Abstract
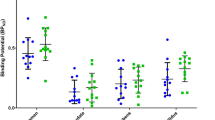
The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between specific symptom severity and D2/3 receptor availability in extrastriatal regions in outpatients with schizophrenia to shed light on the role of extrastriatal dopaminergic neurotransmission in the pathophysiology of symptoms of schizophrenia. Sixteen schizophrenia patients receiving relatively low-dose maintenance atypical antipsychotics and seventeen healthy controls underwent 3-Tesla magnetic resonance imaging and high-resolution positron emission tomography with [18F]fallypride. For D2/3 receptor availability, the binding potential with respect to non-displaceable compartment (BPND) was derived using the simplified reference tissue model. The BPND values were lower in patients on antipsychotic treatment than in controls across all regions with large effect sizes (1.03–1.42). The regions with the largest effect size were the substantia nigra, amygdala, and insula. Symptoms of schizophrenia were assessed using a five-factor model of the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS). The region of interest-based analysis showed that PANSS excitement factor score had a significant positive correlation with the [18F]fallypride BPND in the insula. The equivalent dose of antipsychotics was not significantly correlated with PANSS factor scores or regional BPND values. The voxel-based analysis also revealed a significant positive association between the PANSS excitement factor and the [18F]fallypride BPND in the insula. The present study revealed a significant association between excitement symptom severity and D2/3 receptor availability in the insula in schizophrenia, suggesting a possible important role of D2/3 receptor-mediated neurotransmission in the insula and related limbic system in the pathophysiology of this specific symptom cluster.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Takahashi H, Higuchi M, Suhara T (2006) The role of extrastriatal dopamine D2 receptors in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 59:919–928
Kim JH, Abi-Dargham A (2009) Psychiatric Disorders. In: Van Heertum RL, Tikofsky RS, Ichise M (eds) Functional cerebral SPECT and PET imaging, 4th edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 187–200
Agid O, Mamo D, Ginovart N, Vitcu I, Wilson AA, Zipursky RB, Kapur S (2007) Striatal vs extrastriatal dopamine D2 receptors in antipsychotic response—a double-blind PET study in schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 32:1209–1215
Kessler RM, Woodward ND, Riccardi P, Li R, Ansari MS, Anderson S, Dawant B, Zald D, Meltzer HY (2009) Dopamine D2 receptor levels in striatum, thalamus, substantia nigra, limbic regions, and cortex in schizophrenic subjects. Biol Psychiatry 65:1024–1031
Slifstein M, Kegeles LS, Xu X, Thompson JL, Urban N, Castrillon J, Hackett E, Bae SA, Laruelle M, Abi-Dargham A (2010) Striatal and extrastriatal dopamine release measured with PET and [(18)F] fallypride. Synapse 64:350–362
Lehrer DS, Christian BT, Kirbas C, Chiang M, Sidhu S, Short H, Wang B, Shi B, Chu KW, Merrill B, Buchsbaum MS (2010) 18F-fallypride binding potential in patients with schizophrenia compared to healthy controls. Schizophr Res 122:43–52
Buchsbaum MS, Christian BT, Lehrer DS, Narayanan TK, Shi B, Mantil J, Kemether E, Oakes TR, Mukherjee J (2006) D2/D3 dopamine receptor binding with [F-18]fallypride in thalamus and cortex of patients with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 85:232–244
Kegeles LS, Slifstein M, Xu X, Urban N, Thompson JL, Moadel T, Harkavy-Friedman JM, Gil R, Laruelle M, Abi-Dargham A (2010) Striatal and extrastriatal dopamine D2/D3 receptors in schizophrenia evaluated with [18F]fallypride positron emission tomography. Biol Psychiatry 68:634–641
