Abstract
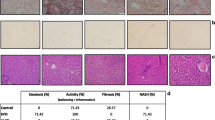
Patients with liver cirrhosis frequently show some degree of protein-energy malnutrition and obviously require nutritional support. In this study, the treatment of rats consisted of thead libitum oral intake of a 300 mg/liter thioacetamide solution, used as drinking water for four months. Thioacetamide treatment produced a severe alteration in the plasma fatty acid profile with significant decreases of these, which mimicked changes described in human cirrhosis. This hepatotoxic agent causes nodular cirrhosis, with loss of the normal architecture of the liver and disruption of the vascular pattern. The goal of the study was to evaluate the influence of n-3 and n-6 series long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid dietary supplementation in experimental animals and to assess the effects of those dietary components on structural recovery in the liver. Significant increases of saturated and monounsaturated fatty acids as well as n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids were seen only in the animals given the n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplemented diet. However, only rats given the standard diet exhibited some degree of histological regeneration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arias MA, Boyer JL, Fausto N, Jakoby WB, Schachter DA, Shafritz DA: The Liver: Biology and Pathobiology, New York, Raven Press, 1994
Kretzschmar M, Machnik G, Müller A, Splinter F-K, Zimmermann T, Klinger W: Experimental treatment of thioacetamide-induced liver cirrhosis by metenolone acetate. A morphological and biochemical study. Exp Pathol 42:37–46, 1991
Bergasa NV, Borque MJ, Wahl LM, Rabin L, Jones EA: Modulation on thioacetamide-induced hepatocellular necrosis by prostaglandins is associated with novel histologic changes. Liver 12:168–174, 1992
Dyroff MC, Neal RA: Identification of the major protein adduct formed in rat liver after thioacetamide administration. Cancer Res 41:3430–3435, 1981
Trennery PN, Waring RH: Early changes in thioacetamide-induced liver damage. Toxicol Lett 19:299–307, 1983
Anghileri LJ, Heidbreder M, Weiler G, Dermietzel R: Hepatocarcinogenesis by thioacetamide: Correlations of histological and biochemical changes, and possible role of cell injury. Exp Cell Biol 45:34–47, 1977
Becker FF: Thioacetamide hepatocarcinogenesis. J Natl Cancer Inst 71:553–558, 1983
Dasgupta A, Chatterjee R, Chowdhury JR: Thioacetamideinduced hepatocarcinoma in rats. Oncology 38:249–253, 1981
Gupta DN: Production of cancer of the bile ducts with thioacetamide. Nature 175:257, 1955
Müller D, Sommer M, Kretzschmar M, Zimmermann T, Buko VU, Lukivskaya OJ, Dargel R: Lipids peroxidation in thioacetamide-induced macronodular rat liver cirrhosis. Arch Toxicol 65:199–203, 1991
Nozu F, Takeyama N, Tanaka T: Changes of hepatic fatty acid metabolism produced by chronic thioacetamide administration in rats. Hepatology 15:1099–1106, 1992
Zimmermann T, Franke H, Dargel R: Studies on lipid and lipoprotein metabolism in rat liver cirrhosis induced by different regimens of thioacetamide administration. Exp Pathol 30:109–117, 1986
Zimmermann T, Müller A, Machnik G, Franke H, Schubert H, Dargel R: Biochemical and morphological studies on production and regression of experimental liver cirrhosis induced by thioacetamide in Uje: WIST rats. Z Versuchstierkd 30:165–180, 1987
Cabré E, Periago JL, Abad-Lacruz A, Gil A, González-Huix F, Sánchez de Medina F, Gassull MA: Polyunsaturated fatty acid deficiency in liver cirrhosis: Its relation to associated proteinenergy malnutrition (preliminary report). Am J Gastroenterol 83:712–717, 1988
Cabré E, Periago JL, Abad-Lacruz A, et al: Plasma fatty acid profile in advanced cirrhosis: Unsaturation deficit of lipid fractions. Am J Gastroenterol 85:1597–1604, 1990
Cabré E, Periago JL, González J, González-Huix F, Abad-Lacruz A, Gil A, Sánchez-Medina F, Esteve-Comas M, Fernández-Bañares F, Planas R, Gassull MA: Plasma polyunsaturated fatty acids in liver cirrhosis with or without chronic hepatic encephalopathy: A preliminary study. JPEN 16:359–363, 1992
