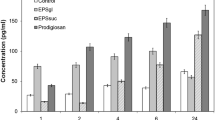
Abstract
Fractions obtained from Pseudomonas aeruginosa suppressed microcrystal synovitis in pigeons, adjuvant arthritis and experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in rats, the tuberculin reaction in guinea-pigs and the homograft reaction and antibody formation in mice. Products of gram-negative bacteria thus impair nonimmunological inflammatory processes as well as in vivo manifestations of immune-mediated reactions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. L. Floersheim, W. H. Hopff, M. Gasser andK. Bucher,Impairment of Cell Mediated Immunity by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Clin. exp. Immun.9, 241 (1971).
T. Arai, M. Otake, S. Enomoto andS. Kuwahara,Determination of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Biochemical Test Methods. II. Acylamidase Test, a Modified Biochemical Test for the Identification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Jap. J. Microbiol.14, 279 (1970).
G. L. Floersheim, V. Baltzer andK. Bucher,Prüfung von Antiphlogistica an einer experimentellen Arthritis der Taube, Helv. physiol. Acta21, 205 (1963).
G. L. Floersheim, K. Brune andK. Seiler,Effect of Procarbazine, Colchicine and Other Cytotoxic Agents on the Urate Arthritis in Pigeons, Agents and Actions, in press.
G. Benzi, A. Crema andG. M. Frigo,Action of Some Drugs on the ‘One-Footed Position Test’ in the Pigeon, J. pharm. Sci.54, 1689 (1965).
M. Absher andW. R. Stinebring,Endotoxin Like Properties of Poly I. Poly C, an Interferon Stimulator, Nature223, 715 (1969).
G. L. Floersheim andJ. J. Szeszak,Poly I. Poly C and Endotoxin Share Immunosuppressive Properties and Increase the Sensibility of Hexobarbital and α-Amanitin, Agents and Actions2, 150 (1971).
R. Perper, B. Alvarez, H. Schroder andC. Colombo,Adjuvant Arthritis: A Model to Separate Anti-Inflammatory from Immunosuppressive Agents, Fed. Proc.31, 386 (1971).
N. K. Jerne, A. A. Nordin andC. Henry,The Agar Plaque Technique for Recognizing Antibody-Producing Cells, in:Cell-Bound Antibodies (Eds. B. Amos and H. Koprowski; The Wistar Institute Press, Philadelphia 1963), p. 109.
G. L. Floersheim,Suppression of Cellular Immunity by Gram-Negative Bacteria, Antibiotica Chemother., Basel15, 407 (1969).
G. L. Floersheim,Pharmakologische Beeinflussbarkeit cellulärer Immunität, Z. naturw.-med. Grundlagenforsch.2, 307 (1965).
H. H. Stone, K. S. Given andJ. D. Martin,Delayed Rejection of Skin Homografts in Pseudomonas Sepsis, Surgery Gynec. Obstet.124, 1047 (1967).
K. Kano, K. Kimura, S. Hiraku, H. Ono, H. Terashima, K. Shibata andY. Nakao,Studies on New Anti-Inflammatory Substances from Bacteria, Yakugaku Zasshi89, 1741 (1969).
F. Quagliata andA. Taranta,Suppression of Adjuvant Disease by Bacterial Extracellular Products, Ann. Rheum. Dis., in press.
R. E. Franzl andPh. D. McMaster,The Primary Immune Response in Mice. I. The Enhancement and Suppression of Hemolysin Production by a Bacterial Endotoxin, Exp. Med.127, 1087 (1968).
S. G. Bradley andD. W. Watson,Suppression by Endotoxin of the Immune Response to Actinophage in the Mouse, Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. Med.117, 570 (1964).
H. Finger, H. Fresenius andM. Angerer,Bacterial Endotoxins as Immunosuppressive Agents, Experientia27, 456 (1971).
F. Malakian andJ. H. Schwab,Immunosuppressant from Group A Streptococci, Science159, 880 (1968).
A. Malakian andJ. H. Schwab,Biological Characterization of an Immunosuppressant from Group A Streptococci, J. exp. Med.134, 1253 (1971).
E. E. Hanna andD. W. Watson,Host-Parasite Relationship Among Group A Streptococci. IV. Suppression of Antibody Response by Streptoccal Pyrogenic Exotoxin, J. Bact.95, 14 (1968).
E. O. Terino, J. Miller andW. W. L. Glenn,Tolerance Induction and Skin Graft Prolongation by Competing Antigens, Surgery56, 256 (1964).
G. L. Floersheim,A Study of Combined Treatment with Chemical Immunosuppressants and Anti-Lymphocyte Serum to Prolong Skin Allograft Survival, Transplantation8, 392 (1969).
M. Landy, R. P. Sanderson, M. T. Bernstein andE. M. T. Lerner,Involvement of Thymus in Immune Response of Rabbits to Somatic Polysaccarides of Gram-Negative Bacteria, Science147, 1591 (1965).
C. Levaditi,Action Leukotoxique du Streptocoque des Plaies de Guerre. Considérations sur le méchanisme de le phagocytose, C. r. Soc. biol.81, 1064 (1918).
B. J. Archer,Remission in Rheumatoid Arthritis Following Fever Therapy with Liver Damage, N. Y. St. J. Med.51, 2657 (1951).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Floersheim, G.L., Borel, J.F., Wiesinger, D. et al. Antiarthritic and immunosuppressive effects of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Agents and Actions 2, 231–235 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02087047
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02087047