Summary
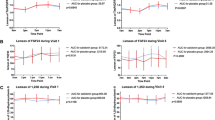
The effect of intravenous salmon calcitonin (SCT) infusion on the net rate of loss from plasma of recently injected45Ca has been studied in conscious fasted rats, some of which had been previously thyroparathyroidectomized (TPTX). The45Ca was injected 10 h prior to or 1 or 2 h after the initiation of the infusion. Salmon calcitonin (0.05–0.2 MRC mU/g body weight/h) infusion produced the expected hypocalcemia and hypophosphatemia. The drop in plasma calcium levels produced by the hormone was lowered further by the addition of phosphate to the infusate.
Plasma45Ca changes, during SCT infusion, followed a biphasic pattern when the radionuclide injection preceded SCT infusion by 10 h. During the first part of the infusion, the rate of loss of45Ca from plasma was greater in SCT-treated than in control rats. Later, this pattern reversed, and the rate of loss of45Ca from plasma became slower in SCT-treated animals. If45Ca was injected after SCT infusion was initiated only the second phase of the biphasic effect was observed; i.e., disappearance of45Ca from plasma was slower in SCT-infused than in control rats.
These data are considered to support the hypothesis that rapid and opposing calcium fluxes exist between bone fluid and plasma, and that calcitonin acts by decreasing the calcium efflux from bone fluid. The calcium moved in this efflux system includes some that has only recently entered bone fluid from plasma. This is the explanation given for the initial decrease in plasma45Ca concentrations following SCT infusion. The reverse effect in the second phase can be explained as the result of a secondary reduction in calcium influx to bone fluid from plasma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borle, A.D., Briggs, R.N.: Microdetermination of calcium in biological material by automatic fluorometric titration. Anal. Chem.40, 339–344 (1968)
Chausmer, A., Mittleman, R., Wallach, S.: Studies of thryro-calcitonin action. Endocrinology79, 131–137 (1966)
Chen, P.S., Tanbara, T.Y., Warren, H.: Microdetermination of phosphorus. Anal. Chem.28, 1756–1758 (1965)
Doppelt, S.H., Talmage, R.V.: Calcitonin and the bone fluid compartment. Clin. Orthop.118, 242–250 (1976)
Grubb, S.A., Edwards, D., Talmage, R.V.: Effect of endogenous and infused parathyroid hormone on plasma concentrations of recently administered45Ca. Calcif. Tiss. Res.24, 209–214. (1977).
Hirsch, P.: Thyrocalcitonin inhibition of bone resorption induced by parathyroid extract in thyroparathyroidectomized rats. Endocrinology80, 539–541 (1967)
Johnston, C.C., Deiss, W.P.: Inhibitory effect of thyrocalcitonin on calcium release in vivo and in bone metabolism in vitro. Endocrinology78, 1139–1143 (1966)
Kenny, A.D., Heiskell, C.A.: Effect of crude thyrocalcitonin on calcium and phosphorus metabolism in rats. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med.120, 269–271 (1965)
Klein, D.C., Morii, H., Talmage, R.V.: Effect of thyrocalcitonin, administered during peritoneal lavage, on removal of bone salts and their radioisotopes. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med.124, 627–633 (1967)
Neuman, W.F.: The presence of a soluble “regulator” phase (secondary calcium phosphate) in bone. In: Calcium regulating hormones (Talmage, R.V., Owens, M., Parsons, J.A., eds.), pp. 1004–1008, Amsterdam: Excerpta Medica 1975
O'Riordan, J.L.H., Aurbach, G.D.: Mode of action of thryrocalcitonin. Endocrinology82, 377–383 (1968)
Scarpace, P., Neuman, W.F.: The blood: bone disequilibrium, II: Evidence against the active accumulation of calcium or phosphate into the bone extracellular fluid. Calcif. Tiss. Res.20, 151–158 (1976)
Talmage, R.V., Anderson, J.J.B., Cooper, C.W.: The influence of calcitonins on the disappearance of radiocalcium and radiophosphorus from plasma. Endocrinology90, 1185–1192 (1972)
Talmage, R.V., Doppelt, S.H., Fondren, F.B.: An interpretation of acute changes in plasma45Ca following parathyroid hormone administration to thyroparathyroidectomized rats. Calcif. Tiss. Res.22, 117–128 (1976)
Talmage, R.V., Elliott, J.R.: Removal of calcium from bone as influenced by the parathyroids. Endocrinology62, 717–722 (1958)
Talmage, R.V., Grubb, S.A.: A laboratory model demonstrating osteocyte-osteoblast control of plasma calcium concentrations. Clin. Orthop.122, 299–306 (1977)
Woods, K.R., Armstrong, W.D.: Action of parathyroid extract on stable bone mineral using radiocalcium as tracer. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med.91, 255–258 (1956)
Yamaguchi, M., Takei, Y., Yamamoto, T.: Effect of thyrocalcitonin on calcium concentration in liver of intact and thyroparathyroidectomized rats. Endocrinology96, 1004–1008 (1975)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grubb, S.A., Markham, T.C. & Talmage, R.V. Effect of salmon calcitonin infusion on plasma concentrations of recently administered45Ca. Calc. Tis Res. 24, 201–208 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02223317
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02223317