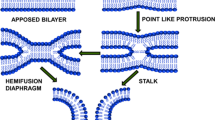
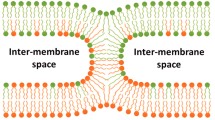
Summary
The factors involved in the regulation of biological membrane fusion and models proposed for the molecular mechanism of biomembrane fusion are reviewed. The results obtained in model systems are critically discussed in the light of the known properties of biomembranes and characteristics of biomembrane fusion. Biological membrane fusion is a local-point event; extremely fast, non-leaky, and under strict control. Fusion follows on a local and most probably protein-modulated destabilization, and a transition of the interacting membranes from a bilayer to a non-bilayer lipid structure. The potential role of type II non-bilayer preferring lipids and of proteins in the local destabilization of the membranes is evaluated. Proteins are not only responsible for the mutual recognition of the fusion partners, but are most likely also to be involved in the initiation of biomembrane fusion, by locally producing or activating fusogens, or by acting as fusogens.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Ahkong, Q. F., and Lucy, J. A., Localized osmotic swelling and cell fusion in erythrocytes: possible implications for exocytosis. J. Cell. Sci.91 (1988) 597–601.
Akabas, M. H., Cohen, F. S., and Finkelstein, A., Separation of the osmotically driven fusion event from vesicle-planar membrane attachment in a model system for exocytosis. J. Cell Biol.98 (1984) 1063–1071.
Altstiel, L., and Branton, D., Fusion of coated vesicles with lysosomes: measurement with a fluorescence assay. Cell32 (1983) 921–929.
Baker, P. F., Exocytosis in electropermeabilized cells: clues to mechanism and physiological control, in: Current Topics in Membranes and Transport, vol. 32, pp. 115–138. Eds N. Düzgünes and F. Bronner. Academic Press, San Diego 1988.
Balch, W. E., Dunphy, W. G., Braell, W. A., and Rothman, J. E., Reconstitution of the transport of protein between successive compartments of the Golgi measured by the coupled incorporation of N-acetylglucosamine. Cell39 (1984) 405–416.
Batenburg, A. M., Hibbeln, J. C. L., Verkleij, A. J., and De Kruijff, B. Melittin induces HII phase formation in cardiolipin model membranes. Biochim. biophys. Acta903 (1987) 142–154.
Beckers, C. J. M., and Balch, W. E., Calcium and GTP: essential components in vesicular trafficking between the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus. J. Cell Biol.108 (1989) 1245–1256.
Beckers, C. J. M., Block, M. R., Glick, B. S., Rothman, J. E., and Balch, W. E., Vesicular transport between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi stack requires the NEM-sensitive fusion protein. Nature339 (1989) 397–398.
Bentz, J., and Ellens, H., Membrane fusion: kinetics and mechanisms. Coll. Surf.30 (1988) 65–112.
Block, M. R., Glick, B. S., Wilcox, C. A., Wieland, F. T., and Rothman, J. E., Purification of an N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive protein catalyzing vesicular transport. Proc. natl. Acad. Sci. USA85 (1988) 7852–7856.
Blumenthal, R., Membrane fusion, in: Current Topics in Membranes and Transport, vol. 29, pp. 203–254. Eds. R. D. Klausner, C. Kempf and J. van Renswoude. Academic Press, Orlando 1987.
Bourne, H. R., Do GTPases direct membrane traffic in secretion? Cell53 (1988) 669–671.
Brocklehurst, K. W., and Pollard, H. B., Osmotic effects in membrane fusion during exocytosis, in: Current Topics in Membranes and Transport, vol. 32, pp. 203–225. Eds N. Düzgünes and F. Bronner. Academic Press, San Diego 1988.
Burger, K. N. J., Knoll, G., Frederik, P. M., and Verkleij, A. J., Influenza virus mediated membrane fusion: the identification of fusion intermediates using modern cryotechniques. NATO ASI Series, Vol. 40, pp. 185–196. Ed. J.A.F Op den Kamp. Springer-Verlag, Berlin 1990.
