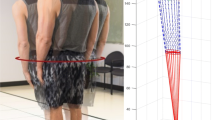
Abstract
In adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS), surgical planning currently relies on spinal flexibility evaluation using lateral bending radiographs. The aim was to evaluate the feasibility of non-invasive dynamic analysis of trunk kinematics and muscle activity in patients with AIS before surgical correction. During various lateral trunk bending tasks, erector spinae (18 sites) and abdominal (four sites) muscle activity was sampled using surface electrodes in ten AIS patients and in ten controls. Simultaneously, the spatial displacements of infrared emitting diodes located on the trunk were sampled. Parameters considered were the heterolateral-to-homolateral root-mean-square EMG ratios R at each site and total lateral bending and thoracic and lumbar curvature angle courses. Main alterations concerned apical muscle activity during left bending tasks. ANOVA results showed a significant effect of side (p=2.1×10−9), EMG recording site (p=1.9×10−16), pathology (p=3.9×10−16) and task (p=2.2×10−11) on R ratios. The R ratio at T10 and L1 for a simple lateral bending task during left bending averaged 4.8 (SD 4.3) and 3.0 (SD 3.1) in AIS patients, and 2.3 (SD 2.8) and 1.3 (SD 0.4) in controls (p=6.4×10−4 and 2.5×10−3, LSD post hoc). This preliminary study allowed the development of a functional, noninvasive, non-irradiating dynamic tool for pre-operative evaluation in AIS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aronsson, D. D., Stokes, I. A., Ronchetti, P. J., andRichards, B. S. (1996): ‘Surgical correction of vertebral axial rotation in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: prediction by lateral bending films’,J. Spinal Disord.,9, pp. 214–219
Alexander, M. A., andSeason, E. H. (1978): ‘Idiopathic scoliosis: an electromyographic study’,Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil.,59, pp. 314–315
Avikainen, V. J., Rezasoltani, A., andKauhanen, H. A. (1999): ‘Asymmetry of paraspinal EMG-time characteristics in idiopathic scoliosis’,J. Spinal Disord,12, pp. 61–67
Behensky, H., Krismer, M., andBauer, R. (1998): ‘Comparison of spinal mobility after Harrington and CD instrumentation’,J. Spinal Disord,11, pp. 155–162
Bylund, P., Jansson, E., Dahlberg, E., andEriksson, E. (1987): ‘Muscle fiber types in thoracic erector spinae muscles. Fiber types in idiopathic and other forms of scoliosis’,Clin. Orthop.,214, pp. 222–228
Chan, Y. L., Cheng, J. C., Guo, X., King, A. D., Griffith, J. F., andMetreweli, C. (1999): ‘MRI evaluation of multifidus muscles in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis’,Pediatr. Radiol.,29, pp. 360–363
Cheung, K. M., andLuk, K. D. (1997): ‘Prediction of correction of scoliosis with use of the fulcrum bending radiograph’,J. Bone Joint Surg.,79-A, pp. 1144–1150
Coussement, A., Faure, C., andCoussement, N. (1980): ‘Repères et mesures en radiodiagnostic’, 3rd edn (Expansion Scientifique Française, Paris, 1980)
Donovan, W. H., Dwyer, A. P., andBedbrook, G. M. (1980): ‘Electromyographic activity in paraspinal musculature in patients with idiopathic scoliosis before and after Harrington instrumentation’,Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil.,61, pp. 413–417
Ford, D. M., Bagnall, K. M., McFadden, K. D., Greenhill, B. J., andRaso, V. J. (1984): ‘Paraspinal muscle imbalance in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis’,Spine,9, pp. 373–376
Gram, M. C., andHasan, Z. (1999): ‘The spinal curve in standing and sitting postures in children with idiopathic scoliosis’,Spine,24, pp. 169–177
Guth, V., Abbink, F., Gotze, H. G., andHeinrichs, W. (1978): ‘Ganguntersuchung an Patienten mit idiopathischen Skoliosen und der Einfluss des Milwaukee-Korsetts auf das Gangbild’,Z. Orthop. Ihre Grenzgeb.,116, pp. 631–640
Hopf, C., Scheidecker, M., Steffan, K., Bodem, F., andEysel, P. (1998): ‘Gait analysis in idiopathic scoliosis before and after surgery: a comparison of the pre-and postoperative muscle activation pattern’,Eur. Spine J.,7, pp. 6–11
Hopf, C. (2000): ‘Kriterien zur Behandlung idiopathischer Skoliosen zwischen 40 degrees und 50 degrees. Operative vs. konservative Therapie’,Orthopäde,29, pp. 500–506
Hsu, J. D., Slager, U. T., Swank, S. M., andRobinson, M. H. (1988): ‘Idiopathic scoliosis a clinical, morphometric and histopathological correlation’,J. Pediatr. Orthop.,8, pp. 147–152
