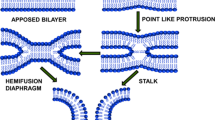
Abstract
Exocytosis is considered as four separate steps: adhesion, fusion/pore formation, pore widening, and content discharge. Experiments on both synthetic and natural membranes are presented to show each of these steps. Major differences are seen in the two fusing systems. These differences are discussed in terms of molecular mechanisms of fusion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akabas, M. H., Cohen, F. S. and Finkelstein, A. (1984). Separation of the osmotically driven fusion event from vesicle-planar membrane attachment in a model system for exocytosis.J. Cell. Biol. 98:1063–1071.
Breckenridge, L. J. and Almers, W. (1987). Final steps in exocytosis observed in a cell with giant secretory granules.Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 84: 1945–1949.
Boys, C. V. (1959).Soap Bubbles. Dover Publications, Inc. New York, NY, pp. 101–103.
Chandler, D. E. (1987). Current topics in membranes and transport, exocytosis and endocytosis: membrane fusion events captured in rapidly frozen cells.Dev. Biol. 5:435–459.
Chandler, D. E. and Heuser, J. E. (1980). Arrest of membrane fusion events in mast cells by quick freezing.J. Cell Biol. 86:666–674.
Chi, E. Y. and Lagunoff, D. (1975). Abnormal mast cell granules in the beige mouse.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 23:117–122.
Cohen, F. S., Akabas, M. H. and Finkelstein, A. (1982). Osmotic swelling of phospholipid vesicles causes them to fuse with a planar phospholipid bilayer membranes.Science 217:458–460.
Cohen, F. S., Akabas, M. H., Zimmerberg, J. and Finkelstein, A. (1984). Parameters affecting the fusion of unilamellar phospholipid vesicles with planar bilayer membrane.J. Cell Biol. 98:1054–1062.
Cohen, F. S., Zimmerberg, J. and Finkelstein, A. (1980). Fusion of phospholipid vesicles with planar phospholipid bilayer membranes. II. Incorporation of a vesicular membrane marker into the planar membrane.J. Gen. Physiol. 75:251–270.
Duzgunes, N. (1985). Membrane Fusion. In:Subcellular Biochemistry (D. B. Roodyn, Ed.), Plenum Press, New York, Chapter 5, pp. 195–286.
Duzgunes, N., Wilshut, J., Fraley, R. and Papahadjopoulos, D. (1981). Studies on the mechanism of membrane fusion: role of head group composition in calcium and magnesium induced fusion of mixed phospholipid vesicles.Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 642:182–195.
Evans, E. A. and Parsegian, V. A. (1983). Energetics of membrane deformation and adhesion in cell and vesicle aggregation.Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 416:13–33.
Fernadez, M., Neher, E. and Gomperts, B. D. (1984). Capacitance measurements reveal stepwise fusion events in degranulating mast cells.Nature (London) 312:453–455.
Finkelstein, A., Zimmerberg, J. and Cohen, F. S. (1986). Osmotic swelling of vesicles: its role in the fusion of vesicles with planar phospholipid bilayer membranes and its possible role in exocytosis.Ann. Rev. Physiol. 48:163–174.
Green, D. P. L. (1978). The induction of the acrosome reaction in guinea-pig sperm by the divalent metal caption ionophore A23187.J. Cell Sci. 32:137–151.
Green, D. P. L. (1982). The course of the acrosome reaction in guinea-pig sperm.J. Cell. Sci. 54:161–171.
Gruner, S., Parsegian, V. A. and Rand, R. P. (1986). Lipid vesicles and membranes.Faraday Discuss. Chem. Soc. 81:29–37.
Guldbrand, L., Jonsson, B., Wennerstrom, H. and Linse, P. (1984). Electrical double-layer forces—a Monte-Carlo study.J. Chem. Phys. 80:2221–2228.
Holz, R. W. (1986). The role of osmotic forces in exocytosis from adrenal chromaffin cells.Ann. Rev. Physiol. 48:175–190.
Holz, R. W. and Senter, R. A. (1986). The effects of osmolality and ionic strength on secretion from adrenal chromaffin cells permeabilized with digitonin.J. Neurochem. 46:1835–1842.
Kachar, B., Fuller, N. and Rand, R. P. (1986). Morphological responses to calcium-induced interaction of phosphatidylserine-containing vesicles.Biophys. J. 50:779–788.
Kwok, R. and Evans, E. (1981). Thermoelasticity of large lecithin bilayer vesicles.Biophys. J. 35: 637–652.
LeNeveu, D. M., Rand, R. P. and Parsegian, V. A. (1976). Measurement of forces between lecithin bilayers.Nature (Lond.) 259:601–603.
Llinas, R., Steinberg, I. Z. and Walton, K. (1982). Relationship between presynaptic calcium current and postsynaptic potential in squid giant synapse.Biophys. J. 33:323–352.
Lutzner, M. A., Lowrie, C. T. and Jordan, H. W. (1967). Giant granules in leukocytes of the beige mouse.J. Hered. 58:299–300.
Marra, J. (1986). Direct measurement of the interaction between phosphatidylglycerol bilayers in aqueous electrolyte solutions.Biophys. J. 50:815–825.
Martin, F. J. and MacDonald, R. C. (1976). Phospholipid exchange between bilayer membrane vesicles.Biochemistry 15:321–327.
Marty, A. and Neher, E. (1983). Tight-seal whole-cell recording. In:Single-Channel Recording (B. Sakmann and E. Neher, Eds.), Plenum Press, New York, Chapter 7, pp. 107–122.