Talvik M, Nordström AL, Olsson H, Halldin C, Farde L (2003) Decreased thalamic D2/D3 receptor binding in drug-naive patients with schizophrenia: a PET study with [11C]FLB 457. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 6:361–370
Yasuno F, Suhara T, Okubo Y, Sudo Y, Inoue M, Ichimiya T, Takano A, Nakayama K, Halldin C, Farde L (2004) Low dopamine d(2) receptor binding in subregions of the thalamus in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 161:1016–1022
Kambeitz J, Abi-Dargham A, Kapur S, Howes OD (2014) Alterations in cortical and extrastriatal subcortical dopamine function in schizophrenia: systematic review and meta-analysis of imaging studies. Br J Psychiatry 204:420–429
Gründer G, Landvogt C, Vernaleken I, Buchholz HG, Ondracek J, Siessmeier T, Härtter S, Schreckenberger M, Stoeter P, Hiemke C, Rösch F, Wong DF, Bartenstein P (2006) The striatal and extrastriatal D2/D3 receptor-binding profile of clozapine in patients with schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:1027–1035
Gründer G, Fellows C, Janouschek H, Veselinovic T, Boy C, Bröcheler A, Kirschbaum KM, Hellmann S, Spreckelmeyer KM, Hiemke C, Rösch F, Schaefer WM, Vernaleken I (2008) Brain and plasma pharmacokinetics of aripiprazole in patients with schizophrenia: an [18F]fallypride PET study. Am J Psychiatry 165:988–995
Kegeles LS, Slifstein M, Frankle WG, Xu X, Hackett E, Bae SA, Gonzales R, Kim JH, Alvarez B, Gil R, Laruelle M, Abi-Dargham A (2008) Dose-occupancy study of striatal and extrastriatal dopamine D2 receptors by aripiprazole in schizophrenia with PET and [18F]fallypride. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:3111–3125
Kessler RM, Ansari MS, Riccardi P, Li R, Jayathilake K, Dawant B, Meltzer HY (2005) Occupancy of striatal and extrastriatal dopamine D2/D3 receptors by olanzapine and haloperidol. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:2283–2289
Kessler RM, Ansari MS, Riccardi P, Li R, Jayathilake K, Dawant B, Meltzer HY (2006) Occupancy of striatal and extrastriatal dopamine D2 receptors by clozapine and quetiapine. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:1991–2001
Vernaleken I, Janouschek H, Raptis M, Hellmann S, Veselinovic T, Bröcheler A, Boy C, Cumming P, Hiemke C, Rösch F, Schäfer WM, Gründer G (2010) Dopamine D2/3 receptor occupancy by quetiapine in striatal and extrastriatal areas. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 13:951–960
Abi-Dargham A, Gil R, Krystal J, Baldwin RM, Seibyl JP, Bowers M, van Dyck CH, Charney DS, Innis RB, Laruelle M (1998) Increased striatal dopamine transmission in schizophrenia: confirmation in a second cohort. Am J Psychiatry 155:761–767
Laruelle M, Abi-Dargham A, van Dyck CH, Gil R, D’Souza CD, Erdos J, McCance E, Rosenblatt W, Fingado C, Zoghbi SS, Baldwin RM, Seibyl JP, Krystal JH, Charney DS, Innis RB (1996) Single photon emission computerized tomography imaging of amphetamine-induced dopamine release in drug-free schizophrenic subjects. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:9235–9240
Howes OD, Bose SK, Turkheimer F, Valli I, Egerton A, Valmaggia LR, Murray RM, McGuire P (2011) Dopamine synthesis capacity before onset of psychosis: a prospective [18F]-DOPA PET imaging study. Am J Psychiatry 168:1311–1317
Talvik M, Nordström AL, Okubo Y, Olsson H, Borg J, Halldin C, Farde L (2006) Dopamine D2 receptor binding in drug-naïve patients with schizophrenia examined with raclopride-C11 and positron emission tomography. Psychiatry Res 148:165–173
Glenthoj BY, Mackeprang T, Svarer C, Rasmussen H, Pinborg LH, Friberg L, Baaré W, Hemmingsen R, Videbaek C (2006) Frontal dopamine D(2/3) receptor binding in drug-naive first-episode schizophrenic patients correlates with positive psychotic symptoms and gender. Biol Psychiatry 60:621–629