Chandler, D. E., Comparison of quick-frozen and chemically fixed sea-urchin eggs: structural evidence that cortical granule exocytosis is preceded by a local increase in membrane mobility. J. Cell Sci.72 (1984) 23–36.
Chandler, D. E., Exocytosis and endocytosis: membrane fusion events captured in rapidly frozen cells, in: Current Topics in Membranes and Transport, vol. 32, pp. 169–202. Eds N. Düzgünes and F. Bronner. Academic Press, San Diego 1988.
Chandler, D. E., and Heuser, J. E., Membrane fusion during secretion. Cortical granule exocytosis in Sea urchin eggs as studied by quick-freezing and freeze-fracture. J. Cell Biol.83 (1979) 91–108.
Chandler, D. E., and Heuser, J. E., Arrest of membrane fusion events in mast cells by quick-freezing. J. Cell Biol.86 (1980) 666–674.
Chandler, D. E., Whitaker, M., and Zimmerberg, J., High molecular weight polymers block cortical granule exocytosis in Sea urchin eggs at the level of granule matrix disassembly. J. Cell Biol.109 (1989) 1269–1278.
Cheek, T. R., and Burgoyne, R. D., Cyclic AMP inhibits both nicotine-induced actin disassembly and catecholamine secretion from bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J. Cell Biol.262 (1987) 11663–11666.
Chernomordik, L. V., Kozlov, M. M., Melikyan, G. B., Abidor, I. G., Markin, V. S., and Chizmadzhev, Y. A., The shape of lipid molecules and monolayer membrane fusion. Biochim. biophys. Acta812 (1985) 643–655.
Chernomordik, L. V., Melikyan, G. B., and Chizmadzhev, Y. A., Biomembrane fusion: a new concept derived from model studies using two interacting planar lipid bilayers. Biochim. biophys. Acta906 (1987) 309–352.
Creutz, C. E., Cis-unsaturated fatty acids induce the fusion of chromaffin granules aggregated by synexin. J. Cell Biol.91 (1981) 247–256.
Creutz, C. E., Zaks, W. J., Hamman, H. C. and Martin, W. H., The roles of Ca2+-dependent membrane binding proteins in the regulation and mechanism of exocytosis, in: Cell Fusion, pp. 45–68. Ed. A. W. Sowers. Plenum Press, New York 1987.
Davey, J., Hurtley, S. M., and Warren, G., Reconstitution of an endocytic fusion event in a cell-free system. Cell43 (1985) 643–652.
De Kruijff, B., Cullis, P. R., Verkleij, A. J., Hope, M. J., Van Echteld, C. J. A., and Taraschi, T. F., Lipid polymorphism and membrane function, in: The Enzymes of Biological Membranes, vol. 1, 2nd edn, pp. 131–204. Ed. A. N. Martonosi. Plenum Press, New York 1985.
De Kruijff, B., Cullis, P. R., Verkleij, A. J., Hope, M. J., Van Echteld, C. J. A., Taraschi, T. F., Van Hoogevest, P., Killian, J. A., Rietveld, A., and Van Der Steen, A. T. M., Modulation of lipid polymorphism by lipid protein interactions, in: Progress in Protein-Lipid Interactions, pp. 89–142. Eds. A. Watts and J. J. H. H. M. De Pont. Elsevier Publishers, Amsterdam 1985.
De Lisle, R. C., and Williams, J. A., Regulation of membrane fusion in secretory exocytosis. A. Rev. Physiol.48 (1986) 225–238.
Diaz, R., Mayorga, L. S., and Stahl, P., In vitro fusion of endosomes following receptor-mediated endocytosis. J. biol. Chem.263 (1988) 6093–6100.
Diaz, R., Mayorga, L. S., Weidman, P. J., Rothman, J. E., and Stahl, P. D., Vesicle fusion following receptor-mediated endocytosis requires a protein active in Golgi transport. Nature339 (1989) 398–400.
Düzgünes, N., Membrane fusion, in: Subcellular Biochemistry, vol. 11. pp. 195–287. Ed. D. B. Roodyn. Plenum Press, New York 1985.
