Abstract
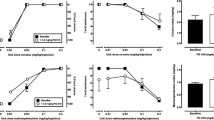
The ability of dopamine D1 antagonists to produce acute extrapyramidal syndromes (EPS) in nonhuman primates is unclear. Some studies in monkeys show that D1 antagonists produce acute dystonia, whereas other studies do not report these effects. The central issues that have yielded conflicting results revolve around prior treatment status (neuroleptic-naive versus neuroleptic sensitized) and route of administration (oral versus parenteral). In this study, separate groups of neuroleptic drug-naive cebus monkeys were tested once weekly with intramuscularly administered SCH 23390, a D1 antagonist, or haloperidol, a D2 antagonist, across a dose range of 0.01–0.25 mg/kg, and a saline control. Both active drugs, but not saline, produced clinically identical syndromes of acute dystonia and bradykinesia, though haloperidol induced higher symptom scores over a longer duration. Sedation and locomotor activity were unchanged by SCH 23390, but decreased with haloperidol. Factors regarding acute EPS liability in nonhuman primate models and clinical implications in man are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Casey DE (1988) Tardive dyskinesia and dopamine receptor hypersensitivity: pros and cons. In: Belmaker RH, Sandler M, Dahlström (eds) Neurology and neurobiology, vol. 42C, Progress in catecholamine research, part C: clinical aspects. Alan R. Liss, New York, pp 9–12
Casey DE (1989a) Clozapine: neuroleptic-induced EPS and tardive dyskinesia. Psychopharmacology 99:S47-S53
Casey DE (1989b) Serotonergic aspects of acute extrapyramidal syndromes in nonhuman primates. Psychopharmacol Bull 25:457–459
Casey DE (1991a) Extrapyramidal syndromes in nonhuman primates: typical and atypical neuroleptics. Psychopharmacol Bull 27:47–50
Casey DE (1991b) SCH 23390 and psychosis. Lancet 338:185
Casey DE (1991c) Neuroleptic drug-induced extrapyramidal syndromes and tardive dyskinesia. Schizophr Res 4:109–120
Casey DE, Keepers GA (1988) Neuroleptic side effects: acute extrapyramidal syndromes and tardive dyskinesia. In: Casey DE, Christensen AV (eds) Psychopharmacology: current trends. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 74–93
Casey DE, Gerlach J, Christensson E (1980) Dopamine, acetylcholine, and GABA effects in acute dystonia in primates. Psychopharmacology 70:83–87
Christensen AV (1990) Long-term effects of dopamine D1 and D2 antagonists in vervet monkeys. Behav Neurol 3:49–60
Christensen AV, Arnt J, Hyttel J, Larsen JJ, Svendsen O (1984) Pharmacological effects of a specific dopamine D1 antagonist SCH 23390 in comparison with neuroleptics. Life Sci 34:1529–1540
Coffin VL, Latranyi MB, Chipkin RE (1989) Acute extrapyramidal syndrome in cebus monkeys: development mediated by dopamine D2 but not D1 receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 249:769–774
Farde L (1992) Selective D1- or D2-dopamine receptor blockade induces akathisia in humans — a PET-study with [11C] SCH 23390 and [11C] raclopride. Psychopharmacology 107:23–29
Farde L, Halldin C, Stone-Elander S, Sedvall G (1987) PET-analysis of human dopamine receptor subtypes using [11C] SCH 23390 and [11C] raclopride. Psychopharmacology 92:278–284
Farde L, Wiesel F-A, Halldin C, Sedvall G (1988) Central D2-dopamine receptor occupancy in schizophrenic patients treated with antipsychotic drugs. Arch Gen Psychiatry 45:71–78
Gerlach J, Lublin H (1988) Tardive dyskinesia may be due to an increased D1/D2 receptor ratio in the brain. Schizophr Res 1:230
Gerlach J, Kistrup K, Korsgaard S (1987) Effect of selective and D2 dopamine receptor antagonists and agonists in cebus monkeys: implications for acute and tardive dyskinesias. In: Dahl SG, Gram LS, Paul SN, Potter WV (eds) Clinical pharmacology in psychiatry. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 236–242
Gessa GL, Canu A, Del Zompo M, Burrai C, Serra G (1991a) Lack of acute antipsychotic effect of SCH 23390, a selective dopamine D1 receptor antagonist. Lancet 337:854–855
Gessa GL, Ganu A, Del Zompo M, Burrai C, Serra G (1991b) SCH 23390 and psychosis. Lancet 338:185–186
Hansen L, Gerlach J (1991) Dopamine 1 and 2 receptor interaction in the development of dystonia and hypersensibility in cebus monkeys. Biol Psychiatry 29:275S
Hyttel J (1983) SCH 23390: the first selective dopamine D1 antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol 91:153–154
Iorio LC, Barnett A, Leitz FH, Houser VP, Korduba CA (1983) SCH 23390, a potential benzazepine antipsychotic with unique interactions on dopaminergic systems. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 226:462–468
Liebman J, Neale R (1980) Neuroleptic-induced acute dyskinesias in squirrel monkeys. Correlation with propensity to cause extrapyramidal side effects. Psychopharmacology 68:25–29
Meltzer HY, Matsubara S, Lee JC (1989) Classification of typical and atypical antipsychotic drugs on the basis of dopamine D1, D2 and serotonin pKi values. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 251:238–246
Peacock, L, Lublin H, Gerlach J (1990) The effects of dopamine D1 and D2 receptor agonists and antagonists in monkeys withdrawn from long-term neuroleptic treatment. Eur J Pharmacol 186:49–59
Seeman P, Lee T, Chau-Wong M, Wong K (1976) Antipsychotic drug doses and neuroleptic/dopamine receptors. Nature 261:717–719
Waddington JL (1986) Behavioral correlates of the action of selective D1 dopamine receptor antagonists. Biochem Pharmacol 35:3661–3667
Waddington JL, O'Boyle KM (1989) Drugs acting on brain dopamine receptors: a conceptual re-evaluation five years after the first selective D1 antagonist. Pharmacol Ther 43:1–52
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Casey, D.E. Dopamine D1 (SCH 23390) and D2 (haloperidol) antagonists in drug-naive monkeys. Psychopharmacology 107, 18–22 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244960
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244960