Neher, E. and Marty, A. (1982). Discrete changes of cell membrane capacitance observed under conditions of enhanced secretion in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 79:6712–6716.
Niles, W. D. and Cohen, F. S. (1978a) Video fluorescence microscopy of vesicle fusion with planar membranes.Biophys. J. 51: 44a.
Niles, W. D. and Cohen, F. S. (1987b). Video fluorescence microscopy studies of phospholipid vesicle fusion with a planar phospholipid membrane. Nature of membrane-membrane interactions and detection of contents released.J. Gen. Phys. In press.
Parsegian, V. A., Fuller, N. L. and Rand, R. P. (1979). Measured work of deformation and repulsion of lecithin bilayers.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 76:2750–2754.
Parsegian, V. A. and Rand, R. P. (1983). Membrane interaction and deformation.Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 416:1–12.
Parsegian, V. A., Rand, R. P. and Rau, D. C. (1986). Osmotic stress for the direct measurement of intermolecular forces. In:Methods in Enzymology, Vol. 127,Biomembranes; Protons and Water: Structure and Translocation (L. Packer, Ed.), Academic Press, New York, Chapter 29, pp. 400–416.
Parsegian, A. V., Rau, D. and Zimmerberg, J. (1986). Structural transitions induced by osmotic stress. In:Membranes, Metabolism, and Dry Organisms (C. Leopold, Ed.) Cornell University Press, Ithaca, Chapter 18, pp. 306–317.
Plattner, H. (1981). Membrane behaviour during exocytosis.5:435–459.
Portis, A., Newton, C., Pangborn, W. and Papahadjopolous, D. (1979). Studies on the mechanism of membrane fusion: evidence for an intermembrane Ca-phospholipid complex, synergism with Mg, and inhibition by spectrin.Biochemistry 18:780–790.
Rand, R. P., Fuller, N. L. and Lis, L. J. (1900). Myelin swelling and measurement of forces between myelin membranes.Nature (Lond.) 279:258–260.
Rand, R. P. and Parsegian, V. A. (1986). Mimicry and mechanism in phospholipid models of membrane fusion.Ann. Rev. Physiol. 48:201–212.
Rau, D. C., Lee, B. and Parsegian, V. A. (1984). Measurement of the repulsive force between polyelectrolyte molecules in ionic solution: Hydration forces between parallel DNA double helices.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 81:2621–2625.
Rau, D. C. and Parsegian, V. A. (1985).Biophys. J. 47:68a.
Rau, D. C. and Parsegian, V. A. (1986). Dissection of the solvent entropy change driving molecular assembly.Biophys. J. 49:301a.
Schuel, H. (1978). Secretory functions of egg cortical granules in fertilization and development: A critical review.Gamete. Res. 1:299–382.
Schwartz, G. J. and Al-Awqati, Q. (1986). Regulation of transepithelial H+ transport by exocytosis and endocytosis.Ann. Rev. Physiol. 48:153–161.
Tanford, C. (1973)The Hydrophobic Effect: Formation of Micelles and Biological Membranes, John Wiley & Sons, N.Y., pp. 94–111.
Wade, J. B. (1986). Role of membrane fusion in hormonal regulation of epithelial transport.Ann. Rev. Physiol. 48:213–223.
Walter, A., Steer, C. J. and Blumenthal, R. (1986). Polylysine induces pH-dependent fusion of acidic lipid vesicles: a model for polycation fusion.Biophys. Biochim. Acta 861:319–330.
Whitaker, M. and Zimmerberg, J. (1987). Inhibition of exocytosis in sea urchin eggs by polymer solutions.J. Physiol. In press.
Wilschut, J. and Hoeckstra, D. Eds. (1987).Cellular Membrane Fusion. Marcel Dekker, NY.
Woodbury, D. J. (1986c). Correlation of channel incorporation and content release during fusion of unilamellar vesicles with a planar bilayer.Biophys. J. 49:132a.
Zimmerberg, J. (1987). Fusion of phospholipid vesicles to planar phospholipid membranes. In:Cellular Membrane Fusion (J. Wilschut and D. Hoeckstra, Eds.), Marcel Dekker, New York.
Zimmerberg, J., Cohen, F. S. and Finkelstein, A. (1980). Fusion of phospholipid vesicles with planar phospholipid bilayer membranes. I. Discharge of vesicular contents across the planar membrane.J. Gen. Physiol. 75:251–270.
Zimmerberg, J., Curran, M., Cohen, F. S. and Brodwick, M. (1986). Simultaneous electrical and optical measurements show that membrane fusion precedes secretory granule swelling during exocytosis of beige mouse mast cells.Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 84:1585–1589.
Zimmerberg, J. and Parsegian, V. A. (1987). Water movement during channel opening and closing.J. Bioenergetics and Biomembranes 19:351–358.
Zimmerberg, J., Sardet, C. and Epel, D. (1985). Exocytosis of sea urchin egg cortical vesiclesin vitro is retarded by hypersomotic sucrose: kinetics of fusion monitored by quantitative light-scattering microscopy.J. Cell. Biol. 101:2398–2410.
Zimmerberg, J. and Whitaker, M. (1985). Irreversible swelling of secretory granules during exocytosis caused by calcium.Nature 315:581–584.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zimmerberg, J. Molecular mechanisms of membrane fusion: Steps during phospholipid and exocytotic membrane fusion. Biosci Rep 7, 251–268 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01121447
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01121447