Abstract
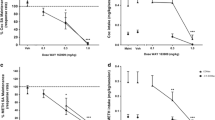
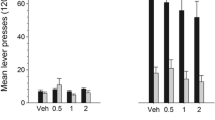
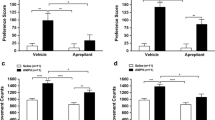
Repeated administration of stimulants induces conditioned place preference (CPP). Dopamine receptor supersensitivity is developed in stimulant-induced CPP animals; however, dopamine receptor subtypes associated with the development of supersensitivity in CPP animals are largely unknown. The present preclinical study aimed to examine whether dopamine D1 or D2 receptor antagonists exert inhibitory effects on stimulant-induced psychological behaviors. Additionally, the authors aimed to elucidate the role of dopamine receptor supersensitivity on the development of reward-related behavior. Sprague Dawley rats subjected to methamphetamine- and cocaine-induced CPP tests were treated with dopamine D1 (SCH23390) or D2 (sulpiride) receptor antagonists. Following the CPP experiment, rats were challenged with apomorphine (dopamine receptor agonist), and locomotor activity was measured. Methamphetamine- and cocaine-induced CPP was reduced with the administration of SCH23390, but not sulpiride. In addition, the apomorphine challenge evoked an increase in locomotor activity in stimulant-pre-treated rats, reflecting dopamine receptor supersensitivity. SCH23390 pre-treatment inhibited the development of dopamine receptor supersensitivity, while sulpiride demonstrated no inhibitory effects. These results suggest that the dopamine D1 receptor antagonist SCH23390 inhibits the development of dopamine receptor supersensitivity which is associated with the development of CPP.




Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
22 November 2019
In the originally published article, the name of the first author was incorrectly presented as Su Mi Gu. The correct name is Sun Mi Gu, which is also given above.
References
Adams JU, Careri JM, Efferen TR, Rotrosen J (2001) Differential effects of dopamine antagonists on locomotor activity, conditioned activity and conditioned place preference induced by cocaine in rats. Behav Pharmacol 12:603–611
Baker DA, Fuchs RA, Specio SE, Khroyan TV, Neisewander JL (1998) Effects of intraaccumbens administration of SCH-23390 on cocaine-induced locomotion and conditioned place preference. Synapse 30:181–193
Berridge KC, Robinson TE (2016) Liking, wanting, and the incentive-sensitization theory of addiction. Am Psychol 71:670–679
Blum K, Chen TJ, Downs BW, Bowirrat A, Waite RL, Braverman ER, Madigan M, Oscar-Berman M, DiNubile N, Stice E, Giordano J, Morse S, Gold M (2009) Neurogenetics of dopaminergic receptor supersensitivity in activation of brain reward circuitry and relapse: proposing "deprivation-amplification relapse therapy" (DART). Postgrad Med 121:176–196
Bock R, Shin JH, Kaplan AR, Dobi A, Markey E, Kramer PF, Gremel CM, Christensen CH, Adrover MF, Alvarez VA (2013) Strengthening the accumbal indirect pathway promotes resilience to compulsive cocaine use. Nat Neurosci 16:632–638
Brehm N, Bez F, Carlsson T, Kern B, Gispert S, Auburger G, Cenci MA (2015) A Genetic Mouse Model of Parkinson's Disease Shows Involuntary Movements and Increased Postsynaptic Sensitivity to Apomorphine. Mol Neurobiol 52:1152–1164
Briand LA, Flagel SB, Seeman P, Robinson TE (2008) Cocaine self-administration produces a persistent increase in dopamine D2 High receptors. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 18:551–556
Caine SB, Koob GF (1994) Effects of dopamine D-1 and D-2 antagonists on cocaine self-administration under different schedules of reinforcement in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 270:209–218
Carati C, Schenk S (2011) Role of dopamine D1- and D2-like receptor mechanisms in drug-seeking following methamphetamine self-administration in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 98:449–454
Chen Y, Song R, Yang RF, Wu N, Li J (2014) A novel dopamine D3 receptor antagonist YQA14 inhibits methamphetamine self-administration and relapse to drug-seeking behaviour in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 743:126–132
Collins GT, Woods JH (2007) Drug and reinforcement history as determinants of the response-maintaining effects of quinpirole in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 323:599–605
Cornish JL, Lontos JM, Clemens KJ, McGregor IS (2005) Cocaine and heroin ('speedball') self-administration: the involvement of nucleus accumbens dopamine and mu-opiate, but not delta-opiate receptors. Psychopharmacology 180:21–32
Galaj E, Ewing S, Ranaldi R (2018) Dopamine D1 and D3 receptor polypharmacology as a potential treatment approach for substance use disorder. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 89:13–28
Graham DL, Hoppenot R, Hendryx A, Self DW (2007) Differential ability of D1 and D2 dopamine receptor agonists to induce and modulate expression and reinstatement of cocaine place preference in rats. Psychopharmacology 191:719–730
Kim HS, Jang CG, Oh KW, Oh S, Rheu HM, Rhee GS, Seong YH, Park WK (1998) Effects of ginseng total saponin on morphine-induced hyperactivity and conditioned place preference in mice. J Ethnopharmacol 60:33–42
Kim HS, Jang CG, Park WK (1996) Inhibition by MK-801 of morphine-induced conditioned place preference and postsynaptic dopamine receptor supersensitivity in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 55:11–17
Kim HS, Kang JG, Seong YH, Nam KY, Oh KW (1995) Blockade by ginseng total saponin of the development of cocaine induced reverse tolerance and dopamine receptor supersensitivity in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 50:23–27
