Abstract
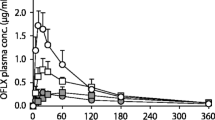
The effect of ferrous fumarate on the relative bioavailability of ciprofloxacin after a single 500 mg oral dose of ciprofloxacin was studied in eight healthy males. Blood samples were collected at regular intervals 0–24 h post-dose. Urine was collected during 24 h to determine the cumulative urine excretion of ciprofloxacin. Ciprofloxacin concentrations in serum and urine were determined by high pressure liquid chromatography. Mean area under the serum concentration—time curve decreased significantly (P<0.001) after ciprofloxacin was taken with 200 mg ferrous fumarate. The relative bioavailability was 30% when ciprofloxacin was given with ferrous fumarate. The maximum blood level decreased from 2.1±0.9 (control) to 0.6±0.2 mg/l (with ferrous fumarate). Further studies are needed to determine if chronic treatment with ferrous fumarate further decreases the relative bioavailability. For the moment administration of ciprofloxacin with ferrous fumarate should therefore be avoided.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brouwers JRBJ. Pharmacokinetics of the newer fluoroquinolones Pharm Weekbl [Sci] 1987;9(Suppl):S16–22.
Brouwers JRBJ, Van der Kam HJ, Sijtsma J, Koks CHW. Important drug interaction of oral ciprofloxacin with sucralfate and magnesium citrate solution. Pharm Weekbl [Sci] 1989;11(Suppl E):E13.
Yuk JH, Nightingale CN, Quintiliani R. Ciprofloxacin levels when receiving sucralfate. JAMA 1989;262:901.
Grasela ThE, Schentag JJ, Sedman AJ, et al. Inhibition of enoxacin absorption by antacids or ranitidine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1989;33:615–7.
Rubinstein E, Segev S. Drug interactions of ciprofloxacin with other non-antibiotic agents. Am J Med 1987;82(Suppl 4A):119–23.
Polk RE, Healy DP, Sahai J, Drab L, Racht E. Effect of ferrous sulphate and multivitamins with zinc on absorption of ciprofloxacin in normal volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1989;33:1841–4.
Groeneveld C, Brouwers JRBJ. Quantitative determination of ofloxacin, ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and pefloxacin in serum by HPLC. Pharm Weekbl [Sci] 1986;8:79–84.
Timmers K, Sternglanz R. Ionization and divalent cation constants of nalidixinic and oxolinic acids. Bioinorg Chem 1978;9:145–55.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brouwers, J.R.B.J., Van der Kam, H.J., Sijtsma, J. et al. Decreased ciprofloxacin absorption with concomitant administration of ferrous fumarate. Pharmaceutisch Weekblad Scientific Edition 12, 182–183 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01980042
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01980042