Düzünes, N., and Bronner, F., Eds., Membrane fusion in fertilization, cellular transport and viral infection, in: Current Topics in Membranes and Transport, vol. 32. Academic Press, San Diego 1988.
Düzgünes, N., Paiement, J., Freeman, K. B., Lopez, N. G., Wilschut, J., and Papahadjopoulos, D., Modulation of membrane fusion by ionotropic and thermotropic phase transitions. Biochemistry23 (1984) 3486–3494.
Ellens, H., Bentz, J., and Szoka, F. C., Fusion of phosphatidylethanolamine-containing liposomes and mechanism of the Lα-HII phase transition. Biochemistry25 (1985) 4141–4147.
Forest, C. L., Mating structure-cell adhesion molecules: Their role in fertilization inChlamydomonas. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci.494 (1987) 202–204.
Friend, D. S., and Heuser, J. E., Orderly particle arrays on the mitochondrial outer membrane in rapidly frozen sperm. Anat. Rec.199 (1981) 159–175.
Frye, R. A., and Holz, R. W., Arachidonic acid release and catecholamine secretion from digitonin-treated chromaffin cells: Effects of micromolar calcium, phorbol ester, and protein alkylating agents. J. Neurochem.44 (1985) 265–273.
Glick, B. S., and Rothman, J. E., Possible role for fatty acylcoenzyme A in intracellular protein transport. Nature326 (1987) 309–312.
Gomperts, B. D., Calcium shares the limelight in stimulus-secretion coupling. TIBS11 (1986) 290–292.
Gruenberg, J. E., and Howell, K. E., Reconstitution of vesicle fusions occurring in endocytosis with a cell-free system. EMBO J.5 (1986) 3091–3101.
Harter, C., James, P., Bächi, T., Semenza, G., and Brunner, J., Hydrophobic binding of the ectodomain of influenza hemagglutinin to membranes occurs through the ‘fusion peptide’. J. biol. Chem.264 (1989) 6459–6464.
Heuser, J. E., Reese, T. S., Dennis, M. J., Jan, Y., Jan, L., and Evans, L., Synaptic vesicle exocytosis captured by quick freezing and correlated with quantal transmitter release. J. Cell Biol.81 (1979) 275–300.
Heuser, J. E., Reese, T. S., and Landis, D. M. D., Functional changes in frog neuromuscular junctions studied with freeze-fracture. J. Neurocytol.3 (1974) 109–131.
Hoekstra, D., and Kok, J. W., Entry mechanisms of enveloped viruses. Implications for fusion of intracellular membranes. Biosci. Rep.9 (1989) 273–305.
Hope, M. J., and Cullis, P. R., The role of non-bilayer lipid structures in the fusion of human erythrocytes induced by lipid fusogens. Biochim. biophys. Acta640 (1981) 82–90.
Hui, S. W., Stewart, T. P., Boni, L. T., and Yeagle, P. L., Membrane fusion through point defects in bilayers. Science212 (1981) 921–923.
Jackson, R. C., and Crabb, J. H., Cortical exocytosis in the Sea urchin egg, in: Current Topics in Membranes and Transport, vol. 32, pp. 45–85. Eds. N., Düzgünes and F. Bronner. Academic Press, San Diego 1988.
Killian, J. A., Timmermans, J. W., Keur, S., and De Kruijff, B., The tryptophans of gramicidin are essential for the lipid structure modulating effect of the peptide, Biochim. biophys. Acta820 (1985) 154–156.
Knight, D. E., and Baker, P. F., The phorbol ester TPA increases the affinity of exocytosis for calcium in ‘leaky’ adrenal medullary cells. FEBS Lett.22 (1983) 98–100.
Knoll, G., Burger, K. N. J., Bron, R., Van Meer, G., and Verkleij, A. J., Fusion of liposomes with the plasma membrane of epithelial cells: Fate of incorporated lipids as followed by freeze-fracture and autoradiography of plastic sections. J. Cell Biol.107 (1988) 2511–2521.
