Abstract
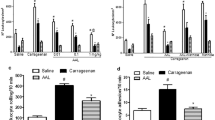
Evidence suggests that prolactin (PRL) may have a role in immune function, but no data exist on the possible interference between PRL and inflammatory processes, in spite of the known correlation between inflammatory and immune reactions. In the present study the activity of prolactin on rat paw oedema was investigated. Repeated administrations of ovine PRL or a hyperprolactinaemia induced by pituitary gland graft provoked an evident increase of the inflammatory response induced by carrageenan. This effect was also present when adrenalectomised animals were used. Indomethacin completely suppressed the proinflammatory effect of ovine PRL; bromocriptine reduced the paw oedema, but when both bromocriptine and PRL were administered the two opposite effects seem to annul each other. Also phospholipase A2-induced paw oedema was potentiated by PRL pretreatment and inhibited by bromocriptine, whereas in dextran or serotonin-induced paw oedema both PRL and bromocriptine were ineffective. A possible involvement of prostaglandins and/or of phospholipase A2 in the pro-oedemigenic activity of PRL is suggested.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. S. Nicoll,Physiological actions of prolactin. InHandbook of Physiology, Sect. 7, vol. IV, Part 2. (Eds. E. Knobil and W. H. Sawyer) pp. 253–292, American Physiological Society, Washington DC 1974.
J. Meites,Biological functions of prolactin in mammals. InProlactin gene family and its receptors. (Ed. K. Hoshino) pp. 123–130, Elsevier, Amsterdam 1988.
D. H. Russell,Prolactin and immunomodulation. InProlactin gene family and its receptors. (Ed. K. Hoshino) pp. 155–165, Elsevier, Amsterdam 1988.
E. W. Bernton, M. S. Meltzer and J. W. Holaday,Suppression of macrophage activation and T-lymphocyte function in hypoprolactinemic mice. Science239, 401–404 (1988).
L. J. Jara, C. Lavalle, A. Fraga, C. Gomez-Sanchez, L. H. Silveira, P. Martinez-Osuna, B. F. Germain and L. R. Espinoza,Prolactin, immunoregulation, and autoimmune diseases. Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism20, 273–284 (1991).
E. W. Bernton, J. E. Beach, J. W. Holaday, R. C. Smallridge and H. G. Fein,Release of multiple hormones by a direct action of interleukin-1 on pituitary cells. Science238, 519–521 (1987).
M. Arisawa, G. D. Snyder, W. H. Yu, L. R. De Palatis, R. H. Ho, S. M. Mc Cann,Physiologically significant inhibitory hypothalamic action of substance P on prolactin release in the male rat. Neuroendocrinology52, 22–27 (1990).
A. M. Camoratto and L. Grandison,Platelet-activating factor stimulates prolactin release from dispersed rat anterior pituitary cells in vitro. Endocrinology124, 1502–1506 (1989).
E. Nagy, I. Berczi, G. E. Wren, S. L. Asa and K. Kovacs,Immunomodulation by bromocriptine. Immunopharmacology6, 231–243 (1983).
R. Di Carlo and R. Meli,Interactions between prolactin and immune processes. Acta Neurologica,13, 380–385 (1991).
M. Carrier, D. H. Russell, J. C. Wild, R. W. Emery and J. G. Copeland,Prolactin as a marker of rejection in human heart transplantation. J. Heart Transplant.6, 290–292 (1987).
P. C. Hiestand, J. M. Gale and P. Mekler,Soft immunosuppression by inhibition of prolactin release: Synergism with cyclosporine in kidney allograft survival and in the localized graft-versus-host reaction. Transplantation Proceedings18, 870–872 (1986).
R. Di Carlo, G. Muccioli, G. Bellussi, C. Ghè, D. Lando and N. Mascolo,Prolactin and inflammatory processes. Abstracts of the 4th International Congress on Prolactin, Charlottesville, Virginia, p. 108 (1984).
R. J. Flower, L. Parente, P. Persico and J. A. Salmon,A comparison of the acute inflammatory response in adrenalectomised and sham-operated rats. Br. J. Pharmacol.87, 57–62 (1986).
A. J. Lewis, D. J. Nelson and M. F. Sugrue,On the ability of prostaglandin E 1 and arachidonic acid to modulate experimentally induced oedema in the rat paw. Br. J. Pharmacol55, 51–56 (1975).
M. Di Rosa, J. P. Giroud and D. A. Willoughby,Studies of the mediators of the acute inflammatory response induced in rats in different sites by carrageenan and turpentine. J. Pathol. Bact.104, 15–29 (1971).
M. Di Rosa and D. A. Willoughby,Screens for antiinflammatory drugs. J. Pharm. Pharmacol23, 297–298 (1971).
R. J. Gryglewski,Some experimental models for the study of inflammation and anti-inflammatory drugs. Agents and Actions3, 17–23 (1977).
G. Cirino, S. H. Peers, J. L. Wallace and R. J. Flower,A study of phospholipase A 2-induced oedema in rat paw. Eur. J. Pharmacol.166, 505–510 (1989).
J. A. Rillema and B. E. Wild,Prolactin activation of phospholipase A 2 activity in membrane preparations from mammary gland. Endocrinology100, 1219–1222 (1977).
J. R. Dave,Prolactin regulation of membrane fluidity and prostaglandin formation. InActions of Prolactin on Molecular Processes. (Ed. J. A. Rillema) pp. 69–105, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL 1987.
C. Robyn and S. Meuris,The state of art in human prolactin. InProlactin gene family and its receptors. (Ed. K. Hoshino) pp. 29–39, Elsevier, Amsterdam 1988.
A. I. Esquifino, N. A. Villanua and C. Agrasal,Possible role of prolactin in growth regulation. Riv. Espanola Fisiol.43, 455–462 (1987).
I. Berczi and E. Nagy,Prolactin and other lactogenic hormones. InPituitary Function and Immunity. (Ed. I. Berczi) pp. 161–183, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL 1986.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Di Carlo, R., Meli, R. & Muccioli, G. Effects of prolactin on rat paw oedema induced by different irritants. Agents and Actions 36, 87–92 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01991234
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01991234