Abstract
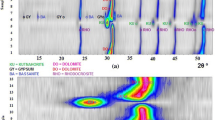
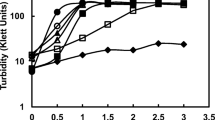
The precipitation of calcium carbonate by 27 strains ofDeleya halophila using solid and liquid media containing different NaCl concentrations (2.5, 7.5, or 20%, wt/vol) as sole salt, and two incubation temperatures (22° and 32°C) have been studied. All the strains tested were able to precipitate calcium carbonate under the different environmental conditions assayed. Crystals formed were calcite and vaterite; the ratio of calcite to vaterite was dependent on total salts and on the type of medium.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Bavendamm W (1932) Die mikrobiologische Kalkfällung in der tropischen See. Arch Microbiol 3:205–276
Berry LG (ed) (1974) Selected powder diffraction data for minerals. Philadelphia: Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards
Berry LG (ed) (1981) Selected powder diffraction data for minerals, supplement 1. Philadelphia: Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards. International Center for Diffraction Data.
Billy C (1980) Problèmes posés par le métabolism de quelques bactéries calcifiantes aérobies, I, Etude d'une association bacterienne halophile productrice d'aragonite en milieu marin. Vieu Milieu: 165–169
Black M (1933) The precipitation of calcium carbonate on the Bahama Bank. Geol Mag 70:455–466
Boquet E, Boronat A, Ramos-Cormenzana A (1973) Production of calcite (calcium carbonate) crystals by soil bacteria is a general phenomenon. Nature (London) 246:527–529
Cailleau P, Jacquin C, Dragone D, Giron A, Roques H, Humbert L (1979) Influence des ions étrangers et de la matière organique sur la cristallisation des carbonates de calcium. Rev L'Inst Franc Pétrole 34:83–112
Doetsch R, Cook TM (eds) (1973) Introduction to bacteria and their ecobiology. Lancaster: Medical and Technical Publishing.
Ducloix J, Dupuis T (1987) Influence de la matière organique des sols sur la cristallogenese des carbonates de calcium. In: Soil micromorphology. Proceedings of the VIIth International Work Meeting on Soil Micromorphology. Paris: Federoff M, Bresson LM, Courty MA. AFES
Erlich HL (1981) Geomicrobiology. New York: Marcel Dekker Inc.
Ferrer MR, Quevedo-Sarmiento J, Bejar V, Delgado R, Ramos-Cormenzana A, Rivadeneyra MA (1988a) Calcium carbonate formation byDeleya halophila: effect of salt concentration and incubation temperature. Geomicrobiol J 6:49–57
Ferrer MR, Quevedo-Sarmiento J, Rivadeneyra MA, Bejar V, Delgado R, Ramos-Cormenzana A (1988b) Calcium carbonate precipitation by two groups of moderately halophilic microorganisms at different temperatures and salt concentrations. Curr Microbiol 17:221–227
Greenfield LJ (1963) Metabolism and concentration of calcium and magnesium and precipitation of calcium carbonate by marine bacterium. Ann NY Acad Sci 109:23–45
Kamiya K, Sakka S, Tereda K (1977) Aragonite formation through precipitation of calcium carbonate monohydrate. Water Res Bull 12:1095–1102
Kitano Y, Hood DW (1962) Calcium carbonate crystals formed from sea water by inorganic processes. J Oceanograph Soc Jpn 18:208–219
Kitano Y, Akira T, Arakaki T (1979) Magnesian calcite synthesis from calcium bicarbonate solution containing magnesium and barium ions. Geochem J 13:181–185
Klug HP, Alexander LE (eds) (1974) X-ray diffraction procedures for polycrystalline and amorphous material. New York: John Wiley and Sons Inc.
Krumbein W (1979) Phototrophic and chemoorganotrophic activity of bacteria and algae as related to beachrock formation and degradation (Gulf of Agaba, Sinai). Geomicrobiol J 1:139–203
McCallum MF, Guhathakurta K (1970) The precipitation of calcium carbonate from seawater by bacteria isolated from Bahama bank sediments. J Appl Bacteriol 33:649–655
Morita RY (1980) Calcite precipitation by marine bacteria. Geomicrobiol J 2:63–82
Oppenheimer CH (1961) Note on the formation of spherical aragonite bodies in the presence of bacteria from the Bahama bank. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 23:295–296
Quesada E, Ventosa A, Ruiz-Berraquero F, Ramos-Cormenzana A (1984).Deleya halophila, a new species of moderately halophilic bacteria. Int J Syst Bacteriol 34:287–292
Quesada E, Bejar V, Valderrama MJ, Ramos-Cormenzana A (1987) Growth characteristics and salt requirement ofDeleya halophila in a defined medium. Curr Microbiol 16:21–25
Rivadeneyra MA, Ramos-Cormenzana A, Garcia-Cervigon A (1985b) Étude de l'influence du repport Mg/Ca sur la formation de carbonate par des bacteria telluriques. Can J Microbiol 31:229–231
Sayoko Y, Kitano Y (1985) Transformation of aragonite to calcite through heating. Geochem J 19:245–249
Schultz LG (1964) Quantitative interpretation of mineralogical composition from X-ray and chemical data for the Pierre Shale. Geol Surv Prof Paper. Washington DC: US Government Printing Office
Shinano H (1972) Studies of marine microorganisms taking part in the precipitation of calcium carbonate. IV. A taxonomy study of marine bacteria taking part in the precipitation of calcium carbonate. Bull Jpn Soc Sci Fisheries 38:825–832
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rivadeneyra, M.A., Delgado, R., Quesada, E. et al. Precipitation of calcium carbonate byDeleya halophila in media containing NaCl as sole salt. Current Microbiology 22, 185–190 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02092132
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02092132