Abstract
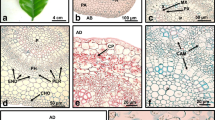
Somatic embryogenesis fromTheobroma cacao L. flower buds, as previously reported on five Forastero hybrid genotypes, was tested on several other genotypes, belonging to the three cocoa-tree groups: Forastero, Trinitario and Criollo. The results gave evidence of genotypic efficiencies. Explants were cultivated under two successive conditions: callogenesis and expression media. The morphological and histological responses were different for embryogenic or non-embryogenic genotypes. For embryogenic genotypes, only staminodes and stamen filaments were able to produce somatic embryos: after a few days on the expression medium, groups of callus cells went through the meristematic and then embryonic stages, and finally formed somatic embryos. Many of them showed abnormalities. Simultaneously, some embryogenic cells were visible. These started to divide to form pro-embryos which however were unable to evolve into proper somatic embryos.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ButtonJ, KochbaJ & BornmanCH (1974) Fine structure of an embryoid development from embryogenic ovular callus of ‘Shamouti’ Orange (Citrus sinensis Osb.). J. Exp. Bot. 25: 446–457
ChateletP, Michaux-FerrièreN & DublinP (1992) Potentialités embryogènes du nucelle et du tégument interne de graines immatures de Cacaoyer (Theobroma cacao L.). C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris 315: 55–62
ElMaâtaouiM, EspagnacH & Michaux-FerrièreN (1990) Histology of callogenesis and somatic embryogenesis induced in stem fragments of cork oak (Quercus suber) culturedin vitro. Ann. Bot. 66: 183–190
EmonsAMC (1994) Somatic embryogenesis: cell biological aspects. Acta Bot. Neerl. 43: 1–14
Esan EB (1975) Tissue culture studies on cocoa (Theobroma cacao L.). A supplementation of current research. In: Proceedings, Fifth International Conference on Cacao Research Idaban, Nigeria (pp 116–125)
FisherDB (1968) Protein staining of ribboned epon sections for light microscopy. Histochemie 16: 92–96
FuentesSI, SuarezR, VillegasT, Castro AceroL & HernandezG (1993) Embryogenic response of Mexican Alfalfa (Medicago sativa) varieties. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 34: 299–302
HalperinW & WetherellDF (1965) Ontogeny of adventive embryos of wild carrot. Science 147: 756–758
HalperinW & JensenAJ (1967) Ultrastructural changes during growth and embryogenesis in carrot cell cultures. J. Ultrastructure Research 18: 428–443
Janick J (1986) Somatic embryogenesis in cacao and jojoba. In: Proceedings of the International Society for Tropical Horticulture, Vol 30 (pp 209–213). XXXIV Annual Meeting, San Jose, Costa Rica
LitzRE (1986) Tissue culture studies withTheobroma cacao. In: DimickP S (ed) Cacao Biotechnology Symposium Proceedings (pp 111–120). University Park, PA, Pennsylvania State University Press
Lopez-BaezO, BollonH, EskesA & PetiardV (1993) Embryogenèse somatique de cacaoyerTheobroma cacao L. à partir de pièces florales. C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris 316: 579–584
LuC & VasilIK (1985) Histology of somatic embryogenesis inPanicum maximum (Guinea grass). Am. J. Bot. 72: 1908–1913
MaheswaranG & WilliamsEG (1985) Origin and development of somatic embryos formed directly on immatured embryos ofTrifolium repens in vitro. Ann. Bot. 56: 619–630
MartojaR & MartojaM (1967) Initiation aux techniques de l'histologie animale. Masson et Cie, Paris
MerkleSA, HoeyMT, Watson-PauleyBA & SchlarbaumS (1993) Propagation ofLiriodendron hybridsvia somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 34: 191–198
Michaux-FerrièreN, DublinP & SchwendimanJ (1987) Etude histologique de l'embryogenèse somatique à partir d'explants foliaires deCoffea arabica L. Café Cacao Thé 31: 103–114
Michaux-FerrièreN & CarronMP (1989) Histology of early somatic embryogenesis inHevea brasiliensis: the importance of the timing of subculturing. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 19: 243–256
Michaux-FerrièreN, GroutH & CarronMP (1992) Origin and ontogenesis of somatic embryos inHevea brasiliensis (Euphorbiaceae). Am. J. Bot. 79: 174–180
Michaux-FerrièreN & SchwendimanJ (1992) Histology of somatic embryogenesis. In: DattéeY, DumasC & GallaisA (Ed) Reproductive biology and plant breeding (pp 247–259). Springer-Verlag, Berlin
MurashigeT & SkoogF (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Phys. Plant. 15: 473–497
PedrosoMC & PaisMS (1993) Direct embryo formation in leaves ofCamellia japonica L.. Plant Cell Rep. 12: 639–643
PenceVC, HasegawaPM & JanickJ (1980) Initiation and development of asexual embryos ofTheobroma cacao in vitro. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 98: 1–4
Pence VC (1989) Cacao (Theobroma cacao L.). In: YPS Bajaj (ed) Biotechnology in Agriculture and Forestry, Vol 5. Trees II. (pp 203–221)
QuinnJ, SimonJE & JanickJ (1980) Histology of zygotic and somatic embryogenesis in borage. J. Am. Soc. Hort. Sci. 4: 516–520
SharpWR, SöndahlMR, CaldasLS & MaraffaSB (1980) The physiology ofin vitro asexual embryogenesis. Horticultural Reviews. 30: 268–310
SchwendimanJ, PannetierC & Michaux-FerrièreN (1988) Histology of somatic embryogenesis from leaf explants of the oil palmElaeis guineesis Jacq. Ann. Bot. 62: 43–52
SchwendimanJ, PannetierC & Michaux-FerrièreN (1990) Histology of embryogenic formations duringin vitro culture of oil palmElaeis guineensis Jacq. Oléagineux. 45: 409–418
SöndahlMR, LiuS, BellatoCM & BraginA (1993) Cacao somatic embryogenesis. Acta Horticulturae 336: 245–248
StewardFC, MapesMO & MearsK (1958) Growth and organized development of cultured cells. II. Organization in cultures grown from freely suspended cells. Am. J. Bot. 45: 705–708
Verdeil JL (1993) Etude de la régénération du cocotier (Cocos nucifera L.) par embryogenèse somatique à partir d'explants inflorescentiels. Thesis. Paris VI University
WilliamsEG & MaheswaranG (1986) Somatic embryogenesis: factors influencing coordinated behaviour of cells as an embryogenic group. Ann. Bot. 57: 443–462
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alemanno, L., Berthouly, M. & Michaux-Ferrière, N. Histology of somatic embryogenesis from floral tissues cocoa. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 46, 187–194 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02307094
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02307094