Abstract
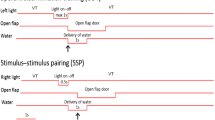
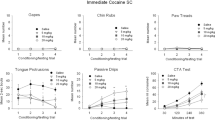
The acquisition of associative tolerance to the analgesic effects of morphine was investigated by giving independent groups of rats 1, 3, 5, 8, 14, 20, or 30 administrations of drug either explicitly paired or unpaired with a distinctive context. Tolerance, assessed on a tail-flick device using dose-response curve (DRC) methodology, developed more rapidly and reached greater magnitude when morphine and the distinctive context were explicitly paired rather than explicitly unpaired. Tolerance magnitude in both conditions reached a maximum at eight conditioning sessions. It is argued that the tolerance found in both treatment groups was associatively controlled. The function of handling and injection cues as conditioned stimuli, and the deleterious effects of latent inhibition and partial reinforcement on conditioned excitation and conditioned inhibition are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker AG, Baker PA (1985) Does Inhibition differ from excitation, proactive interference, contextual conditioning and extinction? In: Miller RR, Spear NE (eds) Information processing in animals: conditioned inhibition. Erlbaum, Hillsdale, New Jersey, pp 151–184
Baker TB, Tiffany ST (1985) Morphine tolerance as habituation. Psychol Rev 92:78–108
Cohen J, Cohen P (1975) Applied multiple regression/correlational analysis for the behavioral sciences. Erlbaum, Hillsdale, New Jersey
Dafters RI, Bach L (1985) Absence of environment-specificity in morphine tolerance acquired in nondistinctive environments: habituation or stimulus overshadowing? Psychopharmacology 87:101–106
Dafters RI, Odber J (1989) Effects of dose, interdose interval and drug-signal parameters on morphine analgesic tolerance: implications for current theories of tolerance. Behav Neurosci 103:1082–1090
Dafters RI, Odber J, Miller J (1988) Associative and non-associative tolerance to morphine: support for a dual-process habituation model. Life Sci 42:1897–1906
Fowler H, Kleiman M, Lysle DT (1985) Factors affecting the acquisition and extinction of conditioned inhibition suggest a “slave” process. In: Miller RR, Spear NE (eds) Information processing in animals: conditioned inhibition. Erlbaum, Hillsdale, New Jersey, pp 113–150
Goudie AJ, Demellweek C (1986) Conditioning factors in drug tolerance. In: Goldberg SR, Stolerman IP (eds) Behavioral analysis of drug dependence. Academic Press, New York, pp 225–285
Krank MD, Hinson RE, Siegel S (1984) The effect of partial reinforcement on tolerance to morphine induced analgesia and weight loss in the rat. Behav Neurosci 98:79–85
LoLordo VM, Fairless JL (1985) Pavlovian conditioned inhibition: the literature since 1969. In: Miller RR, Spear NE (eds) Information processing in animals: conditioned inhibition. Erlbaum, Hillsdale, New Jersey, pp 1–50
Maude-Griffin PM, Tiffany ST (1989) Associative morphine tolerance in the rat: examination of compensatory responding and cross-tolerance with stress-induced analgesia. Behav Neur Biol 51:11–33
Rescorla RA (1985) Conditioned inhibition and facilitation. In: Miller RR, Spear NE (eds) Information processing in animals: conditioned inhibition. Erlbaum, Hillsdale, New Jersey, pp 299–326
Rescorla RA, Wagner AR (1972) A theory of Pavlovian conditioning: variations in the effectiveness of reinforcement and nonreinforcement. In: Black AH, Prokasy WF (eds) Classical conditioning II: current research and theory. Appleton Century Crofts, New York, pp 64–99
Siegel S (1975) Evidence from rats that tolerance is a learned response. J Comp Physiol Psychol 89:323–325
Siegel S (1977) Morphine tolerance acquisition as an associative process. J Exp Psychol [Anim Behav] 3:1–13
Siegel S (1989) Pharmacological conditioning and drug effects. In: Goudie AJ, Emmett-Oglesby MW (eds) Psychoactive drugs: tolerance and sensitization. Humana, Clifton, New Jersey, pp 115–180
Tiffany ST, Baker TB (1981) Morphine tolerance in rats: congruence with a Pavlovian paradigm. J Comp Physiol Psychol 95:747–762
Tiffany ST, Drobes D, Cepeda-Benito A (1992) Contribution of associative and nonassociative processes to the development of morphine tolerance. Psychopharmacology 109:185–190
Tiffany ST, Maude-Griffin PM (1988) Tolerance to morphine in the rat: associative and nonassociative effects. Behav Neurosci 102:534–543
Tiffany ST, Petrie EC, Martin EM, Baker TB (1983) Drug signals enhance morphine tolerance development in hypophysectomized rats. Psychopharmacology 79:84–85
Wolgin DL (1989) The role of instrumental learning in behavioral tolerance to drugs. In: Goudie AJ, Emmett-Oglesby MW (eds) Psychoactive drugs: tolerance and sensitization. Humana, Clifton, New Jersey, pp 17–114
Yoburn BC, Morales R, Kelly DD, Inturrisi EC (1984) Constraints on the tail-flick assay: morphine analgesia and tolerance are dependent upon locus of tail stimulation. Life Sci 34:1755–1762
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cepeda-Benito, A., Tiffany, S.T. Effect of number of conditioning trials on the development of associative tolerance to morphine. Psychopharmacology 109, 172–176 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245496
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245496