Abstract
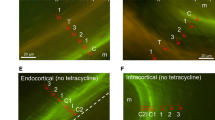
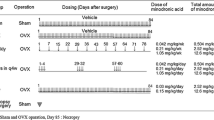
The purpose of this study was to determine the short-term effects of various systemic doses of disodium ethane-1-hydroxy-1,1-diphosphonate (EHDP) on bone organic matrix and to relate these effects to the corresponding dose-related changes in bone mineral. EHDP was administered daily by subcutaneous injection at doses of 0.25, 2.5 and 40 mg/kg body weight for periods of one and two weeks. At both time intervals, rat tibiae were quantitatively analyzed for mineral content (ash, calcium and phosphorus) and for organic matrix content (matrix weight, nitrogen and certain amino acids). The latter data were correlated with semiquantitative histological analyses of the tibiae. Results of this study demonstrate that the short term effects of EHDP on bone chemistry and histology are variable and depend on the systemic dose and the duration of treatment. Systemic doses of 0.25 and 2.5 mg/kg EHDP following daily administration for one week resulted in transitory decreases in bone mineral content compared to controls. Following two weeks of treatment, both of these dose levels resulted in increased bone mineral content and, in addition, the 2.5 mg/kg dose resulted in tibiae which contained more organic matrix compared to control bones. In contrast to the low dose effects, a high systemic dose of EHDP—e.g. 40 mg/kg administered daily for 1 or 2 weeks—appears to act solely by inhibiting mineralization of newly-formed matrix.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belcher, R., Godbert, A. L.: Semi-micro quantitative organic analysis, p. 102. New York: Longman, Green and Co. 1954
Block, R. J., Weiss, K. W.: Amino acid handbook—methods and results of protein analysis, p. 18. Springfield, Ill.: Charles C. Thomas 1956
Dayhoff, M. O.: Atlas of protein sequence and structure, p. D-291. Silver Spring, Maryland: The National Biomedical Research Foundation 1972
Dunnett, C. W.: Multiple comparison procedure for comparing several treatments with a control. J. Amer. Stat. Assoc.50, 1096–1121 (1955)
Fingerhut, B., Poock, A., Miller, H.: Automated fluorometric method for the determination of serum calcium. Clin. Chem.15, 870–878 (1969)
Fiske, C. H., Subbarow, Y.: The colorimetric determination of phosphorus. J. biol. Chem.66, 375–400 (1925)
Fleisch, H., Russell, R. G. G.: A review of the physiological and pharmacological effects of pyrophosphate and diphosphonates on bones and teeth. J. dent. Res.51, Suppl. to No. 2, 324–332 (1972)
Fleisch, H., Russell, R. G. G., Bisaz, S., Casey, P. A., Mühlbauer, R. C.: The influence of pyrophosphate analogues (diphosphonates) on the precipitation and dissolution of calcium phosphatein vitro andin vivo. Calcif. Tiss. Res.2,Suppl. 10–10A (1968)
Fleisch, H., Russell, R. G. G., Bisaz, S., Mühlbauer, R. C., Williams, D. A.: The inhibitory effect of phosphonates on the formation of calcium phosphate crystalsin vitro and on aortic and kidney calcificationin vivo. Europ. J. clin. Invest.1, 12–18 (1970)
Francis, M. D.: The inhibition of calcium hydroxyapatite crystal growth by polyphosphonates and polyphosphates. Calcif. Tiss. Res.3, 151–162 (1969)
Francis, M. D., Russell, R. G. G., Fleisch, H.: Diphosphonates inhibit formation of calcium phosphate crystalsin vitro and pathological calcificationin vivo. Science165, 1264–1266 (1969)
Gasser, A. B., Morgan, D. B., Fleisch, H., Richelle, L. J.: The influence of two diphosphonates on calcium metabolism in the rat. Clin. Sci.43, 31–45 (1972)
Gehrke, C. W., Kuo, K., Zumwalt, R. W.: The complete gas-liquid chromatographic separation of the twenty protein amino acids. J. Chromatography57, 209–217 (1971)
Gehrke, C. W., Roach, D., Zumwalt, R. W., Stalling, D. L., Wall, L. L.: Quantitative gasliquid chromatography of amino acids in biological fluids. Columbia, Missouri: Analytical Biochemistry Laboratories, Inc. 1968
Gray, J. A., Opdyke, D. L.: A device for thin sectioning of hard tissues. J. dent. Res.41, 172–181 (1962)
King, W. R., Francis, M. D., Michael, W. R.: Effect of disodium ethane-1-hydroxy-1,1-diphosphonate on bone formation. Clin. Orthop.78, 251–270 (1971)
Martin, J. H., Lynn, J. A., Nickey, W. M.: A rapid polychrome stain for epoxy-embedded tissue. Amer. J. clin. Path.46, 250–251 (1966)
Michael, W. R., King, W. R., Francis, M. D.: Effectiveness of diphosphonates in preventing osteoporosis of disuse in the rat. Clin. Orthop.78, 271–276 (1971)
Miller, S. C., Jee, W. S. S.: The effectiveness of diphosphonates in inhibiting bone resorption in rats. Abstract, 51st General Session of the International Association for Dental Research 1973
Mühlbauer, R. C., Russell, R. G. G., Williams, D. A., Fleisch, H.: The effects of diphosphonates, polyphosphates and calcitonin on “immobilization osteoporosis” in rats. Europ. J. clin. Invest.1, 336–344 (1970)
Pisano, J. J.: Gas-liquid chromatography of amino acid derivatives. Methods in enzymology, vol. XXV, part B, p. 39. New York: Academic Press 1972
Russell, R. G. G., Kislig, A. M., Casey, P. A., Fleisch, H., Thornton, J., Schenk, R., Williams, D. A.: Effect of diphosphonates and calcitonin on the chemistry and quantitative histology of rat bone. Calcif. Tiss. Res.11, 179–195 (1973)
Russell, R. G. G., Mühlbauer, R. C., Bisaz, S., Williams, D. A., Fleisch, H.: The influence of pyrophosphate, condensed phosphates, phosphonates and other phosphate compounds on the dissolution of hydroxyapatitein vitro and on bone resorption induced by parathyroid hormone in tissue culture and in thyroparathyroid-ectomized rats. Calcif. Tiss. Res.6, 183–196 (1970)
Schenk, R., Merz, W. A., Mühlbauer, R., Russell, R. G. G., Fleisch, H.: Effect of ethane-1-hydroxy-1,1-diphosphonate (EHDP) and dichloromethylene diphosphonate (Cl2MDP) on the calcification and resorption of cartilage and bone in the tibial epiphysis and metaphysis of rats. Calcif. Tiss. Res.11, 209–217 (1973)
Spurlock, B. O., Skinner, M. S., Kattine, A. A.: A simple rapid method for staining epoxyembedded specimens for light microscopy with the polychromatic stain paragon-1301. Amer. J. clin. Path.46, 252–258 (1966)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosenblum, I.Y. The effects of disodium ethane-1-hydroxy-1, 1-diphosphonate (EHDP) on mineral and organic components of rat bone. Calc. Tis Res. 16, 239–250 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02008231
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02008231