Summary
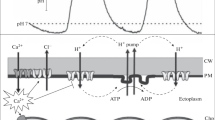
The value of the potential difference between the vacuole and the external medium,ψ vo, and the effects of metabolic inhibitors upon it indicate that, under certain external conditions, there are two main factors determining the potential across the plasmalemma. At all external pH there is a passive diffusion potential and at pH≧6 there is an active electrogenic component of potential. Calculations of ionic permeabilities of K+, Na+ and Cl− from their respective passive fluxes and application of the Goldman equation indicate that H+ permeability is approximately 25 times K+ permeability at pH 4 and 5 and possibly at pH≧6.ψ vo does not respond to increases in [K+]0 when a large electrogenic component of potential is present, even though the calculated value ofP K under these conditions is such as to predict significant changes inψ vo. It is suggested that this anomaly may be due to intrinsic properties of the electrogenic pump. There is evidence that the electrogenic pump is an active H+ efflux which calculations indicate is about 12 nmoles m−2 sec−1 at pH 5. However the electrogenic potential does not appear to be related to formation of acid and alkali regions in the external solution adjacent to cells ofChara.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown, D. F., Ryan, T. E., Barr, C. E. 1973. The effect of light and darkness in relation to external pH on calculated H+ fluxes inNitella.In: Ion Transport in Plants. W. P. Anderson, editor. p. 141. Academic Press, London, New York
Carpenter, D. O., Alving, B. O. 1968. A contribution of an electrogenic Na+ pump to membrane potential inAplysia neurones.J. Gen. Physiol. 52:1
Coster, H. G. L. 1973. The double fixed charge membrane. Solution-membrane ion partition effects and membrane potentials.Biophys. J. 13:133
Findlay, G. P., Hope, A. B. 1964. Ionic relations of cells ofChara australis. VII. The separate electrical characteristics of the plasmalemma and tonoplast.Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 17:62
Findlay, G. P., Hope, A. B., Pitman, M. G., Smith, F. A., Walker, N. A. 1969. Ion fluxes in cells ofChara corallina.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 183:565
Finkelstein, A. 1964. Carrier model for active transport of ions across a mosaic membrane.Biophys. J. 4:421
Goldman, D. E. 1943. Potential, impedence and rectification in membranes.J. Gen. Physiol. 27:37
Gutknecht, J. 1967. Ion fluxes and short-circuit current in internally perfused cells ofValonia ventricosa.J. Gen. Physiol. 50:1821
Higinbotham, N. 1970. Movement of ions and electrogenesis in higher plant cells.Amer. Zool. 10:393
Hodgkin, A. L., Katz, B. 1949. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of the giant axon of the squid.J. Physiol. 108:37
Hogg, J., Williams, E. J., Johnston, R. J. 1968. A simplified method for measuring membrane resistances inNitella translucens.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 150:518
Hope, A. B. 1965. Ionic relations of cells ofChara australis. X. Effects of bicarbonate ions on electrical properties.Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 18:789
Hope, A. B., Aschberger, P. A. 1970. Effects of temperature on membrane permeability to ions.Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 23:1047
Hope, A. B., Richards, J. L. 1971. Proton fluxes and permeability in Characean cells.First Europ. Biophys. Congr., Proc., Vol. III
Hope, A. B., Simpson, A., Walker, N. A. 1966. The efflux of chloride from cells ofNitella andChara.Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 19:355
Hope, A. B., Walker, N. A. 1960. Ionic relations of cells ofChara australis. III. Vacuolar fluxes of sodium.Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 13:277
Hope, A. B., Walker, N. A. 1961. Ionic relations of cells ofChara australis. IV. Membrane potential differences and resistances.Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 14:26
