Abstract
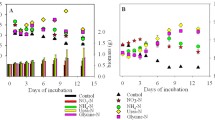
In-situ experiments were performed during different seasons to determine uptake rates of PO 43- , NH 4+ and NO 3- within ecologically representative ranges of nutrient concentrations, of dominant macroalgae in the Baltic Sea. Uptake rates were governed by nutrient concentrations, water temperature and thallus morphology, but not by the phylogenetic affinity of the species. Nitrogen uptake rates were always higher than those of phosphorus at the same concentrations, and NH 4+ −N uptake rates exceeded those of NO 3- −N. The lowest uptake rates occurred among the late successional, long-lived, coarse species with low surface: volume ratios (Fucus vesiculosus, Furcellaria lumbricalis andPhyllophora truncata). The highest uptake rates were measured for short-lived, opportunistic algae, filamentous or with numerous hairs, (Cladophora glomerata, Enteromorpha ahlneriana, Scytosiphon lomentaria, Dictyosiphon foeniculaceus andCeramium tenuicorne). The latter group also had the highest Vmax:kmax ratios, which indicates a more competitive advantage for nutrient uptake at low concentrations.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Bahr, L. M., Jr.: Functional taxonomy: an immodest proposal. Ecol. Modelling15, 211–233 (1982)
Birch, P. B., D. M. Gordon and A. J. McComb: Nitrogen and phosphorus nutrition ofCladophorain the Peel-Harvey system. Bot. mar.24, 381–387 (1981)
Bird, K. T.: Simultaneous assimilation of ammonium and nitrate byGelidium nudifrons (Gelidiales: Rhodophyta). J. Phycol12, 238–241 (1976)
Bird, K. T.: Non-photosynthetic carbon fixation and N-nutrient uptake and assimilation inGracilaria spp.Abstracts, First int. Phycological Congr., St. John's, Newfoundland Canada, August 8th–14th, 1982, p a4 1982
Bird, K. T., C. Habig and T. DeBusk: Nitrogen allocation and storage patterns inGracilaria tikvahiae (Rhodophyta). J. Phycol.18, 344–348 (1982)
Carlberg, S. (Ed.): New Baltic manual. ICES Cooperative Research Reports, Ser. A, No. 29, 145 pp. 1972
Chapman, A. R. O. and J. S. Craigie: Seasonal growth inLaminaria longicruris: relations with dissolved inorganic nutrients and internal reserves of nitrogen. Mar. Biol.40, 197–205 (1977)
Chapman, A. R. O., J. W. Markham and K. Lüning: Effects of nitrate concentration on the growth and physiology ofLaminaria saccharina (Phaeophyta) in culture. J. Phycol.14, 195–198 (1978)
DeBoer, J. A.: Nutrients.In: The biology of seaweeds, pp 356–392. Ed. by C. S. Lobban and M. J. Wynne. Oxford: Blackwell Scient. Publ. 1981
DeBoer, J. A. and F. Whoriskey: Red algal hair cells: possible role in nutrient uptake. J. Phycol.17, Suppl. p 14 (1989)
D'Elia, C. F. and J. A. DeBoer: Nutritional studies of two red algae. II. Kinetics of ammonium and nitrate uptake. J. Phycol.14, 266–272 (1978)
Espinoza, J. and A. R. O. Chapman: Ecotypic differentiation ofLaminaria longicruris in relation to seawater nitrate concentration. Mar. Biol.74, 213–218 (1983)
FitzGerald, W. J., Jr.: Environmental parameters influencing the growth ofEnteromorpha clathrata (Roth) J. Ag. in the intertidal zone on Guam. Bot. mar.21, 207–220 (1978)
Gerard V. A.: Growth and utilization of internal nitrogen reserves by the giant kelpMacrocystis pyrifera in a low-nitrogen environment. Mar. Biol.66, 27–35 (1982)
Gordon, D. M., P. B. Birch and A. J. McComb: Effects of inorganic phosphorus and nitrogen on the growth of an estuarineCladophora in culture. Bot. mar.24, 93–106 (1981)