Knoll, G., Verkleij, A. J., and Plattner, H., Cryofixation of dynamic processes in cells and organelles, in: Cryotechniques in Biological Electron Microscopy, pp. 258–271. Eds R. A. Steinbrecht and K. Zierold. Springer-Verlag, Berlin 1987.
Leikin, S. L., Kozlov, M. M., Chernomordik, L. V., Markin, V. S., and Chizmadzhev, Y. A., Membrane fusion: overcoming of the hydration barrier and local restructuring. J. theor. Biol.129 (1987) 411–425.
Leyton, L., and Saling, P., 95 kD sperm proteins bind ZP3 and serve as tyrosine kinase substrates in response to zona binding. Cell57 (1989) 1123–1130.
Lucy, J. A., The fusion of biological membranes. Nature227 (1970) 814–817.
Lucy, J. A., Mechanisms of chemically induced cell fusion. Cell Surf. Rev.5 (1978) 267–304.
Lucy, J. A., Do hydrophobic sequences cleaved from cellular polypeptides induce membrane fusion reactions in vivo? FEBS Lett.166 (1984) 223–231.
Lucy, J. A., and Ahkong, Q. F., An osmotic model for the fusion of biological membranes. FEBS Lett.199 (1986) 1–11.
Mandel, L. J., and Eaton, D. C., Cell calcium and the control of membrane transport. 40th Annual Symposium of the Society of General Physiologist. Rockefeller University Press, New York 1987.
Mayorga, L. S., Diaz, R., and Stahl, P. D., Regulatory role for GTP-binding proteins in endocytosis. Science244 (1989) 1475–1477.
Melancon, P., Glick, B. S., Malhotra, V., Weidman, P. J., Serafini, T., Gleason, M. L., Orci, L., and Rothman, J. E., Involvement of GTP-binding “G” proteins in transport through the Golgi stack. Cell51 (1987) 1053–1062.
Menco, B. P. M., A survey of ultra-rapid cryofixation methods with particular emphasis on applications to freeze-fracturing, freezeetching and freeze-substitution. J. Electr. Microsc. Techn.4 (1986) 177–240.
Morré, D. J., Paulik, M., and Nowack, D., Transition vesicle formation in vitro. Protoplasma132 (1986) 110–113.
Nieva, J. L., Goni, F. M., and Alonso, A., Liposome fusion catalytically induced by phospholipase C. Biochemistry28 (1989) 7364–7367.
Nowack, D. D., Morré, D. M., Paulik, M., Keenan, T. W., and Morré, D. J., Intracellular membrane flow: Reconstitution of transition vesicle formation and function in a cell-free system. Proc. natl Acad. Sci. USA84 (1987) 6098–6102.
Op den Kamp, J. A. F., Lipid asymmetry in membranes. A. Rev. Biochem.48 (1979) 47–71.
Orci, L., and Perrelet, A., Ultrastructural aspects of exocytotic membrane fusion. Cell Surf. Rev.5 (1978) 629–656.
Palade, G. E., and Bruns, R. R., Structural modulations of plasmalemmal vesicles. J. Cell Biol.37 (1968) 633–649.
Papahadjopoulos, D., Portis, A., and Pangborn, W., Calcium-induced lipid phase transitions and membrane fusion. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci.308 (1978) 50–66.
Parente, R. A., Nir, S., and Szoka, F. C., pH-dependent fusion of phosphatidylcholine small vesicles. Induction by a synthetic amphipathic peptide. J. biol. Chem.263 (1988) 4724–4730.
Perrin, D., Langley, O. K., and Aunis, D., Anti-α-fodrin inhibits secretion from permeabilized chromaffin cells. Nature326 (1987) 498–501.
Pinto da Silva, P., and Nogueira, M. L., Membrane fusion during secretion. A hypothesis based on electron microscope observation ofPhytophthora palmivora zoospores during encystment. J. Cell Biol.73 (1977) 161–181.
Plattner, H., Membrane behaviour during exocytosis. Cell Biol. Int. Rep.5 (1981) 435–459.