Kim HS, Kim KS (1999) Inhibitory effects of ginseng total saponin on nicotine-induced hyperactivity, reverse tolerance and dopamine receptor supersensitivity. Behav Brain Res 103:55–61
Kim HS, Kim KS, Oh KW (1999) Inhibition by ginsenosides Rb1 and Rg1 of cocaine-induced hyperactivity, conditioned place preference, and postsynaptic dopamine receptor supersensitivity in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 63:407–412
Kim HS, Lim HK (1999) Inhibitory effects of velvet antler water extract on morphine-induced conditioned place preference and DA receptor supersensitivity in mice. J Ethnopharmacol 66:25–31
Kim HS, Park WK, Jang CG, Oh S (1996) Inhibition by MK-801 of cocaine-induced sensitization, conditioned place preference, and dopamine-receptor supersensitivity in mice. Brain Res Bull 40:201–207
Koob GF, Le Moal M (2001) Drug addiction, dysregulation of reward, and allostasis. Neuropsychopharmacology: official publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology 24:97–129
Kuribara H (1995) Dopamine D1 receptor antagonist SCH 23390 retards methamphetamine sensitization in both combined administration and early posttreatment schedules in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 52:759–763
Liao RM, Chang YH, Wang SH (1998) Influence of SCH23390 and spiperone on the expression of conditioned place preference induced by d-amphetamine or cocaine in the rat. Chin J Phys 41:85–92
Mashhoon Y, Tsikitas LA, Kantak KM (2009) Dissociable effects of cocaine-seeking behavior following D1 receptor activation and blockade within the caudal and rostral basolateral amygdala in rats. Eur J Neurosci 29:1641–1653
Merritt KE, Bachtell RK (2013) Initial d2 dopamine receptor sensitivity predicts cocaine sensitivity and reward in rats. PLoS One 8:e78258
Mohd-Yusof A, Veliz A, Rudberg KN, Stone MJ, Gonzalez AE, McDougall SA (2016) Effects of D2 or combined D1/D2 receptor antagonism on the methamphetamine-induced one-trial and multi-trial behavioral sensitization of preweanling rats. Psychopharmacology 233:893–903
Nakajima S, O'Regan NB (1991) The effects of dopaminergic agonists and antagonists on the frequency-response function for hypothalamic self-stimulation in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 39:465–468
Novak G, Seeman P, Le Foll B (2010) Exposure to nicotine produces an increase in dopamine D2(High) receptors: a possible mechanism for dopamine hypersensitivity. Int J Neurosci 120:691–697
Robinson TE, Berridge KC (1993) The neural basis of drug craving: an incentive-sensitization theory of addiction. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 18:247–291
Samaha AN (2014) Can antipsychotic treatment contribute to drug addiction in schizophrenia? Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 52:9–16
Seeman P, Weinshenker D, Quirion R, Srivastava LK, Bhardwaj SK, Grandy DK, Premont RT, Sotnikova TD, Boksa P, El-Ghundi M, O'Dowd BF, George SR, Perreault ML, Mannisto PT, Robinson S, Palmiter RD, Tallerico T (2005) Dopamine supersensitivity correlates with D2High states, implying many paths to psychosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:3513–3518
Self DW (2014) Diminished role for dopamine D1 receptors in cocaine addiction? Biol Psychiatry 76:2–3
Sorge RE, Clarke PB (2009) Rats self-administer intravenous nicotine delivered in a novel smoking-relevant procedure: effects of dopamine antagonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 330:633–640
Sun L, Song R, Chen Y, Yang RF, Wu N, Su RB, Li J (2016) A selective D3 receptor antagonist YQA14 attenuates methamphetamine-induced behavioral sensitization and conditioned place preference in mice. Acta Pharmacol Sin 37:157–165
Yun JS, Kim HS, Lee MK, Oh KW, Jang CG, Park WK, Seong YH, Lee SC, Oh SK (2001) Inhibitory effects of MK-801 on contextual sensitization to climbing behavior and on development of tolerance to hypothermia induced by a single high dose of apomorphine. Pharmacol Res 44:473–479
Funding
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (2017R1C1B5017929) and the research grant of the Chungbuk National University in 2018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JTH and JSY were responsible for the study concept and design. SMG performed experiments and drafted the manuscript. HJC performed data analysis and drafted the manuscript. SWS drafted the manuscript. All authors critically reviewed the content and approved the final version for publication.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All animals were treated in Association for Assessment and Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care International-accredited facilities, operating according to the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. All experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Chungbuk National University.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original version of this article was revised; In the originally published article, the name of the first author was incorrectly presented as Su Mi Gu. The correct name is Sun Mi Gu, which is also given above.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, S.M., Cha, H.J., Seo, S.W. et al. Dopamine D1 receptor antagonist reduces stimulant-induced conditioned place preferences and dopamine receptor supersensitivity. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 393, 131–138 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-019-01694-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-019-01694-3