Guterstam, B., I. Wallentinus and R. Iturriaga.In situ primary production ofFucus vesiculosus andCladophora glomerata. Kieler Meeresforsch., Sonderh.4, 257–266 (1978)
Haines, K. C. and P. A. Wheeler: Ammonium and nitrate uptake by the marine macrophytesHypnea musciformis (Rhodophyta) andMacrocystis pyrifera (Phaeophyta). J. Phycol.14, 319–324 (1978)
Hanisak, M. D. and M. M. Harlin: Uptake of inorganic nitrogen byCodium fragile subsp.tomentosoides (Chlorophyta). J. Phycol.14, 450–454 (1978)
Harlin, M. M.: Nitrate uptake byEnteromorpha spp. (chlorophyceae): applications to aquaculture systems. Aquaculture15, 373–376 (1978)
Harlin, M. M. and J. S. Craigie: Nitrate uptake byLaminaria longicruris (Phaeophyceae). J. Phycol.14, 464–467 (1978)
Harlin, M. M., B. Thorne-Miller and G. B. Thurseby: Ammonium uptake byGracilaria sp. (Florideophyceae) andUlva lactuca (Chlorophyceae) in closed system fish culture.In: Proc. IXth Intern. Seaweed Symp. Santa Barbara, California (USA), 20–27 August 1977, pp 285–292. Ed. by A. Jensen and J. R. Stein. Princeton: Science Press 1979
Healey, F. P.: Slope of the Monod equation as an indicator of advantage in nutrient competition. Microb. Ecol.5, 281–286 (1980)
Indergaard, M. and A. Jensen: Nitrate and phosphate uptake in small populations ofLaminaria digitata (Phaeophyceae).In: Proc. Xth Intern. Seaweed Symp., Göteborg, Sweden, August 11–15, 1980, pp 411–417. Ed. by T. Levring. Berlin: Walter de Gruyter 1981
Kanwisher, J. W.: Photosynthesis and respiration in some seaweeds.In: Some contemporary studies in marine science, pp 407–420. Ed. by H. Barnes. London: Allen and Unwin 1966
Kautsky, L.: Primary production and uptake kinetics of ammonium and phosphate byEnteromorpha compressa in an ammonium sulfate industry outlet area. Aquat. Bot.12, 23–40 (1982)
Kautsky, N. and I. Wallentinus: Nutrient release from a BalticMytilus-red algal community and its role in benthic and pelagic productivity. Ophelia, Suppl1, 17–30 (1980)
King, R. J. and W. Schramm: Photosynthetic rates of benthic marine algae in relation to light intensity and seasonal variations. Mar. Biol.37, 215–222 (1976)
Lapointe, B. E.: The effects of light and nitrogen on growth, pigment content, and biochemical composition ofGracilaria foliifera v. angustissima (Gigartinales, Rhodophyta). J. Phycol.17, 90–95 (1981)
Lapointe, B. E. and J. H. Ryther: The effects of nitrogen and seawater flow rate on the growth and biochemical composition ofGracilaria foliifera var.angustissima in mass outdoor cultures. Bot. mar.22, 529–537 (1979)
Larsson, U.: Produktionsbegränsande ämnen. Delrapport till “Eutrofiering i marin miljö”, National Swedish Environment Protection Board, Stockholm: mimeogr. (In Swedish) 1983
Littler, M. M.: The effects of bottle volume, thallus weight, oxygen saturation levels, and water movement on apparent photosynthetic rates in marine algae. Aquat. Bot.7, 21–34 (1979)
Littler, M. M.: Morphological form and photosynthetic performances of marine macroalgae: tests of a functional/form hypothesis. Bot. mar.22, 161–165 (1980)
Littler, M. M. and K. E. Arnold: Sources of variability in macroalgal primary productivity: sampling and interpretive problems. Aquat. Bot.8, 141–156 (1980)
Littler, M. M. and K. E. Arnold: Primary productivity of marine macroalgal functional-form groups from southwestern North America. J. Phycol.18, 307–311 (1982)
