Summary
The salt sensitivity of cucumbers was investigated in two experiments. The electrical conductivity (EC) of the irrigation water used in the experiments ranged from 0.1 to 4.5 mmho/cm at 25°C. In another experiment the specific sensitivity of cucumbers to various salts was studied.
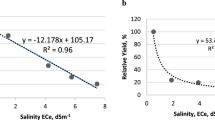
There was a linear decrease in the yields of cucumbers as the salt concentration of the irrigation water increased. The yield reduction was about 17% for a 1 mmho/cm increase in the EC. Cucumbers showed a specific sensitivity to excess calcium and magnesium, but most detrimental was the application of sodium bicarbonate.
Crop analysis showed that when sodium and chloride were added to the irrigation water, chloride was taken up in much greater quantities by the cucumbers than sodium. The addition of certain ions to the irrigation water not only had an effect on the uptake of the particular ion, but also had a significant effect on the uptake of other ions. The greatest changes in the mineral composition of the leaf occurred as a result of the application of sodium bicarbonate to the irrigation water.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abed, A. H., Einfluss von Salzkonzentration und Konzentrationsänderung in der Nährlösung auf Assimilation und Transpiration von Gurkenpflanzen. Dissertation, Fakultät für Gartenbau und Landeskultur der Technischen Universität, Hannover (1973).
Baxter, P. and Belcher, R., The role of the bicarbonate ion in lime induced chlorosis. J. Aust. Inst. Agric. Sci.21, 32–34 (1955).
Boxma, R., Bicarbonate as the most importance soil factor in lime-induced chlorosis in the Netherlands. Plant and Soil37, 233–243 (1972).
Brown, J. C., An evaluation of bicarbonate-induced iron chlorosis. Soil Sci.89, 246–247 (1960).
Clark, R. B., Blank, G. B., Hale, V. Q., and Wallace, A., Behavior of bicarbonate and Sr 85 in soils. Soil Sci.89, 292–295 (1960).
Ende, J. van den, Analysis of greenhouse soils by means of aqueous extracts. Proc. 6th Colloquium Inter. Potash Inst. Florence, 246–255 (1968).
Hilgard, E. W., Soils. Macmillan Co. New York, pp. 78 (1919).
Ploegman, C. and Bierhuizen, J. F., Zouttolerantie van komkommer. Bedrijfsontwikkeling1, 32–39 (1970).
Richards, L. A., Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. U.S.D.A. Agric. Handb.,60, 69–82 (1954).
Shimada, N., Excess injury of calcium and magnesium in the crops. Jpn. Agric. Res. Quart.7, 173–177 (1973).
Sonneveld, C., Koornneef, P. and van den Ende, J., De osmotische druk en het electrische geleidingsvermogen van enkele zoutoplossingen. Meded. Dir. Tuinbouw29, 471–475 (1966).
Sonneveld, C. and van den Ende, J., De invloed van zout gietwater bij de tomatenteelt onder glas. Bedrijfsontwikkeling2, 43–51 (1971).
Sonneveld, C. en van Beusekom, J., De invloed van zout gietwater bij de teelt van peper en paprika onder glas. Landbouwkd. Tijdschr.86, 241–246 (1974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sonneveld, C., Voogt, S.J. Effects of saline irrigation water on glasshouse cucumbers. Plant Soil 49, 595–606 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02183284
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02183284