. A. Kuznetsov, V. V. Levitin and E. V. Nikolaev. 1993a. Continuation techniques and interactive software for bifurcation analysis of ODEs and iterated maps.Physica D 62, 360–371.
Khibnik, A. I., Yu. A. Kuznetsov, V. V. Levitin and E. V. Nikolaev. 1993b.LOCBIF: Interactive LOCal BIFurcation Analyser (version 2). Amsterdam: Computer Algebra Netherlands Expertise Center.
König, P. and T. B. Schillen. 1991. Stimulus dependent assembly formation of oscillatory responses: I. Synchronization.Neural Comput. 3, 155–166.
Kopell, N. 1988. Toward a theory of modeling central pattern generators. InNeural Control of Rhythmic Movements in Vertebrates, A. H. Cohen, S. Rossignol and S. Grillner (Eds), pp. 369–413. New York: Wiley.
Kryukov, V. I. 1991. An attention model based on the principle of dominanta. InNeurocomputers and Attention. Neurobiology, Synchronization and Chaos, A. V. Holden and V. I. Kryukov (Eds), pp. 319–352. Manchester: Manchester University Press.
Kryukov, V. I., G. N. Borisyuk, R. M. Borisyuk, A. B. Kirillov and E. L. Kovalenko. 1990. Metastable and unstable states in the brain. InStochastic Cellular Systems: Ergodicity, Memory, Morphogenesis, R. L. Dobrushin, V. I. Kryukov and A. L. Toom (Eds), pp. 225–357. Manchester: Manchester University Press.
Levitin, V. V. 1989.TraX: Simulation and Analysis of Dynamical Systems. Setauket, New York: Exeter Software.
Li, Z. and J. J. Hopfield. 1989. Modeling the olfactory bulb and its oscillatory processing.Biol Cybern. 61, 379–392.
MacGregor, R. J. 1987.Neural and Brain Modelling. New York: Academic Press.
Malkin, I. G. 1956.Some Problems of the Theory of Nonlinear Oscillations. Moscow: Gostehizdat (in Russian).
Malsburg, von der, C. and W. Schneider. 1986. A neural cocktail-party processor.Biol Cybern. 54, 29–40.
Miller, R. 1991.Cortico-Hippocampal Interplay. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
Nicolis, J. S. 1990.Chaos and Information Processing. A Heuristic Outline. Singapore: World Scientific.
Nicolis, J. S. and I. Tsuda. 1985. Chaotic dynamics of information processing—the “magic number seven plus-minus two” revised.Bull. Math. Biol. 47, 343–365.
Nikolaev, E. V. 1995. Bifurcations of limit cycles of differential equations invariant under involutory symmetry.Matemat. Sbornik. 186, 143–160 (in Russian).
Schillen, T. B. and P. König. 1991. Stimulus dependent assembly formation of oscillatory responses: II. Desynchronization.Neural Comput. 3, 167–177.
Schöner, G., W. Y. Jiang and J. A. S. Kelso. 1990. A synergetic theory of quadrupedal gaits and gait transitions.J. Theor. Biol. 142, 359–391.
Schutter, E. De, T. W. Simon, J. D. Angstadt and R. L. Calabrese. 1993. Modeling a neural oscillator that paces heartbeat in the medicinal leech.Amer. Zool. 33, 16–28.
Shinomoto, S. 1987. A cognitive and associative memory.Biol Cybern. 57, 197–206.
Shuster, H. G. and P. Wagner. 1990a. A model for neuronal oscillations in the visual cortex. I: Mean-field theory and derivation of phase equations.Biol. Cybern. 64, 77–82.
Shuster, H. G. and P. Wagner. 1990b. A model for neuronal oscillations in the visual cortex. II: Phase description of feature dependent synchronization.Biol Cybern. 64, 83.
Skeldon, A. C. 1994. Dynamics of parametrically excited double pendulum.Physica D 75, 541–558.
Sompolinsky, H., D. Golomb and D. Kleinfild. 1990a. Global processing of visual stimuli in a neural network of coupled oscillators.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 7200–7204.
Sompolinsky, H., D. Golomb and D. Kleinfild. 1990b. Phase coherence and computation in neural network of coupled oscillators. InNon-linear Dynamics and Neuronal Networks, W. Singer and H. G. Schuster (Eds). Weinheim: VCW Verlag.
Sompolinsky, H., D. Golomb and D. Kleinfild. 1991. Gooperative dynamics in visual processing.Phys. Rev. A 43, 6990–7011.
Sporns, O., J. A. Gally, G. N. Reeke and G. M. Edelman. 1989. Reentrant signaling among simulated neuronal groups leads to coherency in their oscillatory activity.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86, 7265–7269.
Tsuda, I. 1992. Dynamic link of memory—chaotic memory map in nonequilibrium neural networks.Neural Networks 5, 313–326.
Vinogradova, O. S., E. S. Brazhnik, V. S. Stafekhina and A. B. Belousoy. 1991. Septohippocampal system. Rhythmic oscillations and information selection. InNeurocomputers and Attention. Neurobiology, Synchronization and Chaos, A. V. Holden and V. I. Kryukov (Eds), pp. 129–148. Manchester: Manchester University Press.
Wang, D. L., J. Buhmann and C. von der Malsburg. 1990. Pattern segmentation in associative memory.Neural Comput. 2, 94–106.
Wang, X.-J. and J. Rinzel. 1992. Alternating and synchronous rhythms in reciprocally inhibitory model neurons.Neural Comput. 4, 84–97.
Wang, X.-J. and J. Rinzel. 1993. Spindle rhythmicity in the reticularis thalami nucleus: sinchronization among mutually inhibitory neurons.Neurosci. 53, 899–904.
Wilson, M. A. and J. M. Bower, 1988. A computer simulation of olfactory cortex with functional implications for storage and retrieva of olfactory information. InNeural Inform. Proc. Syst., D. Anderson (Ed.), pp. 114–126. New York: AIP Press.
Wilson, H. R. and J. D. Cowan. 1972. Excitatory and inhibitory interactions in localized populations of model neurons.Biophys. J. 12, 1–24.
Yao, Y. and W. J. Freeman. 1990. Model of biological pattern recognition with spatially chaotic dynamics.Neural Networks 3, 153–170.
Yao, Y., W. J. Freeman, B. Burke and Q. Yang. 1991. Pattern recognition by a distributed neural network: an industrial application.Neural Networks,3, 153–170.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Borisyuk, G.N., Borisyuk, R.M., Khibnik, A.I. et al. Dynamics and bifurcations of two coupled neural oscillators with different connection types. Bltn Mathcal Biology 57, 809–840 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02458296
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02458296