Kim JH, Kim SY, Lee J, Oh KJ, Kim YB, Cho ZH (2012) Evaluation of the factor structure of symptoms in patients with schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res 197:285–289
Levine SZ, Rabinowitz J (2007) Revisiting the 5 dimensions of the Positive and Negative Syndrome scale. J Clin Psychopharmacol 27:431–436
Marder SR, Davis JM, Chouinard G (1997) The effects of risperidone on the five dimensions of schizophrenia derived by factor analysis: combined results of the North American trials. J Clin Psychiatry 58:538–546
American Psychiatric Association (1994) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th edn. American Psychiatric Press, Washington, DC
First MB, Spitzer RL, Gibbon M, Williams JBW (1996) Structured clinical interview for DSM-IV axis I disorders research version (SCID-I). New York State Psychiatric Institute Biometrics Research, New York
Gardner DM, Murphy AL, O’Donnell H, Centorrino F, Baldessarini RJ (2010) International consensus study of antipsychotic dosing. Am J Psychiatry 167:686–693
Kay SR, Fiszbein A, Opler LA (1987) The positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 13:261–276
Guy W (1976) ECDEU assessment manual for psychopharmacology. U.S. Department of Health, Education, and Welfare, Bethesda, MD
Simpson GM, Angus JW (1970) A rating scale for extrapyramidal side effects. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl 212:11–19
Barnes TR (1989) A rating scale for drug-induced akathisia. Br J Psychiatry 154:672–676
Cho ZH, Son YD, Kim HK, Kim KN, Oh SH, Han JY, Hong IK, Kim YB (2008) A fusion PET-MRI system with a high-resolution research tomograph-PET and ultra-high field 7.0 T-MRI for the molecular-genetic imaging of the brain. Proteomics 8:1302–1323
Wienhard K, Schmand M, Casey ME, Baker K, Bao J, Eriksson L, Jones WF, Knoess C, Lenox M, Lercher M, Luk P, Michel C, Reed JH, Richerzhagen N, Treffert J, Vollmar S, Young JW, Heiss WD, Nutt R (2002) The ECAT HRRT: performance and first clinical application of the new high resolution research tomography. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 49:104–110
Mukherjee J, Yang ZY, Das MK, Brown T (1995) Fluorinated benzamide neuroleptics-III. Development of (S)-N-[(1-allyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl]-5-(3-[18F]fluoropropyl)-2, 3-dimethoxybenzamide as an improved dopamine D-2 receptor tracer. Nucl Med Biol 22:283–296
Hong IK, Chung ST, Kim HK, Kim YB, Son YD, Cho ZH (2007) Ultra fast symmetry and SIMD-based projection-backprojection (SSP) algorithm for 3-D PET image reconstruction. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 26:789–803
Wu Y, Carson RE (2002) Noise reduction in the simplified reference tissue model for neuroreceptor functional imaging. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 22:1440–1452
Hurley MJ, Mash DC, Jenner P (2003) Markers for dopaminergic neurotransmission in the cerebellum in normal individuals and patients with Parkinson’s disease examined by RT-PCR. Eur J Neurosci 18:2668–2672
Tzourio-Mazoyer N, Landeau B, Papathanassiou D, Crivello F, Etard O, Delcroix N, Mazoyer B, Joliot M (2002) Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. Neuroimage 15:273–289
Friston KJ, Holmes A, Poline JB, Price CJ, Frith CD (1996) Detecting activations in PET and fMRI: levels of inference and power. Neuroimage 4:223–235
Farrer C, Franck N, Georgieff N, Frith CD, Decety J, Jeannerod M (2003) Modulating the experience of agency: a positron emission tomography study. Neuroimage 18:324–333
Gaura V, Bachoud-Lévi AC, Ribeiro MJ, Nguyen JP, Frouin V, Baudic S, Brugières P, Mangin JF, Boissé MF, Palfi S, Cesaro P, Samson Y, Hantraye P, Peschanski M, Remy P (2004) Striatal neural grafting improves cortical metabolism in Huntington’s disease patients. Brain 127:65–72
