Abstract
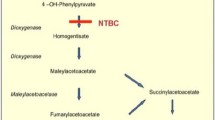
Affected twins with acute hereditary tyrosinaemia type I are described. Attempts at therapy with a phenylalanine-tyrosine-methionine restricted diet supplemented with cysteine, vitamin E and ascorbic acid failed to influence the course of the disorder. The bleeding diathesis was due to a morbid reduction of a number of clotting factors, particularly factor VII, and this was associated with impaired platelet aggregation and release. The liver of one showed a marked reduction in fumarylacetoacetate lyase activity and her urine contained a potent inhibitor of red cell δ-aminolaevulinic acid dehydratase. Biochemical investigations of cultured fibroblasts suggest that these do not express the disorder and are unlikely to prove useful diagnostically.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carson, N. A. J., Biggart, J. D., Bittles, A. H. and Donovan, D. Herditary tyrosinaemia—clinical, enzymatic and pathological study of an infant with the acute form of the disease.Arch. Dis. Child. 51 (1976) 106
Collier, H. B. A study of the determination of 5-aminolaevulinate hydrolase (δ-aminolaevulinate dehydratase) activity in haemolysates of human erythrocytes.Clin. Biochem. 4 (1971) 222
David, J. C. Evidence for the possible formation of a toxic tyrosine metabolite by the liver microsomal drug metabolizing system.Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 292 (1976) 79
Edwards, S. W. and Knox, W. E. Enzymes involved in conversion of tyrosine to acetoacetate.Meth. Enzymol. 2 (1955) 298
Fällström, S.-P., Lindblad, B., Lindstedt, S. and Steen, G. Hereditary tyrosinaemia-fumaryl acetoacetate lyase deficiency.Pediatr. Res. 13 (1979) 78
Hemker, H. C., Veltkamp, J. J., Henson, A. and Loebiger, E. A. Nature of prothrombin synthesis: preprothrombinaemia in vitamin K deficiency.Nature 200 (1963) 589
La Du, B. N. The enzymatic deficiency in tyrosinaemia.Am. J. Dis. Child. 113 (1967) 54
Larochelle, J. L., Prive, M., Belanger, L., Tremblay, M., Claveau, J. C., Aubin, G. and Paradis, D. Tyrosinemie hereditaire: 1 étude clinique et biologique de 62 cas.Pediatrie 28 (1973) 5
Lindblad, B., Lindstedt, S. and Steen, G. On the enzymic deficiency in hereditary tyrosinaemia.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. (USA) 74 (1977) 4641
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L. and Randall, R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent.J. Biol. Chem. 193 (1951) 265
Rubem, M. H., Weston, M. J., Bullock, B., Roberts, J., Langley, P. G., White, Y. S. and Williams, R. Abnormal platelet function and ultrastructure in fulminant hepatic failure.Q. J. Med. 46 (1977) 339
Spencer-Peet, J., Norman, M. E., Lake, B. D., McNamara, J. and Patrick, A. D. Hepatic glycogen storage disease: clinical and laboratory findings in 23 cases.Q. J. Med. 40 (1971) 95
Whelan, D. T. and Zannoni, V. G. Microassay of tyrosine aminotransferase andp-hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid oxidase in mammalian liver and patients with hereditary tyrosinaemia.Biochem. Med. 9 (1974) 19
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gray, R.G.F., Patrick, A.D., Preston, F.E. et al. Acute hereditary tyrosinaemia type I: Clinical, biochemical and haematological studies in twins. J Inherit Metab Dis 4, 37–40 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02263580
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02263580