Abstract
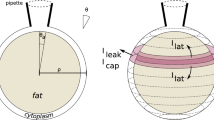
A mathematical description of pH excursions produced in interstitial fluid by a spherical stimulation electrode is presented. The pH is calculated as a function of current density, electrode radius, distance, time, and pulsing regimen for an electrode driven by biphasic current pulses. Calculations indicate that large pH excursions occur around electrodes pulsed at current densities used for neural stimulation. For an electrode with a radius of about 1 μm these transient pH changes extend only a few micrometers from the electrode surface. The practical importance of these pH changes remains to be determined.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altman, P.L. and D.S. Ditter, Editors, Respiration and circulation.Fed. Am. Soc. Exper. Biol. Bethesda, 1971, p. 225.
Brummer, S.B. and M.J. Turner. Electrochemical considerations for safe electrical stimulation of the nervous system with platinum electrodes.IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 24:59, 1977.
Carslaw, H.S. and J.C. Jaeger.Conduction of Heat in Solids, 2nd ed. Oxford University Press, Ely House, London, W. 1, 1959, p. 248.
Cotton, F.A. and G. Wilkinson.Advanced Inorganic Chemistry: A Comprehensive Text, 4th ed. New York: John Wiley and Sons, 1980, pp. 366–367.
Guyton, D.L. and F.T. Hambrecht. Theory and design of capacitor electrodes for chronic stimulation.Med. Bio. Eng. 12:613, 1974.
Johnson, P.F., J.J. Bernstein, G. Hunter, W.W. Dawson, and L.L. Hench. An in vitro and in vivo analysis of anodized tantalum capacitive electrodes: Corrosion response, physiology, and histology.J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2:637–656, 1977.
Johnson, P.F. and L.L. Hench. An in vitro analysis of metal electrodes for use in the neural environment.Brain Behav. Evol. 14:23–45, 1977.
Lambertsen, C.J. InMedical Physiology, vol. 2, edited by V.B. Mountcastle. St. Louis: C.V. Mosby Co., 1980, pp. 1737–38.
Lassiter, W.E. and C.W. Gottschalk. InMedical Physiology, vol. 2, edited by V.B. Mountcastle. St. Louis: C.V. Mosby Co., 1980, pp. 1159–60.
Lilly, J.C. InElectrical Stimulation of the Brain, edited by D.E. Sheer. Texas University Press: Kingsville, 1961, p. 60.
Lilly, J.C., et al. Brief noninjurious electric waveform for stimulation of the brain.Science 121:468, 1955.
Muntwyler, E.Water and Electrolyte Metabolism and Acid-Base Balance. St. Louis: C.V. Mosby Co., 1968, p. 84.
Newman, J.S.Electrochemical Systems. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall, 1973, pp. 217–227.
Robblee, L.S., J.L. Lefko, and S.B. Brummer. Activated Ir: An electrode suitable for reversible charge injection in saline solution.J. Electrochem. Soc. 3:731–733, 1983.
Robinson, R.A. and R.H. StokesElectrolyte Solutions: The Measurement and Interpretation of Conductance, Chemical Potential and Diffusion in Solutions of Simple Electrolytes, 2nd Edition London: Butterworths, 1959, pp. 518, 523.
Ruggeri, R.T. and T.R. Beck. Calculations of the temperature rise produced in body tissue by a spherical electrode.Ann. Biomed. Eng. 13:177–194, 1985.
Welt, L.B.Clinical Disorders of Hydration and Acid-Base Equilibrium. Boston: Little, Brown and Co., pp. 14–20, 1955.
Ibid., pp. 37–38.
Yuen, T.G.H., et al. Histological evaluation of neural damage from electrical stimulation: Consideration for selection of parameters for clinical application.Neurosurgery 9:292–299, 1981.
Reference
J.T. Edsall. Carbon Dioxide, Carbonic Acid, and Bicarbonate Ion: Physical Properties and Kinetics of Interconversion. InCO 2:Chemical, Biochemical and Physiological Aspects, edited by R.E. Forster, et al. NASA Special Publication Series SP-188, 1969.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ballestrasse, C.L., Ruggeri, R.T. & Beck, T.R. Calculations of the pH changes produced in body tissue by a spherical stimulation electrode. Ann Biomed Eng 13, 405–424 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02407769
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02407769