Mikhno A, Devanand D, Pelton G, Cuasay K, Gunn R, Upton N, Lai RY, Libri V, Mann JJ, Parsey RV (2008) Voxel-based analysis of 11C-PIB scans for diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease. J Nucl Med 49:1262–1269
Wong MT, Fenwick PB, Lumsden J, Fenton GW, Maisey MN, Lewis P, Badawi R (1997) Positron emission tomography in male violent offenders with schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res 68:111–123
Blair RJ (2016) The neurobiology of impulsive aggression. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 26:4–9
Williamson P, Allman J (2011) The human illnesses: neuropsychiatric disorders and the nature of the human brain. Oxford University Press, New York
Giakoumatos CI, Tandon N, Shah J, Mathew IT, Brady RO, Clementz BA, Pearlson GD, Thaker GK, Tamminga CA, Sweeney JA, Keshavan MS (2013) Are structural brain abnormalities associated with suicidal behavior in patients with psychotic disorders? J Psychiatr Res 47:1389–1395
Siever LJ (2008) Neurobiology of aggression and violence. Am J Psychiatry 165:429–442
Soyka M (2011) Neurobiology of aggression and violence in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 37:913–920
Hernaus D, Mehta MA (2016) Prefrontal cortex dopamine release measured in vivo with positron emission tomography: implications for the stimulant paradigm. Neuroimage 142:663–667
Slifstein M, van de Giessen E, Van Snellenberg J, Thompson JL, Narendran R, Gil R, Hackett E, Girgis R, Ojeil N, Moore H, D’Souza D, Malison RT, Huang Y, Lim K, Nabulsi N, Carson RE, Lieberman JA, Abi-Dargham A (2015) Deficits in prefrontal cortical and extrastriatal dopamine release in schizophrenia: a positron emission tomographic functional magnetic resonance imaging study. JAMA Psychiatry 72:316–324
Lang FU, Müller-Stierlin AS, Walther S, Stegmayer K, Becker T, Jäger M (2016) Dimensional approaches to schizophrenia: a comparison of the Bern Psychopathology scale and the five-factor model of the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale. Psychiatry Res 239:284–290
Yang YK, Yeh TL, Chiu NT, Lee IH, Chen PS, Lee LC, Jeffries KJ (2004) Association between cognitive performance and striatal dopamine binding is higher in timing and motor tasks in patients with schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res 131:209–216
Heinz A, Knable MB, Coppola R, Gorey JG, Jones DW, Lee KS, Weinberger DR (1998) Psychomotor slowing, negative symptoms and dopamine receptor availability-an IBZM SPECT study in neuroleptic-treated and drug-free schizophrenic patients. Schizophr Res 31:19–26
Klemm E, Grünwald F, Kasper S, Menzel C, Broich K, Danos P, Reichmann K, Krappel C, Rieker O, Briele B, Hotze AL, Möller HJ, Biersack HJ (1996) [123I]IBZM SPECT for imaging of striatal D2 dopamine receptors in 56 schizophrenic patients taking various neuroleptics. Am J Psychiatry 153:183–190
Hurley MJ, Stubbs CM, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1996) Effect of chronic treatment with typical and atypical neuroleptics on the expression of dopamine D2 and D3 receptors in rat brain. Psychopharmacology 128:362–370
Hurley MJ, Stubbs CM, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1996) Dopamine D3 receptors are not involved in the induction of c-fos mRNA by neuroleptic drugs: comparison of the dopamine D3 receptor antagonist GR103691 with typical and atypical neuroleptics. Eur J Pharmacol 318:283–293
Schmitt GJ, Dresel S, Frodl T, la Fougère C, Boerner R, Hahn K, Möller HJ, Meisenzahl EM (2012) Dual-isotope SPECT imaging of striatal dopamine: a comparative study between never-treated and haloperidol-treated first-episode schizophrenic patients. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 262:183–191
