Summary
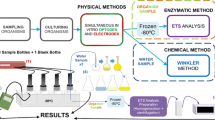
One of the methods to measure decomposition is to measure the rate of respiration by the ETS method. The relative value and the shortcomings of this method, but also the advantages of it as sensitivity, easiness and quickness are stressed. Some examples of application of the method in ocean water, coastal water, marine sediment and salt marsh sediment are given.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BAARS, M.A., J.J. ZIJLSTRA and S.B. TIJSSEN, 1979. Investigations in the euphotic zone of the tropical North Atlantic: programme and hydrography during the Nectar cruises. Neth. J. Sea Res., 13:40–57.
BROBERG, A., 1980. Measurements of electron-transport-system activity in freshwater sediment. 8th Nordic symposium on sediments. In: F. Ö. Andersen, L. Kofoed and E. Lastein, Eds., Salten Skov Laboratory, Denmark, p. 172–193.
DEVOL, A.H., T.T. PACKARD and O. HOLM-HANSEN, 1976. Respiratory electron transport activity and adenosine triphosphate in the oxygen minimum of the eastern tropical North Pacific. Deep-Sea Res., 23:963–973.
GIESKES, W.W.C., G.W. KRAAY and M.A. BAARS, 1979. Current14C methods for measuring primary production: gross underestimates in oceanic waters. Neth. J. Sea Res., 13:58–78.
JOENJE, W. and W.J. WOLFF, 1979. Functional aspects of salt marshes in the Wddden Sea area. In: W.J. Wolff, Ed. Flora and vegetation of the Wadden Sea, 3/160–3/171.
JONES, J.G., and B.M. SIMON, 1979. The measurement of electron transport system activity in freshwater benthic and planktonic samples. J. appl. Bacteriol. 46, 305–315.
NIXON, Sc.W., 1980. Between coastal marshes and coastal waters. A review of twenty years of speculation and research on the role of salt marshes in estuarine productivity and water chemistry. In: P. Hamilton and K.B. MacDonald, Eds., Estuarine and wetland processes with emphasis on modelling, Plenum Press, p. 437–525.
OLANCZUK-NEYMAN, K.M. and J.H. VOSJAN, 1977. Measuring respiratory electron-transportsystem activity in marine sediment. Neth. J. Sea Res. 11, 1–13.
PACKARD, T.T., 1969. The estimation of the oxygen utilization rate in seawater from the activity of the respiratory electron transport system in plankton. Thesis University of Washington, Seattle, 1–115.
PACKARD, T.T., 1971. The measurement of respiratory electron transport activity in marine phytoplankton. J. mar. Res. 29, 235–244.
PACKARD, T.T., 1979. Respiration and respiratory electron transport activity in plankton from the Northwest African upwelling area. J. mar. Res. 37, 711–742.
PACKARD, T.T., M.L. HEALY and F.A. RICHARDS, 1971. Vertical distribution of the activity of the respiratory electron transport system in marine plankton. Limnol. Oceanogr., 16, 60–70.
PACKARD, T.T. and P.J. LEB. WILLIAMS, 1981. Rates of respiratory oxygen consumption and electron transport in surface seawater from the northwest Atlantic. Oceanologica Acta 4, 351–358.
PAMATMAT, M.M., G. GRAF, W. BENGTSSON and C.S. NOVAK, 1981. Heat production, ATP concentration and electron transport activity of marine sediments. Mar. Ecol. Progr. Ser. 4, 135–153.
PAMATMAT, M.M. and H.R. SKJOLDAL, 1979. Metabolic activity, adenosine phosphates and energy change of below ground biomass ofJuncus roemerianus Scheele andSpartina alterniflora Loisel. Estuar. Coast. Mar. Sci. 9, 79–90.
POSTMA, H. and J.W. ROMMETS, 1979. Dissolved and particulate organic carbon in the North Equatorial current of the Atlantic Ocean. Neth. J. Sea Res. 13, 85–98.
RAAPHORST, W. VAN, 1980. Een onderzoek naar de mineralisatieprocessen in het sediment van de kwelders langs de Dollard, gezien in het kader van de totale koolstofhuishouding van dit deel van het Eems-Dollard estuarium. R.I.N.-rapport, 1–131. (Unpubl. report).
SCHINDLER, J.E., D.J. WILLIAMS and A.P. ZIMMERMAN, 1976. Investigation of extracellular electron transport by humic acids. In: J.O. Nriagu, Ed., Environmental biogeochemistry. Ann Arbor Science Publishers Inc. Vol. I, p. 109–115.
SPITZER, D. and M.R. WERNAND, 1981. Optical measurements in the tropical North Atlantic. Oceanologica Acta 4, 69–75.
TEAL, J.M., 1962. Energy flow in the salt marsh ecosystem of Georgia. Ecology 43, 614–624.
TIJSSEN, S.B., 1979. Diurnal oxygen rhythm and primary production in the mixed layer of the Atlantic Ocean at 20°N. Neth. J. Sea Res. 13, 79–84.
VOSJAN, J.H. Sauerstoffaufnahmegeschwindigkeit und ETS-Aktivität im Niederländischen Wattenmeer. III. Internationales Hydromikrobiologisches Symposium, Smolenice, 1980. (In press).
VOSJAN, J.H. and S.B. TIJSSEN, 1978. Respiratory electron transport system (ETS) activity variations in a tidal area during one tidal period. Oceanologica Acta 1, 181–186.
WIESER, W. and M. ZECH, 1976. Dehydrogenases as tools in the study of marine sediments. Marine Biology 36, 113–122.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vosjan, J.H. Respiratory electron transport system activities in marine environments. Hydrobiological Bulletin 16, 61–68 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02255413
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02255413