Littler, M. M. and D. S. Littler: The evolution of thallus and survival strategies in benthic marine macroalgae: field and laboratory tests of a functional form model. Am. Nat.116, 25–44 (1980)
Littler, M. M. and D. S. Littler: Intertidal macrophyte communities from Pacific Baja California and the upper Gulf of California: Relatively constant vs. environmentally fluctuating systems. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser.4, 145–158 (1981)
Littler, M. M., D. S. Littler and P. R. Taylor: Evolutionary strategies in a tropical barrier reef system: functional-form groups of marine macroalgae. J. Phycol.19, 229–237 (1983a)
Littler, M. M., D. R. Martz and D. S. Littler: Effects of recurrent sand deposition on rocky intertidal organisms: importance of substrate heterogeneity in a fluctuating environment. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser.11, 129–139 (1983b)
Littler, M. M. and S. N. Murray: The primary productivity of marine macrophytes from a rocky intertidal community. Mar. Biol.27, 131–135 (1974)
Manley, S. L.: Phosphate uptake byMacrocystis pyrifera. Abstracts, First Intern. Phycological Congr., St. John's, Newfoundland Canada, August 8th–14th, 1982, p a31, 1982
Maynard, J. W. and W. J. Lucas: A reanalysis of the twocomponent phloem loading system inBeta vulgaris. Plant. Physiol.69, 734–739 (1982)
Morgan, K. C. and F. J. Simpson: Cultivation ofPalmaria (Rhodymenia) palmata: effect of high concentrations of nitrate and ammonium on growth and nitrogen uptake. Aquat. Bot.11, 167–171 (1981a)
Morgan, K. C. and F. J. Simpson: The cultivation ofPalmaria palmata: effect of light intensity and nitrate supply on growth and chemical composition. Bot. mar.24, 273–277 (1981b)
Munk, W. H. and G. A. Riley: Absorption of nutrients by aquatic plants. J. mar. Res.11, 215–240 (1952)
North, W., V. Gerard and R. McPeak: Experimental fertilizing of coastalMacrocystis beds.In: Proc. Xth Intern. Seaweed Symp., Göteborg, Sweden, August 11–15, 1980, pp 613–618. Ed. by T. Levring:Berlin: Walter de Gruyter 1981
Odum, E. P., E. Kuenzler and S. M. X. Blunt: Uptake of P32 and primary productivity in marine benthic algae. Limnol. Oceanogr.3, 340–345 (1958)
Parker, H. S.: Influence of relative water motion on the growth, ammonium uptake and carbon and nitrogen composition ofUlva lactuca (Chlorophyta). Mar. Biol.63, 309–318 (1981)
Probyn, T. A. and A. R. O. Chapman: Nitrogen uptake characteristics ofChordaria flagelliformis (Phaeophyta) in batch mode and continuous mode experiments. Mar. Biol.71, 129–133 (1982)
Raven, J. A.: Nutritional strategies of submerged benthic plants: the acquisition of C, N and P by rhizophytes and haptophytes. New Phytol.88, 1–30 (1981)
Raymont, J. E. G.: Plankton and productivity in the oceans, 2nd ed., Vol. 1. Phytoplankton, 489 pp. Oxford: Pergamon Press 1980
Rosemarin, A. S.: Phosphorus nutrition of two potentially competing filamentous algae,Cladophora glomerata (L.) Kütz. andStigeoclonium tenue (Agardh) Kütz. from Lake Ontario. J. Great Lakes Res.8, 66–72 (1982)
Rosenberg, G. and H. W. Paerl: Nitrogen fixation by blue-green algae associated with the siphonous green seaweedCodium decorticatum: effects on ammonium uptake. Mar. Biol.61, 151–158 (1981)
Rosenberg, G. and J. Ramus: Ecological growth strategies in the seaweedsGracilaria foliifera (Rhodophyceae) andUlva sp. (Chlorophyceae): photosynthesis and antenna composition. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser.8, 233–241 (1982a)