Kennelly, K. P., andStokes, M. J. (1993): ‘Pattern of asymmetry of paraspinal muscle size in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis examined by real-time ultrasound imaging. A preliminary study’,Spine,18, pp. 913–917
Khosla, S., Tredwell, S. J., Day, B., Shinn, S. L., andOvalle, W. K. (1980): ‘An ultrastructural study of multifidus muscle in progressive idiopathic scoliosis. Changes resulting from a sarcolemmal defect at the myotendinous junction’,J. Neurol. Sci.,46, pp. 13–31
Kleinman, R. G., Csongradi, J. J., Rinksy, L. A., andBleck, E. E. (1982): ‘The radiographic assessment of spinal flexibility in scoliosis: a study of the efficacy of the prone push film’,Clin. Orthop.,162, pp. 47–53
Lenke, L. G., Betz, R. R., Bridwell, K. H., Clements, D. H., Harms, J., Lowe, T. G., andShufflebarger, H. L. (1998): ‘Intraobserver and interobserver reliability of the classification of thoracic adolescent idiopathic scoliosis’,J. Bone Joint Surg.,80-A, pp. 1097–1106
Lowe, T. G., Edgar, M., Margulies, J. Y., Miller, N. H., Raso, V. J., Reinker, K. A., andRivard, C. H. (2000): ‘Etiology of idiopathic scoliosis: current trends in research’,J. Bone Joint Surg.,82-A, pp. 1157–1168
Mannion, A. F., Meier, M., Grob, D., andMuntener, M. (1998): ‘Paraspinal muscle fibre type alterations associated with scoliosis: an old problem revisited with new evidence’,Eur. Spine J.,7, pp. 289–293
Mason, D. B., Schindler, A., andKing, N. (1998): ‘Estimation of the lumbar curve magnitude with correction of the right thoracic curve in idiopathic scoliosis’,J. Pediatr. Orthop.,18, pp. 602–605
Meier, M. P., Klein, M. P., Krebs, D., Grob, D., andMuntener, M. (1997): ‘Fiber transformations in multifidus muscle of young patients with idiopathic scoliosis’,Spine,22, pp. 2357–2364
Mooney, V., Gulick, J., andPozos, R. (2000): ‘A preliminary report on the effect of measured strength training in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis’,J. Spinal Disord.,13, pp. 102–107
Odermatt, D., Mathieu, P. A., Beauséjour, M., Aubin, C. É., andLabelle, H. (2002). ‘Electromyographic study of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients treated wit the Boston brace’,Submitted to Spine
Reuber, M., Schultz, A., McNeill, T., andSpencer, D. (1983): ‘Trunk muscle myoelectric activities in idiopathic scoliosis’,Spine,8, pp. 447–456
Robinson, C. M., andMcMaster, M. J. (1996): ‘Juvenile idiopathic scoliosis Curve patterns and prognosis in one hundred and nine patients’,J Bone Joint Surg.,78-A, pp. 1140–1148
Sahgal, V., Shah, A., Flanagan, N., Schaffer, M., Kane, W., Subramani, V., andSingh, H. (1983): ‘Morphologic and morphometric studies of muscle in idiopathic scoliosis’,Acta Orthop. Scand.,54, pp. 242–251
Smith, R. M., andEmans, J. S. (1992): ‘Sitting balance in spinal deformity’,Spine,17, pp. 1103–1109
Tachdjian, M. O. (1990): ‘Pediatric Orthopedics’, 2nd edn, Vol. 3, (Saunders, Philadelphia, 1990)
Vaughan, J. J., Winter, R. B., andLonstein, J. E. (1996): ‘Comparison of the use of supine bending and traction radiographs in the selection of the fusion area in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis’,Spine,21, pp. 2469–2473
Vedantam, R., Lenke, L. G., Bridwell, K. H., andLinville, D. L. (2000): ‘Comparison of push-prone and lateral-bending radiographs for predicting postoperative coronal alignment in thoracolumbar and lumbar scoliotic curves’,Spine,25, pp. 76–81
Yekutiel, M., Robin, G. C., andYarom, R. (1981): ‘Proprioceptive function in children wit adolescent idiopathic scoliosis’,Spine,6, pp. 560–566
Zetterberg, C., Aniansson, A., andGrimby, G. (1983): ‘Morphology of the paravertebral muscles in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis’,Spine,8, pp. 457–462
Zetterberg, C., Bjork, R., Ortengren, R., andAndersson, G. B. (1984): ‘Electromyography of the paravertebral muscles in idiopathic scoliosis. Measurements of amplitude and spectral changes under load’,Acta. Orthop. Scand.,55, pp. 304–309
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feipel, V., Aubin, C.E., Ciolofan, O. et al. Electromyogram and kinematic analysis of lateral bending in idiopathic scoliosis patients. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 40, 497–505 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02345446
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02345446