Summary
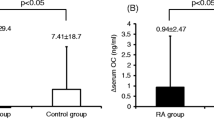
Bone loss is a feature of RA, but the exact mechanisms involved are not clear. The collagen crosslinks deoxypyridinoline (DPYR) and pyridinoline (PYR) are specific indices of ‘mature’ collagen breakdown and reflect increased bone turnover. The aims of the study were to examine crosslink levels in RA and their association with disease activity and the effect of steroids. Urinary crosslinks corrected for creatinine were measured on morning fasting samples by HPLC in 70 postmenopausal women with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) aged 45–65 and compared with 169 postmenopausal healthy age-matched controls from the population. Mean levels of PYR were significantly higher in RA cases than in controls (52.4 versus 37.5 nmols/mmolCr) although mean levels of DPYR did not differ significantly. A weak correlation was found with ESR and PYR (r=0.35) but not with other markers of disease activity. Thirteen of the RA cases were current steroid users and their levels of DPYR and PYR even with low doses, were significantly elevated above those of non-users, ex-users and controls. The finding of raised urinary PYR but not the bone specific DPYR in nonsteroid using RA cases suggests that the increased collagen breakdown does not primarily come from bone but from other sources such as cartilage and synovium. The large increases in collagen excretion in low dose steroid users, may reflect the higher risk of osteoporosis in this group.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi, J.D. Markers of bone turnover in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 1991, 18, 1119–1120.
Magaro, M., Altomorite, L., Mirone, L. et al. Bone GLA protein (BGP) levels and bone turnover in rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol 1989, 28, 207–211.
Als, O.S., Riis, B.J., Gotresdon, A., Christiansen, C., Defos, L.J. Biochemical markers of bone turnover in rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Med Scand 1989, 219, 209–213.
Weismann, M.H., Orth, R.W., Catherwood, B.D. et al. Measures of bone loss in rheumatoid arthritis. Arch Intern Med 1986, 146, 701–704.
Eyre, D.R., Ogushi, H. The hydroxypyridinium crosslinks of skeletal collagens: their measurement, properties and a proposed pathway of formation. Biochem Biophys Res Communi 1980, 92, 403–410.
Eyre, D.R., Koob, T.J., Van Ness, K.P. Quantitation of hydroxypyridinium crosslinks in collagen by high performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem 1984, 137, 380–388.
Black, D., Duncan, A., Robins, S.P. Quantitative analysis of the pyridinium crosslinks of collagen in urine using ion paired reversed phase high performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem 1988, 169, 197–203.
James, I.T., Perrett, D., Thompson, P.W. Rapid assay for hard tissue derived collagen crosslinks using isocratic ion pair reversed phase liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr (Biomed Appl) 1990, 525, 43–57.
Borggreven, J.M.P.M., Hoppenbrouwers, P.M.M., Gorisseu, R. Radiochemical determination of the metabolic activity of collagen in mature dentin. J Dent Res 1979, 58, 2120–2124.
Robins, S.P., Duncan, A., Riggs, B.L. Direct measurement of free hydroxypyridinium crosslinks of collagen in urine as new markers of bone resorption in osteoporosis. In: Osteoporosis, 1990. Eds: Christiansen, C., Overgaard, K. Copenhagen, Denmark, Osteopress 1990, 465–467.
Abbiati, G., Rigoldi, Arrigoni, M., Longoni, A., Fincato, G. Weekly monitoring of free and total urinary pyridinoline in healthy volunteers. In: Osteoporosis, 1990. Eds: Christiansen, C., Overgaard, K. Copenhagen, Denmark, Osteopress, 1990a, 2, 613–615.
Colwell, A., Eastell, R., Assiri, A.M.A., Russell, R.G.G. Effect of diet on deoxypyridinoline excretion. In: Osteoporosis, 1990. Eds: Christiansen, C., Overgaard, K. Copenhagen, Denmark, Osteopress, 1990, 1: 590–591.
Fujimoto, D., Suzuki, M., Uchiyama, A., Miyamoto, S., Inoue, T. Analysis of pyridinole a crosslinking compound of collagen fibers in human urine. J Biochem (Tokyo) 1984, 94, 1133–1136.
Eastell, R., Hamptom, L., Colwell, A., Green, J.R., Assiri, A.M.A., Hesp, R., Russell, R.G.G., Reeve, J. Urinary collagen crosslinks are highly correlated with radioisotopic measurements of bone resorption. In: Osteoporosis, 1990. Eds.: Christiansen, C., Overgaard, K. Copenhagen, Denmark, Osteopress, 1990b, 1, 468–469.
Seibel, M.J., Duncan, A., Robins, S.P. Urinary hydroxypyridinium crosslinks provide indices of cartilage and bone involvement in arthritic disease. J Rheumatol 1989, 16, 964–970.
Arrigoni, M., Abbiati, G., Galimberti, S., Longoni, A., Bartucci, F. Free and total urinary pyridinoline and deoxypyridinoline (LP) analysis: Comparison between 24 hrs. collection and fasting early morning urine samples. In: Osteoporosis, 1990. Eds.: Christiansen, C., Overgaard, K. Copenhagen, Denmark, Osteopress, 1990, 2, 596–598.
Uebelhart, D., Gineyts, E., Chapuy, M.C., Delmas, P.D. Urinary excretion of pyridinium crosslinks: a new marker of bone resorption in metabolic bone disease. Bone and Mineral 1990, 8, 87–96.
Eastell, R., Calvo, M.S., Burritt, M.F., Simmonds, P.S., Colwell, A., Assiri, A.M.A, Mann, K.G., Graham, R., Russell, G., Riggs, B.L. Circadian changes in bone turnover assessed by serum bone gla-protein and urinary deopyridinoline: effect of growth and aging. Bone 1990a, 11, 389 (Abstract P14).
Thompson, P.W., Karamacharya, S., Bhaskaran, V., James, I.T. Comparison of collagen crosslink levels in spot urine samples. Bone 1990, 11, 390 (Abstract P15).
Black, D., Marabani, M., Sturrock, R.D., Robins, S.P. Urinary excretion of the hydroxypyridinium crosslinks of collagen in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 1989, 48, 641–644.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spector, T.D., James, I.T., Hall, G.M. et al. Increased levels of urinary collagen crosslinks in females with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 12, 240–244 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02231535
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02231535