Summary
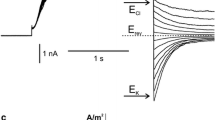
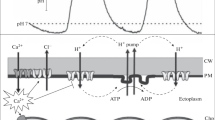
The electrical properties of theChara cell membrane have been studied using a perfusion method based on that of Williamson, R.E. 1975.J. Cell Sci. 17∶655. The vacuole, tonoplast, and inner cytoplasm are removed by a brief rapid perfusion. Electrical properties of the plasmalemma indicate that it remains intact after this perfusion.
The membrane potential difference after perfusion and with no ATP was close to the potassium equilibrium potential; the current-voltage characteristic had a slope that was time- and voltage-dependent, indicating that the steady-state potassium conductance increased with depolarization. At −125 mV the membrane conductance of the plasmalemma depended on [K+]0. This dependence was inhibited by perfusing with 2.0mm ATP or by clamping at a more negative membrane potential. The addition of ATP to the perfusion medium of unclamped cells caused a hyperpolarization ofca. 50 mV, presumably by activating the proton pump. In clamped cells, perfusion with ATP caused currents ofca. 20 mA m−2, whose magnitude depended on pH0. ATP induced membrane conductance changes which were variable. 2.0mm ADP inhibited the proton pump. The intersection points of current-voltage characteristics can set limits on the stalling potential; the resulting stoichiometry of the proton pump appears to be 1.5–2.0 H+ per ATP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberty, R.A. 1972. Calculations of the standard Gibbs free energy, enthalpy and entropy changes for the hydrolysis of ATP at 0°, 25°, 37° and 75°.In: Horizons of Energetics. A. San Pietro and H. Gest, editors. pp. 135–147. Academic Press, New York
Fujii, S., Shimmen, T., Tazawa, M. 1979. Effect of intercellular pH on the light-induced potential change and electrogenic activity in tonoplast-free cells ofChara australis.Plant Cell Physiol. 20:1315
Gradmann, D., Hansen, U.-P., Long, W.S., Slayman, C.L., Warncke, J. 1978. Current-voltage relationships for the plasma membrane and its principal electrogenic pump inNeurospora crassa: I. Steady-state conditions.J. Membrane Biol. 39:333
Heber, U. 1974. Metabolite exchange between chloroplasts and cytoplasm.Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 25:393
Hodgkin, A.L., Katz, B. 1949. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of the giant axon of the squid.J. Physiol. (London) 108:37
Hope, A.B. 1965. Ionic relations of cells ofChara australis. X. Effects of bicarbonate ions on electrical properties.Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 18:789
Hope, A.B., Walker, N.A. 1961. Ionic relations of cells ofChara australis R. Br.: IV. Membrane potential differences and resistances.Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 14:26
Keifer, D.W., Spanswick, R.M. 1978. Activity of the electrogenic pump inChara corallina as inferred from measurements of the membrane potential, conductance and potassium permeability.Plant Physiol. 62:653
Kikuyama, M., Hayama, T., Fujii, S., Tazawa, M. 1979. Relationship between light-induced potential change and internal ATP concentration in tonoplast-freeChara cells.Plant Cell Physiol. 20:993
Kitasato, H. 1968. The influence of H+ on the membrane potential and ion fluxes ofNitella.J. Gen. Physiol. 52:60
Oda, K. 1962. Polarized and depolarized states of the membrane inChara braunii, with special reference to the transition between the two states.Sci. Rep. Tohoku Univ. Ser. IV, Biol. 28:1
Reid, R.J. 1980. A study of adenylate concentrations and chloride active transport inChara corallina. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Sydney
Richards, J.L., Hope, A.B. 1974. The role of protons in determining membrane electrical characteristics inChara corallina.J. Membrane Biol. 16:121
Robinson, R.A., Stokes, R.H. 1955. Electrolyte solutions: The measurement and interpretation of conductance, chemical potential and diffusion in solutions of simple electrolytes. Butter-worths Scientific, London
Saito, K., Senda, M. 1974. The electrogenic ion pump revealed by the external pH effect on the membrane potential ofNitella. Influences of external ions and electric current on the pH effect.Plant Cell Physiol. 15:1007
