Summary
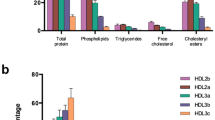
Both Type 1 (insulin-dependent) and Type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetic individuals are at increased risk of developing ischaemic heart disease. Insulin excess, present in both diabetic groups, may play an important pathophysiologic role in accelerating the atherogenic process. In this study, cultured human skin fibroblasts were incubated with varying concentrations of insulin to test the role of insulin on cell cholesterol homeostasis and on HDL3-mediated removal of excess cholesterol from cells. Insulin excess (1-2-100 nmol/l) resulted in a significant dose-dependent reduction in HDL3-mediated cholesterol efflux from the intracellular unesterified cholesterol pool of cultured human skin fibroblasts. Similar insulin concentrations resulted in impaired HDL-mediated cholesterol efflux from the cell membrane but had no effect on non-HDL-mediated efflux. The effect of insulin on cholesterol esterification and biosynthesis was assessed by14C-oleate labelling. The addition of HDL3 (50 μg) resulted in a significant decrease in14C-labelled cholesterol ester, reflecting a decrease in intracellular unesterified cholesterol, which was partially reversed by the addition of insulin. Insulin had no effect on the incorporation of14C-oleate into unesterified cholesterol. During simultaneous incubation of fibroblasts with LDL and HDL, insulin resulted in an increase in cholesterol esterification and inhibited ability of HDL to promote the decrease in esterification. Thus, we have shown that insulin exess counteracts the beneficial effects of HDL that involve removal of cellular cholesterol and may in part promote atherogenesis by this mechanism
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garcia MJ, McNamara PM, Gordon T, Kannell WB (1974) Morbidity and mortality in diabetics in the Framingham population: sixteen year follow-up study. Diabetes 23: 105–111
Chait A, Bierman EL, Brunzell JD (1985) Diabetic macroangiopathy. In: Alberti KGMM, Krall LP (eds) The diabetes annual I. Elsevier Science Publishers, Amsterdam, pp 323–348
Reaven GM (1987) Non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus, abnormal lipoprotein metabolism, and atherosclerosis. Metabolism 36 [Suppl 1]: 1–18
Colwell JA, Lopes-Virella MF, Halushka PV (1981) Pathogenesis of atherosclerosis in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 4: 121–133
Biesbroeck RC, Albers JJ, Wahl PW, Weinberg CR, Bassett ML, Bierman EL (1982) Abnormal composition of high density lipoproteins in non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetes 31: 126–131
Bagdade JD, Subbaiah PV (1989) Whole-plasma and high-density lipoprotein subfraction surface lipid composition in IDDM men. Diabetes 38: 1226–1230
Glomset JA (1968) The plasma lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase reaction. J Lipid Res 9: 155
Rasmussen SM, Heding LG, Parbst E (1975) Serum IRI in insulin treated diabetes during a 24-hour period. Diabetologia 11: 151–158
Werther GA, Jenkins PA, Turner RC, Baum JD (1980) Twenty-four hour metabolic profiles in diabetic children receiving insulin injections once or twice daily. BMJ 281: 414–418
Modan M, Halkin H, Lusky A, Segal P, Fuchs Z, Chetrit A (1988) Hyperinsulinemia is characterized by jointly disturbed plasma VLDL, LDL, and HDL levels. Arteriosclerosis 8: 227–236
Zavaroni I, Bonora E, Pagliara M et al. (1989) Risk factors for coronary artery disease in healthy persons with hyperinsulinemia and normal glucose tolerance. N Engl J Med 320: 702–706
Pyörälä K, Savolainen E, Kaukola S, Haapakoski J (1985) Plasma insulin as coronary heart disease risk factor: relationship to other risk factors and predictive value during 9 1/2 year follow-up on the Helsinki Policemen Study Population. Acta Med Scand 701: 38–52
Eschwege E, Ducimetiere P, Thibult N, Richard J-L, Claude J-R, Rosselin GE (1985) Coronary heart disease mortality in relation with diabetes, blood glucose and plasma insulin levels. The Paris prospective study, ten years later. Horm Metab Res 15: 41–45
Bierman EL (1992) Atherogenesis in diabetes. Arterioscler Thromb 12: 647–659
Laws A, King AC, Haskell WL, Reaven GM (1991) Relation of fasting plasma insulin concentration to high density lipoprotein cholesterol and triglyceride concentrations in men. Arterioscler Thromb 11: 1636–1642
