Abstract
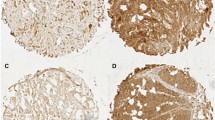
PURPOSE: Recent advances have made possible the treatment of small invasive colorectal cancer by means of polypectomy or endoscopic mucosal resection. CD44 expression in cancer cells was identified as an indicator of lymph-node metastasis, which could be evaluated in specimens removed by colonoscopy. METHODS: The correlation between lymph-node metastasis and the expression of standard-type CD44 in cancer cells was examined immunohistologically using the invaded cancer cells of 61 tissue samples of superficially invasive colorectal cancer. We defined the above as invasive cancer restricted within the colorectal wall. Of the 61 samples, 31 had submucosal invasion and 30 had muscular invasion. RESULTS: Standard-type CD44 expression in the area of invasion in cases with lymph-node metastasis was remarkably down-regulated. In 43 cases with no lymph-node metastasis, 36 (83.7 percent) of patients had CD44 expression in invaded cells, whereas only two of 18 cases (11.1 percent) with lymph-node metastasis had expression of standard-type CD44 in the same area (P<0.0001). A total of 69.6 percent (16/23) of patients with loss of standard-type CD44 expression in invaded sites were found to have positive metastasis in the lymph nodes. These results suggest that standard-type CD44 in invasive colon cancer cells could suppress metastasis to the regional lymph nodes. CONCLUSION: In cases of invasive colorectal cancer, the loss of standard-type CD44 expression in the invaded area is a sensitive marker for metastasis to the lymph nodes. Further investigation with larger patient groups is required to clarify the reliability of loss of standard-type CD44 expression as an indicator for additional surgery after endoscopic resection of submucosal invasive colorectal carcinoma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kudo S. Endoscopic mucosal resection of flat and depressed types of early colorectal cancer. Endoscopy 1993;25:455–61.
Mion F, Desseigne F, Napoleon B, Berger F, Lambert R. Failure of endoscopic detection of a de novo carcinoma of the colon in a patient with adenomatous polyps. Gastrointest Endosc 1992;38:703–6.
Coverlizza S, Risio M, Ferrari A, Fenoglio-Preiser CM, Rossini FP. Colorectal adenomas containing invasive carcinoma. Pathologic assessment of lymph node metastatic potential. Cancer 1989;64:1937–47.
Minamoto T, Mai M, Ogino T,et al. Early invasive colorectal carcinomas metastatic to the lymph node with attention to their nonpolypoid development. Am J Gastroenterol 1993;88:1035–9.
Sugihara K, Muto T, Morioka Y. Management of patients with invasive carcinoma removed by colonoscopic polypectomy. Dis Colon Rectum 1989;32:829–34.
St. John T, Meyer J, Idzerda R, Gallatin WM. Expression of CD44 confers a new adhesive phenotype on transfected cell. Cell 1990;60:45–52.
Caner WG, Wayner EA. Characterization of the class III collagen receptor, a phosphorylated, transmembrane glycoprotein expressed in nucleated human cells. J Biol Chem 1988;263:4193–201.
Ichikawa T, Ichikawa Y, Dong J,et al. Localization of metastasis suppressor gene(s) for prostatic cancer to the short arm of human chromosome 11. Cancer Res 1992;52:3486–90.
Gao AC, Lou W, Dong JT, Isaacs JT. CD44 is a metastasis suppressor gene for prostatic cancer located on human chromosome 11p13. Cancer Res 1997;57:846–9.
Lyzak JS, Yaremko ML, Recant W, Baunoch DA, Joseph L. Role of CD44 in nonpalpable T1a and T1b breast cancer. Hum Pathol 1997;28:772–8.
Wielenga VJ, van der Voort R, Mulder JW,et al. CD44 splice variants as prognostic markers in colorectal cancer. Scand J Gastroenterol 1998;33:82–7
Rudy W, Hoffman M, Schwartz AR,et al. The two major CD44 proteins expressed on a metastatic rat tumor cell line are derived from different splice variants: each one individually suffices to confer metastatic behavior. Cancer Res 1993;53:1262–8.
Matumura Y, Tarin D. Significance of CD44 gene products for cancer diagnosis and disease evaluation. Lancet 1992;340:1053–8.
Nihei Z, Ichikawa W, Kojima K,et al. The positive relationship between the expression of CD44 variant 6 and prognosis in colorectal cancer. Surg Today 1996;26:760–1.
Mulder JR, Kruyt PM, Sewnath M,et al. Colorectal cancer prognosis and expression of exon-v6-containing CD44 proteins. Lancet 1994;344:1470–2.
Finke LH, Terpe HJ, Zorb C, Haensch W, Shang PM. Colorectal cancer prognosis and expression of exon-v6-containing CD44 proteins [letter]. Lancet 1995;345:583.
Jansen RH, Joosten Achjanie SR, Arends JW,et al. CD44v6 is not a prognostic factor in primary breast cancer. Ann Oncol 1998;9:109–11.
Joensuu H, Klemi PJ, Toikkanen S, Jalkanen S. Glycoprotein CD44 expression and its association with survival in breast cancer. Am J Pathol 1993;143:867–74.
Tanaka S, Haruma K, Tatsuta S,et al. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen expression correlates with the metastatic potential of submucosal invasive colorectal carcinoma. Oncology 1995;52:134–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported in part by a Grant from Japanese Ministry of Culture and Education, No 06671241, to Dr. Asao.
About this article
Cite this article
Asao, T., Nakamura, Ji., Shitara, Y. et al. Loss of standard type of CD44 expression in invaded area as a good indicator of lymph-node metastasis in colorectal carcinoma. Dis Colon Rectum 43, 1250–1254 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02237430
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02237430