Latifi R, Killam RW, Dudrick SJ: Nutritional support in liver failure. Surg Clin North Am 1991:71:567–578, 1991
Müller MJ, Rieger A, Willmann O: Metabolic responses to lipid infusions in patients with liver cirrhosis. Clin Nutr 11:193–206, 1992
Christon R, Fernandez Y, Linard A, Périquet A, Deltour P, Mitjavila S: Diet-induced structural and functional modifications in the pig liver endoplasmic reticulum membrane: effect of polyunsaturated fatty acid deficiency. J Nutr Biochem 3:510–518, 1992
Moreira E, Fontana L, Periago JL, Sánchez de Medina F, Gil A: Changes in fatty acid composition of plasma, liver microsomes and erythrocytes in liver cirrhosis induced by microsomes and erythrocytes in liver cirrhosis induced by oral intake of thioacetamide in rats. Hepatology 21:199–206, 1995
Council of Europe: European convention for the protection of vertebrate animals used for experimental and other scientific purposes. Addendum III. Strasbourg, 1982
Philipp BW, Shapiro DJ: Improved methods for the assay and activation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutamy-Co A reductase. J Lipid Res 20:583–593, 1979
Folch J, Less M, Sloane-Stanley GH: A single methods for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J Biochem 226:497–503, 1957
Skipski WP, Barclay M: Thin layer chromatography of lipids.In Methods in Enzymology. JM Lowenstein (ed). New York. Academic Press, 1969, pp 530–598
Morrison MR, Smith LN: Preparation of fatty acid methyl esters and dimethylacetals from lipids with boron fluoride methanol. J Lipid Res 5:600–607, 1968
Reynolds ES: The use of lead citrate at high PH as an electronopaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol 17:208–212, 1963
Dixon WJ, Brown MB, Engelman L, Jennrich RJ: BMDP Statistical Software Manual. Berkeley, University of California Press, 1990
Popper H: Pathological aspects of cirrhosis. Am J Pathol 87:228–257, 1977
Moshage H, Yap S-H: Molecular and cellular biology of the liver. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 9:367–373, 1993
Bissel DM: Lipocyte activation and hepatic fibrosis. Gastroenterology 102:1803–1804, 1992
Franke H, Zimmermann T, Dargel R: Changes in intra-and extrahepatic VLDL in the rat following acute injury by thioacetamide. Virchows Arch (Cell Pathol) 48:277–288, 1985
Muscaritoli M, Cangiano C, Cascino A, Ceci F, Caputo V, Martino P, Serra P, Fanelli FR: Exogenous lipid clearance in compensated liver cirrhosis. JPEN 10:599–603, 1986
Nassar BA, Das UN, Huang Y-S, Ells G, Horrobin DF: The effect of chemical hepatocarcinogenesis on liver phospholipid composition in rats fed n-6 and n-3 fatty acid-supplemented diets. Chem Hepatocarcinogen 199:365–368, 1992
González J, Periago JL, Gil A, Cabré E, Abad-Lacruz A, Gassull MA, Sánchez de Medina F: Malnutrition-related polyunsaturated fatty acid changes in plasma lipid fractions of cirrhotic patients. Metabolism 41:954–960, 1992
Franke H, Zimmermann T, Dargel R: Qualitative and quantitative changes in hepatic lipoprotein particles following acute injury of the rat liver induced by thioacetamide. Virchows Arch (Cell Pathol) 44:99–113, 1983
Yamazaki RK, Shen T, Schade GB: A diet rich in (n-3) fatty acids increased peroxisomal beta-oxidation activity and lowers plasma triacylglycerols without inhibiting glutathionedependent detoxication activities in the rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta 920:62–67, 1987
Herzberg GR: Dietary regulation of fatty acid and triglyceride metabolism. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 69:1637–1647, 1991
Lieber CS, Robin SJ, Li J, De Carli LM, Mak KM, Fasulo JM, Leo MA: Phosphatidyl choline protects against fibrosis and cirrhosis in the baboon. Gastroenterology 106:152–159, 1994
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernández, I., Torres, I., Moreira, E. et al. Influence of administration of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids on process of histological recovery in liver cirrhosis produced by oral intake of thioacetamide. Digest Dis Sci 41, 197–207 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02208605
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02208605