Abstract
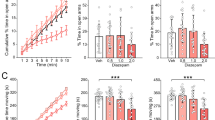
Modafinil is a new drug used in the treatment of narcolepsy. Its administration in mice induced a dose-dependent increase in locomotor activity. The effects of modafinil were compared with those of dexamphetamine on three tests that assessed the anxiety level (drugs were used at doses which induced a roughly similar stimulation of locomotor activity). Dexamphetamine increased the latency of exploration of a white compartment, increased thigmotaxis in an open-field and decreased the time spent in the open arms of an elevated plus-maze. None of these responses was significantly modified by modafinil. We conclude that modafinil does not share the anxiogenic effects of dexamphetamine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bastuji H, Jouvet M (1988) Successful treatment of idiopathic hypersomnia and narcolepsy with modafinil. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 12:695–700
Billiard M, Picard E, Besset A, Mavrel A (1987) Treatment of narcolepsy cataplexy with modafinil, an alpha 1 adrenoreceptor agonist. Communication at the 5th International Congress of Sleep Research, Copenhagen 1987, Book of abstracts, p 471
Brookes LG (1985) Central nervous system stimulants. In: (Iversen SD) Psychopharmacology: recent advances and future prospects. British Association for Psychopharmacology monograph no. 6, Oxford Medical Publications, pp 264–277
Charney DS, Heninger GR, Jatlow PI (1985) Increased anxiogenic effects of caffeine in panic disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry 42:233
Chiueh C, Moore K (1974) Relative potencies ofd- andl- amphetamine in the release of dopamine from cat brain in vivo. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol 7:189–199
Duteil J, De Sereville JE, Boer C, Rambert FA (1990a) Lack of dopaminergic involvement in modafinil, but not amphetamine and methylphenidate, activity in anaesthetized mice and rats: in vivo voltammetry study. Eur J Pharmacol 183 [4]:1406–1407
Duteil J, Rambert F, Pessonnier J, Hermant JF, Gombert R, Assous E (1990b) Central alpha1 adrenergic stimulation in relation to the awakening activity of modafinil: behavioural studies in laboratory animals. Eur J Pharmacol 180:49–58
Ferris R, Tang F, Maxwell R (1972) A comparison of the capacities of isomers of amphetamine, deoxypipradol and methylphenidate to inhibit the uptake of tritiated catecholamines into rat cerebral cortex, hypothalamus, striatum and adrenergic nerves of rabbit aorta. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 181:407–417
Freixanet MG (1978) Medidas conductuales en campo abierto. Rev Psicol Gen Appl 33:657–672
Geller I, Seifter J (1960) The effects of meprobamate, barbiturates,d-amphetamine and promazine on experimentally induced conflict in the rat. Psychopharmacologia 1:482–492
Hermant J, Rambert F, Duteil J (1991) Awakening properties of modafinil: effect on nocturnal activity in monkeys (Macaca mulatta) after acute and repeated administration. Psychopharmacology: 103:28–32
Lapin IP (1993) Anxiogenic effect of phenylethylamine and amphetamine in the elevated plus-maze in mice and its attenuation by ethanol. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 44:241–243
Lin JS, Roussel B, Akaoka H, Fort P, Debilly G, Jouvet M (1992) Role of catecholamines in the modafinil and amphetamine induced wakefulness, a comparative pharmacological study in the cat. Brain Res 591:319–326
Lister GL (1987) The use of a plus-maze to measure anxiety in the mouse. Psychopharmacology 92:180–185
Pellow S, Chopin P, Briley M, File SE (1985) The validation of open: closed arm entries in an elevated plus-maze: a novel test of anxiety in the rat. J Neurosci Methods 14:149–167
Rambert FA, Pessonnier J, Duteil J (1990) Modafinil, amphetamine and methylphenidate-induced hyperactivities in mice involve different mechanisms. Eur J Pharmacol 183 [2]:455–456
Simon P, Panissaud C, Costentin J (1992) Sulpiride anxiogenic-like effect inhibition by a D1 dopamine receptor antagonist. Neuroreport 3:941–942
Simon P, Panissaud C, Costentin J (1993) Anxiogenic effects induced by stimulation of dopamine receptors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 45:685–690
Simon P, Dupuis R, Costentin J (1994) Thigmotaxis as an index of anxiety in mice. Influence of dopaminergic transmissions. Behav Brain Res (in press)
Treit D, Fundytus M (1989) Thigmotaxis as a test for anxiolytic activity in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav [31]:959–962
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simon, P., Panissaud, C. & Costentin, J. The stimulant effect of modafinil on wakefulness is not associated with an increase in anxiety in mice. Psychopharmacology 114, 597–600 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244990
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244990