Plattner, H., Synchronous exocytosis in Paramecium cells, in: Cell Fusion, pp. 69–98. Ed. A. E. Sowers. Plenum Press, New York 1987.
Plattner, H., and Zingsheim, H. P., Electron microscopic methods in cellular and molecular biology. Subcell. Biochem.9 (1983) 1–236.
Pollard, H. B., Pazoles, C. J., Creutz, C. E., and Zinder, O., The chromaffin granule and possible mechanisms of exocytosis. Int. Rev. Cytol.58 (1979) 159–197.
Rand, R. P., Fuller, N., Parsegian, V. A., and Rau, D. C., Variation in hydration forces between neutral phospholipid bilayers: Evidence for hydration attraction. Biochemistry27 (1988) 7711–7722.
Rand, R. P., and Parsegian, V. A., Physical force considerations in model and biological membranes. Can. J. Biochem. Cell Biol.62 (1984) 752–759.
Rink, T. J., Sanchez, A., and Hallam, T. J., Diaglycerol and phorbol ester stimulate secretion without raising cytoplasmic free calcium in human platelets. Nature305 (1983) 317–319.
Rothman, J. E., Urbani, L. J., and Brands, R., Transport of protein between cytoplasmic membranes of fused cells: correspondence to processes reconstituted in a cell-free system. J. Cell Biol.99 (1984) 248–259.
Satir, B., Ultrastructural aspects of membrane fusion. J. supramolec. Struct.2 (1974) 529–537.
Schäfer, T., Karli, U. O., Schweizer, F. E., and Burger, M. M., Docking of chromaffin granules — A necessary step in exocytosis? Biosci. Rep.7 (1987) 269–279.
Scheule, R. K., Fusion of Sindbis virus with model membranes containing phosphatidylethanolamine: implications for protein-induced membrane fusion. Biochim. biophys. Acta899 (1987) 185–195.
Schmidt, W., Patzak, A., Lingg, G., Winkler, H., and Plattner, H., Membrane events in adrenal chromaffin cells during exocytosis: a freeze-etching analysis after rapid cryofixation. Eur. J. Biochem.32 (1983) 31–37.
Schweizer, F. E., Schäfer, T., Tapparelli, C., Crob, M., Karli, U. O., Heumann, R., Thoenen, H., Bookman, R. J., and Burger, M. M., Inhibition of exocytosis by intracellularly applied antibodies against a chromaffin granule-binding protein. Nature339 (1989) 709–712.
Siegel, D. P., Inverted micellar intermediates and the transitions between lamellar, cubic, and inverted hexagonal lipid phases. II. Implications for membrane-membrane interactions and membrane fusion. Biophys. J.49 (1986) 1171–1183.
Siegel, D. P., Membrane-membrane interactions via intermediates in lamellar-to-inverted hexagonal phase transitions, in: Cell Fusion, pp. 81–208. Ed. A. E. Sowers. Plenum Press, New York 1987.
Siegel, D. P., Banschbach, J., Alford, D., Ellens, H., Lis, L. J., Quinn, P. J., Yeagle, P. L., and Bentz, J., Physiological levels of diacylglycerols in phospholipid membranes induce membrane fusion and stabilize inverted phases. Biochemistry28 (1989) 3703–3709.
Sowers, A. E., Ed., Cell Fusion. Plenum Press, New York 1987.
Specian, R. D., and Neutra, M. R., Mechanism of rapid mucus secretion in goblet cells stimulated by acetylcholine. J. Cell Biol.85 (1980) 626–640.
Stegmann, T., Hoekstra, D., Scherphof, G., and Wilschut, J., Kinetics of pH-dependent fusion between influenza virus and liposomes. Biochemistry24 (1985) 3107–3113.
Stegmann, T., Hoekstra, D., Scherphof, G., and Wilschut, J., Fusion activity of influenza-virus. A comparison between biological and artificial target membrane vesicles. J. biol. Chem.261 (1986) 10 966–10 969.