Welborn TA, Wearne K (1979) Coronary heart disease incidence and cardiovascular mortality in Busselton with reference to glucose and insulin concentration. Diabetes Care 2: 154–160
Bergstrom RW, Leonetti DL, Newell-Morris LL, Shuman WP, Wahl PW, Fujimoto WY (1990) Association of plasma triglyceride and C-peptide with coronary heart disease in Japanese-American men with a high prevalence of glucose intolerance. Diabetologia 33: 489–496
Ronnemaa T, Laakso M, Pyörälä K, Puukka P (1991) High fasting plasma insulin is an indicator of coronary heart disease in non-insulin dependent diabetic patients and non-diabetis subjects Arterioscler Thromb 11: 80–90
Brinton EA, Oram JF, Chen C-H, Albers JJ, Bierman EL (1986) Binding of high density lipoprotein to cultured fibroblasts after chemical alteration of apoprotein amino acid residues. J Biol Chem 261: 495–503
Chung BH, Wilkinson T, Geer JC, Segrest JP (1980) Preparative and quantitative isolation of plasma lipoproteins: rapid, single discontinuous density gradient ultracentrifugation in a vertical rotor. J Lipid Res 21: 284–291
Slotte JP, Oram JF, Bierman EL (1987) Binding of high density lipoprotein to cell receptors promotes translocation of cholesterol from intracellular membranes to the cell surface. J Biol Chem 262: 12904–12907
Aviram M, Bierman EL, Oram JF (1989) High density lipoprotein stimulates sterol translocation between intracellular and plasma membrane pools in human monocyte-derived macrophages. J Lipid Res 30: 65–76
Oram JF, Mendez AJ, Slotte JP, Johnson TF (1991) High density lipoprotein apolipoproteins mediate removal of sterol from intracellular pools but not from plasma membranes of cholesterolloaded fibroblasts. Arterioscler Thromb 11: 403–414
Oram JF (1986) Receptor-mediated transport of cholesterol between cultured cells and high density lipoproteins. Methods Enzymol 129: 645–659
Folch J, Lees M, Sloane-Stanley GH (1957) A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues J Biol Chem 226: 497–509
Oram JF, Brinton EA, Bierman EL (1983) Regulation of HDL receptor activity in cultured human skin fibroblasts and human arterial smooth muscle cells. J Clin Invest 72: 1611–1621
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193: 265–275
Chait A, Bierman EL, Albers JJ (1979) Low density lipoprotein receptor activity in cultured human skin fibroblasts: mechanism of insulin-induced stimulation. J Clin Invest 64: 1309
Oppenheimer MJ, Sundquist K, Bierman EL (1989) Downregulation of high density lipoprotein receptor activity in human fibroblasts by insulin and IGF-1. Diabectes 38: 117–122
Stout RW, Vallance Owen J (1969) Insulin and atheroma. Lancet 1: 1078–1080
Stout RW (1977) The effect of insulin and glucose onsterol synthesis in cultured rat arterial smooth muscle cells. Atherosclerosis 27: 271–278
Young JR, Stout RW (1987) Effects of insulin and glucose in the cells of the arterial wall: interaction of insulin with dibutyryl cyclic AMP and low density lipoprotein on arterial cells. Diabete Metab 13: 301–306
Bathena SJ, Avigan J, Schreiner ME (1974) Effect of insulin on sterol and fatty acid synthesis and hydroxymethylglutaryl CoA reductase activity in mammalian cells grown in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 71: 2174–2178
Oppenheimer MJ, Oram JF, Bierman EL (1987) Downregulation of high density lipoprotein receptor activity of cultured fibroblasts by platelet-derived growth factor. Arteriosclerosis 7: 325–332
Far'ias RN, Vinals AL, Morero RD (1986) Fusion of negatively charged phospholipid vesicles by insulin: relationship with lipid fluidity. J Biol Chem 261: 15508–15512
Laakso M, Pyörälä K, Voutilainen E, Marniemi J (1987) Plasma insulin and serum lipids and lipoproteins in middle-aged non-insulin dependent diabetic and non-diabetic subjects. Am J Epidemiol 125: 611–621
Jiao S, Kameda K, Mutsuzuwa Y, Kubo M, Nonaka K, Tarui SC (1986) Influence of endogenous hyperinsulinism on HDL2 level in impaired glucose tolerance. Atherosclerosis 60: 279–286
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brazg, R.L., Bierman, E.L. Insulin excess counteracts the effects of HDL on intracellular sterol accumulation in cultured human skin fibroblasts. Diabetologia 36, 942–947 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02374477
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02374477