Sanders, D. 1980a. Control of Cl influx inChara by cytoplasmic Cl− concentration.J. Membrane Biol. 52:51
Sanders, D. 1980b. The mechanism of Cl− transport at the plasma membrane ofChara corallina: I. Cotransport with H+.J. Membrane Biol. 52:129
Shimmen, T., Kikuyama, M., Tazawa, M. 1976. Demonstration of two stable states of plasmalemma ofChara without tonoplast.J. Membrane Biol. 30:249
Shimmen, T., Tazawa, M. 1977. Control of membrane potential and excitability ofChara cells with ATP and Mg2+.J. Membrane Biol. 37:167
Slayman, C.L., Gradman, D. 1975. Electrogenic proton transport in the plasma membrane ofNeurospora.Biophys. J. 15:968
Smith, P.T., Walker, N.A. 1978. Studies on the perfused plasmalemma ofChara.Proc. Aust. Soc. Biophys. 2:22A
Spanswick, R.M. 1972. Evidence for an electrogenic ion pump inNitella translucens. I. The effect of pH, K+, Na+, light and temperature on the membrane potential and resistance.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 288:73
Spanswick, R.M. 1974. Evidence for an electrogenic ion pump inNitella translucens. II. Control of the light-stimulated component of the membrane potential.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 332:387
Spanswick, R.M. 1980. Biophysical control of electrogenicity in theCharaceae.In: Plant Membrane Transport: Current Conceptual Issues. R.M. Spanswick, W.J. Lucas, and J. Dainty, editors. pp. 305–313. Elsevier North Holland, Amsterdam
Spanswick, R.M., Miller, A.G. 1977. Measurement of the cytoplasmic pH inNitella translucens. Comparison of the values obtained by microelectrode and weak acid methods.Plant Physiol. 59:664
Tazawa, M. 1964. Studies onNitella having artificial cell sap. I. Replacement of the cell sap with artificial solutions.Plant Cell Physiol. 5:33
Tazawa, M., Fujii, S., Kikuyama, M. 1979. Demonstration of light-induced potential change inChara cells lacking tonoplast.Plant Cell Physiol. 20:271
Tazawa, M., Kikuyama, M., Nakagawa, S. 1975. Open-vacuole method for measuring membrane potential and resistance of characeae cells.Plant Cell Physiol. 16:611
Tazawa, M., Kikuyama, K., Shimmen, T. 1976. Electric characteristics and cytoplasmic streaming of characeae cells lacking tonoplast.Cell Struct. Funct. 1:165
Tazawa, M., Kishimoto, U., Kikuyama, M. 1974. Potassium, sodium and chloride in the protoplasm of characeae.Plant Cell Physiol. 15:103
Vorobiev, L.N. 1967. Potassium ion activity in the cytoplasm and the vacuole of cells ofChara andGriffithsia.Nature (London) 216:1325
Walker, N.A. 1960. The electric resistance of the cell membranes in aChara and aNitella species.Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 13:468
Walker, N.A. 1980. The transport systems of charophyte and chlorophyte giant algae, and their integration into modes of behaviour.In: Plant Membrane Transport: Current Conceptual Issues. R.M. Spanswick, W.J. Lucas, and J. Dainty, editors. pp. 287–300. Elsevier North Holland, Amsterdam
Walker, N.A., Beilby, M.J., Smith, F.A. 1979. Amine uniport at the plasmalemma of charophyte cells: I. Current-voltage curves, saturation kinetics, and effects of unstirred layers.J. Membrane Biol. 49:21
Walker, N.A., Hope, A.B. 1969. Membrane fluxes and electrical conductance in characean cells.Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 22:1179
Walker, N.A., Smith, F.A. 1975. Intracellular pH inChara corallina measured by DMO distribution.Plant Sci. Lett. 4:125
Warncke, J., Slayman, C.L. 1980. Metabolic modulation of stoichiometry in a proton pump.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 591:224
Williamson, R.E. 1975. Cytoplasmic streaming inChara: A cell model activated by ATP and inhibited by cytochalasin B.J. Cell Sci. 17:655
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, P.T., Walker, N.A. Studies on the perfused plasmalemma ofChara corallina: I. Current-voltage curves: ATP and potassium dependence. J. Membrain Biol. 60, 223–236 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01992560
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01992560