Rosenberg, G. and J. Ramus: Ecological growth strategies in the seaweedsGracilaria foliifera (Rhodophyceae) andUlva sp. (Chlorophyceae): Soluble nitrogen and reserve carbohydrates. Mar. Biol.66, 251–259 (1982b)
Rosenberg, G. and J. Ramus: Uptake of inorganic nitrogen and seaweed surface area: volume ratios. Aquat. Bot. (In press)
Ryther, J. H., N. Corwin, T. De Busk and L. D. Williams: Nitrogen uptake and storage by the red algaGracilaria tikvahiae (McLachlan 1979). Aquaculture26, 107–115 (1981)
Schramm, W. and W. Booth. Mass bloom of the algaCladophora prolifera in Bermuda: productivity and phosphorus accumulation. Bot. mar.24, 419–426 (1981)
Shepherd, S. A.: Ecological strategies in a deep water red algal community. Bot. mar.24, 457–463 (1981)
Thomas, T. E.: Nitrogen uptake and assimilation in intertidal.Gracilaria verrucosa. Abstracts, First Intern. Phycological. Congr., St. John's, Newfoundlan Canada, August 8th–14th, 1982, p a49, 1982
Thomas, T. E. and D. H. Turpin: Desiccation enhanced nutrient uptake rates in the intertidal algaFucus distichus. Bot. mar.23, 479–481 (1980)
Topinka, J. A.: Nitrogen uptake byFucus spiralis (Phaeophyceae). J. Phycol.14, 241–247 (1978)
Tseng, C. K.: Marine phycoculture in China.In: Proc. Xth Intern. Seaweed Symp., Göteborg, Sweden, August 11–15, 1980, pp 123–152. Ed. by T. Levring. Berlin: Walter de Gruyter 1981
Waite, T. and R. Mitchell: The effects of nutrient fertilization on the benthic algaeUlva lactuca. Bot. mar.15, 151–156 (1972)
Wallentinus, I.: Environmental influences on benthic macrovegetation in the Trosa-Askö area, northern Baltic proper. I. Hydrographical and chemical parameters, and the macrophytic communities. Contrib. Askö Lab. Univ. Stockholm15, 1–138 (1976)
Wallentinus, I.: Productivity studies on Baltic macroalgae. Bot. mar.21, 365–380 (1978)
Wallentinus, I.: Environmental influences on benthic macrovegetation in the Trosa-Askö area, northern Baltic proper. II. The ecology of macroalgae and submersed phanerogams. Contrib. Askö Lab. Univ. Stockholm25, 1–210 (1979)
Wallentinus, I.: Vegetationsklädda bottnar i Östersjön. Delrapport till “Eutrofiering i marin miljö”, National Swedish Environment Protection Board, Stockhom:mimeogr. (In Swedish) 1983
Wallentinus, I.: Partitioning of nutrient uptake between annual and perennial seaweeds in a Baltic archipelago area.In: Proc. XIth Intern. Seaweed Symp., Qingdao, China, June 19–25, 1983. Hydrobiol. (In press)
Wheeler, P. A.: Uptake of methylamine (an ammonium analogue) byMacrocystis pyrifera (Phaeophyta). J. Phycol.15, 12–17 (1979)
Wheeler, W. N.: Effects of boundary layer transport on the fixation of carbon by the giant kelpMacrocystis pyrifera. Mar. Biol.56, 103–110 (1980a)
Wheeler, W. N.: Pigment content and the photosynthetic rate of the fronds ofMacrocystis pyrifera. Mar. Biol.56, 97–102 (1980b)
Wheeler, W. N. and L. M. Srivastava: Seasonal studies on the nitrate physiology ofMacrocystis integrifolia in British Columbia, Canada. Abstracts, First Intern. Phycological Congr., St. John's Newfoundland Canada, August 8th–14th, 1982, p a53, 1982
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by T. Fenchel, Aarhus
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wallentinus, I. Comparisons of nutrient uptake rates for Baltic macroalgae with different thallus morphologies. Mar. Biol. 80, 215–225 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02180189
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02180189