Steinman, R. M., Mellman, I. S., Muller, W. A., and Cohn, Z. A., Endocytosis and the recycling of plasma membrane. J. Cell Biol.96 (1983) 1–27.
Stossel, T. P., Actin filaments and secretion: The macrophage model, in: Methods in Cell Biology, vol. 23, pp. 215–230. Eds. A. R. Hand and C. Oliver. Academic Press, New York 1982.
Strittmatter, W. J., Couch, C. B., and Mundy, D. I., Role of metalloendoprotease in fusion of biological membranes, in: Cell Fusion, pp. 99–121. Ed. A. E. Sowers. Plenum Press, New York 1987.
Van Meer, G., Davoust, J., and Simons, K., Parameters affecting low-pH-mediated fusion of liposomes with the plasma membrane of cells infected with influenza virus. Biochemistry24 (1985) 3593–3602.
Van Venetië, R., and Verkleij, A. J., Analysis of the hexagonal HII phase and its relations to lipidic particles and the lamellar phase. A freeze-fracture study. Biochim. biophys. Acta645 (1981) 262–269.
Verkleij, A. J., Lipidic intramembranous particles. Biochim. biophys. Acta779 (1984) 43–63.
Walworth, N. C., Goud, B., Kastan Kabcenell, A., and Novick, P. J., Mutational analysis of SEC 4 suggests a cyclical mechanism for the regulation of vesicular traffic. EMBO J.8 (1989) 1685–1693.
Weidmann, P. J., Melancon, P., Block, M. R., and Rothman, J. E., Binding of an N-Ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion protein to Golgi membranes requires both a soluble protein(s) and an integral membrane receptor. J. Cell Biol.108 (1989) 1589–1596.
Weiss, R. L., Goodenough, D. A., and Goodenough, U. W., Membrane differentiations at sites specialized for cell fusion. J. Cell Biol.72 (1977) 144–160.
Whitaker, M., How calcium may cause exocytosis in Sea urchin eggs. Biosci. Rep.7 (1987) 383–398.
White, J., Kartenbeck, J., and Helenius, A., Membrane fusion activity of influenza virus. EMBO J.1 (1982) 217–222.
White, J., Kielian, M., and Helenius, A., Membrane fusion proteins of enveloped animal viruses. Quart. Rev. Biophys.16 (1983) 151–195.
Wieslander, A., Rilfors, L., and Lindblom, G., Metabolic changes of membrane lipid composition inAcholeplasma laidlawii by hydrocarbons, alcohols, and detergents: Arguments for effects on lipid packing. Biochemistry25 (1986) 7511–7517.
Wilschut, J., and Hoekstra, D., Membrane fusion: from liposomes to biological membranes. TIBS11 (1984) 479–483.
Wilson, D. W., Wilcox, C. A., Flynn, G. C., Chen, E., Kuang, W. J., Henzel, W. J., Block, M. R., Ullrich, A., and Rothman, J. E., A fusion protein required for vesicle-mediated transport in both mammalian cells and yeast. Nature339 (1989) 355–359.
Woodman, P. G., and Warren, G., Fusion between vesicles from the pathway of receptor-mediated endocytosis in a cell-free system. Eur. J. Biochem.173 (1988) 101–108.
Zieseniss, E., and Plattner, H., Synchronous exocytosis inParamecium cells involves very rapid (≤ 1 s), reversible dephosphorylation of a 65 kD phosphoprotein in exocytosis-competent strains. J. Cell Biol.101 (1985) 2028–2035.
Zimmerberg, J., Molecular mechanisms of membrane fusion: steps during phospholipid and exocytic membrane fusion. Biosci. Rep.7 (1987) 251–268.
Zimmerberg, J., Curran, M., Cohen, F. S., and Brodwick, M., Simultaneous electrical and optical measurements show that membrane fusion precedes secretory granule swelling during exocytosis of beige mouse mast cells. Proc. natl Acad. Sci. USA84 (1986) 1585–1589.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burger, K.N.J., Verkleij, A.J. Membrane fusion. Experientia 46, 631–644 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01939702
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01939702