Jeschke, W. D. 1970. Lichtabhängige Veränderungen des Membranpotentials bei Blattzellen vonElodea densa.Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 62:158
Keynes, R. D. 1969. From frog skin to sheep rumen: A survey of transport of salts and water across multicellular structures.Quart. Rev. Biophys. 2:177
Kitasato, H. 1968. The influence of H+ on the membrane potential and ion fluxes ofNitella.J. Gen. Physiol. 52:60
Lannoye, R. J., Tarr, S. E., Dainty, J. 1970. The effects of pH on the ionic and electrical properties of the internodal cells ofChara australis.J. Exp. Bot. 21:543
Lilley, R. McC., Hope, A. B. 1971. Chloride transport and photosynthesis in cells ofGriffithsia.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 226:161
Lucas, W. J., Smith, F. A. 1973. The formation of alkaline and acid regions at the surface ofChara corallina cells.J. Exp. Bot. 24:1
MacRobbie, E. A. C. 1962. Ionic relations ofNitella translucens.J. Gen. Physiol. 45:861
Marmor, M. F., Gorman, A. L. F. 1970. Membrane potential as the sum of ionic and metabolic components.Science 167:65
Oda, K. 1962. Polarized and depolarized states of the membrane inChara braunii with special reference to the transition between the two states.Sci. Rep. Tôhoku Univ., Ser. IV (Biol.) 28:1
Rapoport, S. I. 1970. The sodium-potassium exchange pump: Relation of metabolism to electrical properties of the cell.Biophys. J. 10:246
Raven, J. A. 1967. Ion transport inHydrodictyon africanum.J. Gen. Physiol. 50:1607
Rent, R. K., Johnson, R. A., Barr, C. E. 1972. Net H+ influx inNitella clavata.J. Membrane Biol. 7:231
Saddler, H. D. W. 1970. The membrane potential ofAcetabularia mediterranea.J. Gen. Physiol. 55:802
Saito, K., Senda, M. 1973. The light-dependent effect of external pH on the membrane potential ofNitella.Plant Cell Physiol. 14:147
Slayman, C. L. 1965. Electrical properties ofNeurospora crassa. Effects of external cations on the intracellular potential.J. Gen. Physiol. 49:69
Slayman, C. L. 1970. Movement of ions and electrogenesis in microorganisms.Amer. Zool. 10:377
Smith, F. A. 1967. The control of Na uptake intoNitella translucens.J. Exp. Bot. 18:716
Smith, F. A., Lucas, W. J. 1973. The role of H+ and OH− fluxes in the ionic relations of Characean cells.In: Ion Transport in Plants. W. P. Anderson, editor. p. 223. Academic Press, London, New York
Spanswick, R. M. 1970. The effects of bicarbonate ions and external pH on the membrane potential and resistance ofNitella translucens.J. Membrane Biol. 2:59
Spanswick, R. M. 1972. Evidence for an electrogenic ion pump inNitella translucens. I. The effects of pH, K+, Na+, light and temperature on the membrane potential and resistance.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 288:73
Spanswick, R. M. 1973. Electrogenesis in photosynthetic tissues.In: Ion Transport in Plants. W. P. Anderson, editor. p. 113. Academic Press, London, New York
Spear, D. G., Barr, J. K., Barr, C. E. 1969. Localization of hydrogen ion and chloride ion fluxes inNitella.J. Gen. Physiol. 54:397
Vredenberg, W. J. 1973. Energy control of ion fluxes inNitella as measured by changes in potential, resistance and current-voltage characteristics of the plasmalemma.In: Ion Transport in Plants. W. P. Anderson, editor. p. 153. Academic Press, London, New York
Walker, N. A. 1960. The electric resistance of the cell membranes in aChara and aNitella species.Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 13:468
Walker, N. A., Hope, A. B. 1969. Membrane fluxes and electric conductance in Characean cells.Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 22:1179
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Richards, J.L., Hope, A.B. The role of protons in determining membrane electrical characteristics inChara corallina . J. Membrain Biol. 16, 121–144 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01872410
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01872410