Abstract
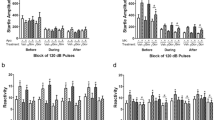
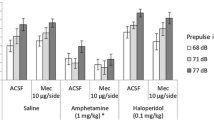
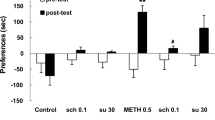
The amplitude of the acoustic startle response is decreased if the startle stimulus is preceded by a nonstartle eliciting stimulus. This sensorimotor gating phenomenon, known as prepulse inhibition, is diminished in schizophrenic individuals. In rats, the dopamine agonist apomorphine disrupts prepulse inhibition and this disruption is reversed by classical and atypical antipsychotics. Furthermore, the ability of antipsychotics to reverse the apomorphine disruption is correlated with clinical potency and D2 receptor affinity. In the present study, the role of the D1 receptor in prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle response was studied; the effects of the D1 receptor antagonist SCH 23390 were examined and compared to the effects of the D2 receptor antagonist eticlopride. Male Sprague-Dawley rats were placed into a startle chamber and presented with auditory stimuli consisting of either 95 or 105 dB noise bursts presented alone or preceded by a 75 dB noise burst. Trials consisting of no stimulus and the 75 dB prepulse stimulus alone were also included. These six trial types (ten each) were randomly presented within a 35-min session. Rats treated with 2.0 mg/kg apomorphine (SC) demonstrated a significant disruption of prepulse inhibition compared to vehicle controls. Pretreatment with the D1 antagonist SCH 23390 (0.01, 0.05, 0.1 mg/kg SC) or the D2 antagonist eticlopride (0.01, 0.05, 0.1 mg/kg SC) attenuated the disruptive effects of apomorphine. These results indicate that selective blockade of either the D1 or D2 receptor subtype is sufficient in reversing the sensorimotor gating deficits produced by apomorphine. The effects of eticlopride and SCH 23390 on prepulse inhibition in saline-treated rats were also examined. Each antagonist produced a dose-related facilitation of prepulse inhibition, suggesting that endogenous DA acting at either receptor subtype plays a role in the tonic modulation of sensorimotor gating.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Braff D, Stone C, Callaway E, Geyer M, Glick I, Bali L (1978) Prestimulus effects on human startle reflex in normals and schizophrenics. Psychophysiology 15: 339–343
Braff D, Grillon C, Geyer MA (1992) Gating and habituation of the startle reflex in schizophrenic patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry 49: 206–215
Cassella JV, Davis M (1986) The design and calibration of a startle measurement system. Physiol Behav 36: 377–383
Davis M (1987) Differential effects of dopamine D1 and D2 agonists (SKF 38393 and quinpirole - LY 171555) and antagonists (SCH 23390 and sulpiride) on the acoustic startle reflex: interactions with apomorphine and cocaine. Soc Neurosci Abstr 13: 830
Davis M (1988) Apomorphine,d-amphetamine, strychnine and yohimbine do not alter prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle reflex. Psychopharmacology 95: 151–156
Davis M, Aghajanian GK (1976) Effects of apomorphine and haloperidol on the acoustic startle response in rats. Psychopharmacology 47: 217–223
Davis M, Mansbach RS, Swerdlow NR, Campeau S, Braff DL, Geyer MA (1990) Apomorphine disrupts the inhibition of acoustic startle induced by weak prepulses in rats. Psychopharmacology 102: 1–4
Ellenbroek BA, Cools AR (1990) Animal models with construct validity for schizophrenia. Behav Pharmacol 1: 469–490
Farde L, Nordstrom A, Wiesel F, Pauli S, Halldin C, Sedvall G (1992) Positron emission tomographic analysis of central D1 and D2 dopamine receptor occupancy in patients treated with classical neuroleptics and clozapine. Arch Gen Psychiatry 49: 538–544
Geyer MA, Swerdlow NR, Mansbach RS, Braff DL (1990) Startle response models of sensorimotor gating and habituation deficits in schizophrenia. Brain Res Bull 25: 485–498
Grillon C, Ameli R, Charney DS, Krystal J, Braff D (1992) Startle gating deficits occur across prepulse intensities in schizophrenic patients. Biol Psychiatry 32: 939–943
