Abstract
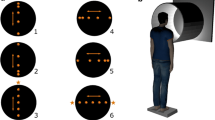
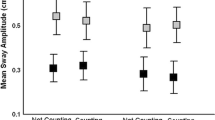
The purpose of this study was to establish whether visual motion parallax participates in the control of postural sway. Body sway was measured in ten normal subjects by photoelectric recordings of head movements and by force-plate posturography. Subjects viewed a visual display (“background”), which briefly moved (2 s) along the y (horizontal) axis, under three different conditions: (1) direct fixation of the background, (2) fixation of a stationary window frame in the foreground, and (3) fixation of the background in the presence of the window in the foreground (“through the window”). In response to background fixation, subjects swayed in the same direction as stimulus motion, but during foreground (window) fixation they swayed in the opposite direction. The earlier forces observed on the force platform occurred at circa 250 ms in both conditions. The results show that motion parallax generates postural responses. The direction of these parallax-evoked postural responses — opposite to other visually evoked postural responses reported so far — is appropriate for stabilizating posture in natural circumstances. The findings show that motion parallax is an important source of self-motion information and that this information participates in the process of automatic postural control. In the “fixating through the window” condition, which does not mimic visual conditions induced by body sway, no consistent postural responses were elicited. This implies that postural reactions elicited by visual motion are not rigid responses to optokinetic stimulation but responses to visual stimuli signalling self-motion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergin PS, Bronstein AM, Murray NMF, Sancovic S, Zeppenfeld K (1995) Bodysway and vibration perception thresholds in normal ageing and in patients with polyneuropathology. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 58:335–340
Bles W, Kapteyn TS, Brandt T, Arnold F (1980) The mechanism of physiological height vertigo. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 89:534–540
Bronstein AM (1986) Suppression of visually evoked postural responses. Exp Brain Res 63:655–658
Bronstein AM (1994) Visually induced body sway in patients with visual vertigo. In: Taguchi K, Igarashi M, Mori S (eds) Vestibular and neural front. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, pp 569–572
Diener HC, Dichgans J, Bacher M, Gompf B (1984) Quantification of postural sway in normals and patients with cerebellar diseases. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 57:134–142
Dichgans J, Brandt T (1978) Visual-vestibular interaction: effects of self-motion perception and postural control. In: Held R, Leibowitz HW, Teuber H-L (eds) Perception. (Handbook of sensory physiology, vol III) Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 755–804
Ellard CG, Goodale MA, MacLaren Scorfield D, Lawrence C (1986) Visual cortical lesions abolish the use of motion parallax in the Mongolian gerbil. Exp Brain Res 64:599–602
Keshner A, Allum JHJ, Pfaltz CR (1987) Postural coactivation and adaption in the sway stabilishing responses of normals and patients with bilateral vestibular deficit. Exp Brain Res 69:77–92
Lee DN, Lishman JR (1975) Visual proprioceptive control of stance. J Hum Mov Stud 1:87–95
Lestienne F, Schoechting JF, Berthoz A (1977) Postural readjustments induced by linear motion of visual scenes. Exp Brain Res 28:363–384
Mauritz KH, Dietz V (1980) Characteristics of postural instability induced by ischemic blocking of leg afferents. Exp Brain Res 38:117–119
Paulus WM, Straube A, Brandt T (1984) Visual stabilisation of posture. Physiological stimulus characteristics and clinical aspects. Brain 107:1143–1163
Pola J, Wyatt HJ, Lustgarten M (1995) Visual fixation of a target and suppression of optokinetic nystagmus: effects of varying target feedback. Vision Res 35:1079–1087
Rogers BJ (1993) Motion Parallax. In: Miles FA, Wallman J (eds), Visual motion and its role in the stabilization of gaze. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, pp 119–137
Roy J-P, Wurtz RH (1990) The role of disparity-sensitive cortical neurons in signalling the direction of self-motion. Nature 348:160–162
Roy J-P, Komatsu H, Wurtz RH (1992) Disparity sensetivity of neurons in monkey extrastriate area MST. J Neurosci 12(7): 2478–2492
Sobel EC (1990) The locust's use of motion parallax to measure distance. J Comp Physiol [A] 167:579–588
Wallach H (1959) Perception of motion. Sci Am 201:56–62
Warren WH, Hannon DJ (1990) Eye movements and optical flow. J Opt Soc Am 7:160–169
Wolsley CJ, Sakellari V, Bronstein AM (1996) Reorientation of visually induced postural responses by different eye-in-orbit and head-on-trunk angular positions. Exp Brain Res 111:283–288
Woollacott MH (1983) Effects of ethanol on postural adjustments in humans. Exp Neurol 80:55–68
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bronstein, A.M., Buckwell, D. Automatic control of postural sway by visual motion parallax. Exp Brain Res 113, 243–248 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02450322
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02450322