Abstract
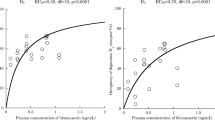
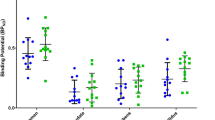
We have studied striatal D2 dopamine binding in schizophrenic patients treated with the novel atypical antipsychotic drug, olanzapine.123I iodobenzamide (IBZM) single photon emission tomography (SPET) was used to estimate striatal dopamine D2 receptor binding in vivo. Patients were recruited from a prospective, double blind controlled trial of olanzapine versus haloperidol treatment. In vivo striatal D2 binding data from olanzapine treated patients (n=6) were compared with previously reported data from typical antipsychotic responsive (n=10); clozapine (n=10); and risperidone (n=6) treated patient groups. Mean % Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale score (BPRS) improvement following olanzapine treatment was 49% (SD 44). The hypothesis that clinical improvement in olanzapine treated patients would be associated with higher mean striatal D2 binding of123I IBZM (reflecting lower levels of D2 occupancy) than typical antipsychotic (1.25±0.05) or risperidone (1.24±0.04) treatment was confirmed. Olanzapine treated patients had similar levels of striatal D2 binding in vivo (1.41±0.06) as those treated with clozapine (1.49±0.04). This preliminary evidence suggests olanzapine is another atypical antipsychotic drug in which therapeutic response is not associated with a high degree of striatal D2 receptor occupancy in vivo.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association (1987) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 3rd edn. American Psychiatric Association, Washington D.C.
Barnes TRE (1989) A rating scale for drug-induced akathisia. Br J Psychiatry 154:672–676
Brucke T, Podreka I, Wenger S et al. (1991) Dopamine D2 receptor imaging with SPECT: studies in different neuropsychiatric disorders. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 11:220–228
Brucke T, Roth J, Podrecka I, Strobi R, Wenger S, Asenbaum S (1992) Striatal dopamine D2 blockade by typical and atypical neuroleptics. Lancet 339:497
Busatto GF, Pilowsky LS, Costa DC, Ell PJ, Verhoeff NPLG, Kerwin RW (1995) Dopamine D2 receptor blockade in vivo with the novel antipsychotics risperidone and remoxipride — an123I IBZM single photon emission tomography (SPET) study. Psychopharmacology 117:55–61
Bymaster FP, Calligaro DO, Falcone JF, March RB, Moore NA, Tye NC, Seeman P, Wong DT (1995) Radioreceptor binding profile of the atypical antipsychotic olanzapine. Neuropsychopharmacology (in press)
Camps M, Cortes R, Gueye B et al. (1989) Dopamine receptors in human brain. Autoradiographic distribution of D2 sites. Neuroscience 28:275–290
Farde L, Nordstrom AL, Wiesel F-A et al. (1992) Positron emission tomographic analysis of central D1 and D2 receptor occupancy in patients treated with classical neuroleptics and clozapine. Arch Gen Psychiatry 49:538–544
Janowsky A, Neve KA, Kinsie MJ, Taylor B, de Paulis T, Belknap J (1992) Extrastriatal dopamine D2 receptors: distribution, pharmacological characterisation and region specific regulation by clozapine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 261:1282–1290
Jarritt PH, Kouris K (1993) Instrumentation for brain SPET: guidelines and quantification. In: Costa DC, Morgan GF, Lassen NA (eds) New trends in nuclear neurology and psychiatry. John Libbey, London, pp 36–95
Kerwin RW (1994) The new atypical antipsychotics. Br J Psychiatry 164:141–148
Leiberman JA, Safferman AZ (1992) Clinical profile of clozapine: adverse reactions and agranulocytosic. Psychiatric Quarterly 63:51–70
Leysen JE, Gommeran WE, Enes A et al. (1992) The biochemical profile of risperidone. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 247:661–670
Lidow MS, Goldman-Rakic PS (1994) A common action of clozapine, haloperidol and remoxipride on D1- and D2-dopaminergic receptors in the primate cerebral cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:4353–4356
Meltzer HY (1989) Clinical studies on the mechanism of action of clozapine: the dopamine: serotonin hypothesis of schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology 99:S18-S27
Moore NA, Calligaro DO, Wong DT, Bymaster F, Tye NC (1993) The pharmacology of olanzapine, and other new antipsychotic agents. Curr Opin Invest Drugs 2:281–293
Nordstrom AL, Farde L, Weisel FA, Forslund K, Pauli S, Halldin C, Uppfeldt G (1993) Central D2 dopamine receptor occupancy in relation to antipsychotic drug effects: a double blind PET study of schizophrenic patients. Biol Psychiatry 33:227–235
Overall JE, Gorham DE (1962) The brief psychiatric rating scale. Psychol Rep 10:799–812
Pickar D, Su T-P, Coppola R, Lee CS, Hsaio JK, Breier A, Weinberger DR (1995) D2 occupancy and dopamine release determined by123I IBZM SPECT following clozapine dose recuction. Schizophr Res 15:96
Pilowsky LS, Costa DC, Ell PJ et al. (1992) Clozapine, single photon emission tomography and the D2 dopamine receptor blockade hypothesis of schizophrenia. Lancet 340:199–202
Pilowsky LS, Costa DC, Ell PJ, Murray RM, Verhoeff NPLG, Kerwin RW (1993) Antipsychotic medication, D2 dopamine receptor blockade and clinical response — a123I IBZM SPET (single photon emission tomography) study. Psychol Med 23:791–799
Pilowsky LS, Costa DC, Ell PJ, Verhoeff NPLG, Murray RM, Kerwin RW (1994) D2 dopamine receptor binding in the basal ganglio of antipsychotic free schizophrenic patients — a123I IBZM single photon emission tomography (SPET) study. Brit J Psychiatry 164:16–26
Reynolds GP, Mason SL (1994) Clozapine has elevated affinity for human frontal cortical dopamine D2-like receptor sites. Schizophr Res 11:113
Satterlee W, Beasley C, Sanger T, Tran P, Tollefson G (1995) Olanzapine, a new ‘atypical’ antipsychotic. Schizophr Res 15:163
Seibyl JP, Woods SW, Zohgbi SS, Baldwin RM, Dey HM, Goddard AW, Zea-Ponce Y, Zubla G, Germine M, Smith EO, Heninger GR, Charney DS, Kung HF, Alavi A, Hoffer PB, Innis RB (1992) Dynamic SPECT imaging of dopamine D2 receptors in human subjects with iodine123-I IBZM. Nucl Med 33:1964–1971
Simpson GM, Angus JWS (1970) A rating scale for extrapyramidal side effects. Acta Psychiatr Scand 212 [Suppl 44]:11–19
Sokoloff P, Giros B, Martres MP (1990) Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel dopamine receptor (D3) as a target for neuroleptics. Nature 347:146–151
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pilowsky, L.S., Busatto, G.F., Taylor, M. et al. Dopamine D2 receptor occupancy in vivo by the novel atypical antipsychotic olanzapine — a123 IBZM single photon emission tomography (SPET) study. Psychopharmacology 124, 148–153 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245615
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245615