Heimer L, Alheid GF, Zaborszky L (1985) Basal ganglia. In: Paxinos G (ed) The rat nervous system. Academic Press, N.Y., pp 37–85
Hoffman HS, Ison JR (1980) Reflex modification in the domain of startle: I. some empirical findings and their implications for how the nervous system processes sensory input. Psychol Rev 87: 175–189
Hoffman DC, Donovan H, Cassella JV (1993) The effects of haloperidol and clozapine on the disruption of sensorimotor gating induced by the noncompetitive glutamate antagonist MK-801. Psychopharmacology 111: 339–344
Hogberg T, Ramsby S, Ogren SO, Norinder U (1987) New selective dopamine D-2 antagonists as antipsychotic agents. Acta Pharm Suec 24: 289–328
Iorio LC, Barnett A, Leitz FH, Houser VP, Korduba CA (1983) SCH 23390, a potential benzazepine antipsychotic with unique interactions on dopamine systems. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 226: 462–468
Mansbach RS, Geyer MA, Braff DL (1988) Dopaminergic stimulation disrupts sensorimotor gating in the rat. Psychopharmacology 94: 507–514
Naudin B, Canu S, Costentin J (1990) Effects of various direct or indirect dopamine agonists on the latency of the acoustic startle response in rats. J Neural Transm [Gen Sect] 82: 43–53
Peng RY, Mansbach RS, Braff DL, Geyer MA (1990) A D2 dopamine receptor agonist disrupts sensorimotor gating in rats: implications for dopaminergic abnormalities in schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 3: 211–218
Rigdon GC (1990) Differential effects of apomorphine on prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle reflex in two rat strains. Psychopharmacology 102: 419–421
Rigdon GC, Viik K (1991) Prepulse inhibition as a screening test for potential antipsychotics. Drug Dev Res 23: 91–99
Schwarzkopf SB, Bruno JP, Mitra T (1991) Dopamine D1/D2 receptor effects on sensory gating in control and neonatally dopamine depleted animals. Am Col Neuropsychopharmacol Abstr 30: 208
Schwarzkopf SB, Mitra T, Hadjiconstantinou M (1992) Sensory gating abnormalities in adult animals resulting from exposure to neonatal hypoxia. Biol Psychiatry 31: 232A
Seeman P (1992) Dopamine receptor sequences: therapeutic levels of neuroleptics occupy D2 receptors, clozapine occupies D4. Neuropsychopharmacology 7: 261–284
Swerdlow NR, Geyer MA (1992) Neuroleptic restoration of startle gating in apomorphine-treated rats predicts clinical antipsychotic potency. Biol Psychiatry 31: 232A
Swerdlow NR, Geyer MA (1993) Clozapine and haloperidol in an animal model of sensorimotor gating deficits in schizophrenia. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 44: 741–742
Swerdlow NR, Braff DL, Masten VL, Geyer MA (1990) Schizophrenic-like sensorimotor gating abnormalities in rats following dopamine infusion into the nucleus accumbens. Psychopharmacology 101: 414–420
Swerdlow NR, Keith VA, Braff DL, Geyer MA (1991) Effect of spiperone, raclopride, SCH 23390 and clozapine on apomorphine inhibition of sensorimotor gating of the startle response in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 256: 530–536
Swerdlow NR, Caine SB, Geyer MA (1992) Regionally selective effects of intracerebral dopamine infusion on sensorimotor gating of the startle reflex in rats. Psychopharmacology 108: 189–195
Wan FJ, Swerdlow NR (1993) Dopamine D1 and D2 agonists reduce sensorimotor gating of acoustic startle in rats. Soc Neurosci Abstr 19: 759
Young KA, Randall PK, Wilcox RE (1991) Dose and time response analysis of apomorphine's effect on prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle. Behav Brain Res 42: 43–48
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoffman, D.C., Donovan, H. D1 and D2 dopamine receptor antagonists reverse prepulse inhibition deficits in an animal model of schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology 115, 447–453 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245567
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245567