Mizrahi R, Rusjan P, Agid O, Graff A, Mamo DC, Zipursky RB, Kapur S (2007) Adverse subjective experience with antipsychotics and its relationship to striatal and extrastriatal D2 receptors: a PET study in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 164:630–637
Craig AD (2004) Human feelings: why are some more aware than others? Trends Cogn Sci 8:239–241
Vernaleken I, Peters L, Raptis M, Lin R, Buchholz HG, Zhou Y, Winz O, Rösch F, Bartenstein P, Wong DF, Schäfer WM, Gründer G (2011) The applicability of SRTM in [(18)F]fallypride PET investigations: impact of scan durations. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 31:1958–1966
Larisch R, Meyer W, Klimke A, Kehren F, Vosberg H, Müller-Gärtner HW (1998) Left-right asymmetry of striatal dopamine D2 receptors. Nucl Med Commun 19:781–787
Vernaleken I, Weibrich C, Siessmeier T, Buchholz HG, Rösch F, Heinz A, Cumming P, Stoeter P, Bartenstein P, Gründer G (2007) Asymmetry in dopamine D(2/3) receptors of caudate nucleus is lost with age. Neuroimage 34:870–878
Besson C, Louilot A (1995) Asymmetrical involvement of mesolimbic dopaminergic neurons in affective perception. Neuroscience 68:963–968
Leroy C, Comtat C, Trébossen R, Syrota A, Martinot JL, Ribeiro MJ (2007) Assessment of 11C-PE2I binding to the neuronal dopamine transporter in humans with the high-spatial-resolution PET scanner HRRT. J Nucl Med 48:538–546
Varrone A, Sjöholm N, Eriksson L, Gulyás B, Halldin C, Farde L (2009) Advancement in PET quantification using 3D-OP-OSEM point spread function reconstruction with the HRRT. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 36:1639–1650
Seeman P (2013) Schizophrenia and dopamine receptors. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 23:999–1009
Slifstein M, Hwang DR, Huang Y, Guo N, Sudo Y, Narendran R, Talbot P, Laruelle M (2004) In vivo affinity of [18F]fallypride for striatal and extrastriatal dopamine D2 receptors in nonhuman primates. Psychopharmacology 175:274–286
Mukherjee J, Yang ZY, Brown T, Lew R, Wernick M, Ouyang X, Yasillo N, Chen CT, Mintzer R, Cooper M (1999) Preliminary assessment of extrastriatal dopamine D-2 receptor binding in the rodent and nonhuman primate brains using the high affinity radioligand, 18F-fallypride. Nucl Med Biol 26:519–527
Graff-Guerrero A, Mamo D, Shammi CM, Mizrahi R, Marcon H, Barsoum P, Rusjan P, Houle S, Wilson AA, Kapur S (2009) The effect of antipsychotics on the high-affinity state of D2 and D3 receptors: a positron emission tomography study with [11C]-(+)-PHNO. Arch Gen Psychiatry 66:606–615
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Brain Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (2016M3C7A1914451) and by a grant of the Korean Health Technology R&D Project, Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea (number: HI14C2750). This research was also supported by the Gachon University Research Fund of 2015 (number: GCU-2015-5031).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Informed consent
The study protocol was approved by the institutional review board of the Gachon University Gil Medical Center, and all procedures used in the study were conducted in accordance with international ethical standard, Declaration of Helsinki. All participants gave their written informed consent prior to their inclusion in the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joo, YH., Kim, JH., Son, YD. et al. The relationship between excitement symptom severity and extrastriatal dopamine D2/3 receptor availability in patients with schizophrenia: a high-resolution PET study with [18F]fallypride. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 268, 529–540 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-017-0821-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-017-0821-y