Abstract
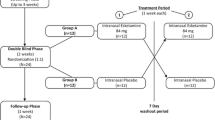
In order to examine if the nootropic drug, aniracetam, was capable of improving cognitive performance, 44 subjects suffering from chronic psychosyndrome after long-term exposure to organic solvents were included in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over study. The treatment periods were 3 months with aniracetam 1 g daily and 3 months with placebo. Neuropsychological tests as well as a physical and neurological examination were performed at entry into the study and after each treatment period, together with an evaluation of the subjects' overall condition. Neither the doctors' nor the subjects' own assessment of the overall condition indicated that the trial medication had had any effect. No significant changes in neuropsychological symptoms were observed. A statistically significant difference in favour of aniracetam was found in only 1 of the 19 neuropsychological test measures, namely a test for constructional ability. However, in another test on visuo-spatial function, a statistically significant result was found in favour of placebo. Thus, aniracetam was found to be ineffective in the treatment of subjects suffering from chronic psychosyndrome after long-term exposure to organic solvents.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anti-Poika M (1982) Prognosis of symptoms in patients with diagnosed chronic organic solvent intoxication. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 51:81–89
Bech P, Rafaelsen OJ (1980) The use of rating scales exemplified by a comparison of the Hamilton and the Bech-Rafaelsen Melancholia scale. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl 285:128–131
Bruhn P, Arlien-Søborg P, Gyldensted C, Christensen EL (1981) Prognosis in chronic toxic encephalopathy. Acta Neurol Scand 64:259–272
Cumin R, Bandle EF, Gamzu E, Haefely WE (1982) Effects of the novel compound aniracetam (Ro 13-5057) upon impaired learning and memory in rodents. Psychopharmacology 78:104–111
Giurgia C, Lefevre D, Lescrenier C, David-Remacle M (1971) Pharmacological protection against hypoxia-induced amnesia in rats. Pharmacologica 20:160–168
Hjorter A, Brown E, Jakobsen K, Viskum P, Gyntelberg F (1987) Organic brain syndrome treated with oxiracetam. Acta Neurol Scand 75:271–276
Mindus P, Cronholm B, Levander SE, Scalling D (1976) Piracetam-induced improvement of mental performance. Acta Psychiatr Scand 54:150–160
Saletu B, Grunberger J, Linzmayer L (1980) Quantitative EEG and psychometric analyses in assessing CNS-activity of Ro 13-5057 (aniracetam) — a cerebral insufficiency improver. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 2(5):269–285
Sourander LB, Portin R, Mølsa Pekka, Lahdes A, Rinne UK (1987) Senile dementia of the Alzheimer type treated with aniracetam: a new nootropic agent. Psychopharmacology 91:90–95
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Somnier, F.E., Østergaard, M.S., Boysen, G. et al. Aniracetam tested in chronic psychosyndrome after long-term exposure to organic solvents. Psychopharmacology 101, 43–46 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02253716
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02253716