Summary
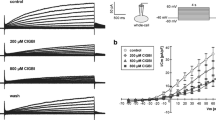
Ehrlich ascites tumor cells resuspended in hypotonic medium initially swell as nearly perfect osmometers, but subsequently recover their volume within 5 to 10 min with an associated KCl loss. 1. The regulatory volume decrease was unaffected when nitrate was substituted for Cl−, and was insensitive to bumetanide and DIDS. 2. Quinine, an inhibitor of the Ca2+-activated K+ pathway, blocked the volume recovery. 3. The hypotonic response was augmented by addition of the Ca2+ ionophore A23187 in the presence of external Ca2+, and also by a sudden increase in external Ca2+. The volume response was accelerated at alkaline pH. 4. The anti-calmodulin drugs trifluoperazine, pimozide, flupentixol, and chlorpromazine blocked the volume response. 5. Depletion of intracellular Ca2+ stores inhibited the regulatory volume decrease. 6. Consistent with the low conductive Cl− permeability of the cell membrane there was no change in cell volume or Cl− content when the K+ permeability was increased with valinomycin in isotonic medium. In contrast, addition of the Ca2+ ionophore A23187 in isotonic medium promoted Cl− loss and cell shrinkage. During regulatory volume decrease valinomycin accelerated the net loss of KCl, indicating that the conductive Cl− permeability was increased in parallel with and even more than the K+ permeability. It is proposed that separate conductive K+ and Cl− channels are activated during regulatory volume decrease by release of Ca2+ from internal stores, and that the effect is mediated by calmodulin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aull, F. 1981. Potassium chloride cotransport in steady-state ascites tumor cells. Does bumetanide inhibit?Biochim. Biophys. Acta 643:339–345
Aull, F. 1982. Specific drug sensitive transport pathways for chloride and potassium ions in steady-state Ehrlich mouse ascites tumor cells.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 688:740–746
Bui, A.H., Wiley, J.S. 1981. Cation fluxes and volume regulation by human lymphocytes.J. Cell. Physiol. 108:47–54
Cala, P.M. 1980. Volume regulation byAmphiuma red blood cells. The membrane potential and its implications regarding the nature of the ion-flux pathways.J. Gen. Physiol. 76:683–708
Cala, P.M. 1983. Volume regulation by red blood cells: Mechanisms of ion transport.Mol. Physiol. 4:33–52
Chipperfield, A.R. 1980. An effect of chloride on (Na+K) cotransport in human red blood cells.Nature (London) 286:281–282
Chipperfield, A.R. 1981. Chloride dependence of frusemide-and phloretin-sensitive passive sodium and potassium fluxes in human red cells.J. Physiol. (London) 312:435–444
Christoffersen, G.R.J., Simonsen, L. 1983. Intracellular Ca2+ activity during slow synaptic hyperpolarizations inHelix pomatia.Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 76C:351–364
Dunham, P.B., Ellory, J.C. 1981. Passive potassium transport in low potassium sheep red cells: Dependence upon cell volume and chloride.J. Physiol. (London) 318:511–530
Dunham, P.B., Stewart, G.W., Ellory, J.C. 1980. Chloride-activated passive potassium transport in human erythrocytes.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77:1711–1715
Ellory, J.C., Dunham, P.B. 1980. Volume-dependent passive potassium transport in LK sheep red cells.In: Membrane Transport in Erythrocytes. Alfred Benzon Symposium XIV. U.V. Lassen, H.H. Ussing and J.O. Wieth, editors. pp. 409–423. Munksgaard, Copenhagen
Ellory, J.C., Dunham, P.B. Logue, P.J., Stewart, G.W. 1982. Anion-dependent cation transport in erythrocytes.Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London B. 299:483–495
Garcia-Sancho, J., Sanchez, A., Herreros, B. 1982. All-or-none response of the Ca2+-dependent K+ channel in inside-out vesicles.Nature (London) 296:744–746
Geck, P., Pietrzyk, C., Burckhardt, B.-C., Pfeiffer, B., Heinz, E. 1980. Electrically silent co-transport of Na+, K+ and Cl− in Ehrlich cells.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 600:432–447
Grinstein, S., Clarke, C.A., DuPre, A., Rothstein, A. 1982a. Volume-induced increase of anion permeability in human lymphocytes.J. Gen. Physiol. 80:801–823
Grinstein, S., Clarke, C.A., Rothstein, A. 1982b. Increased anion permeability during volume regulation in human lymphocytes.Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London B. 299:509–518
Grinstein, S., DuPre, A., Rothstein, A. 1982c. Volume regulation by human lymphocytes. Role of calcium.J. Gen. Physiol. 79:849–868
Heinz, E., Geck, P., Pietrzyk, C. 1975. Driving forces of amino acid transport in animal cells.Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 264:428–441
Hempling, H.G. 1960. Permeability of the Ehrlich ascites tumor cell to water.J. Gen. Physiol. 44:365–379
Hendil, K.B., Hoffmann, E.K. 1974. Cell volume regulation in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells.J. Cell. Physiol. 84:115–125
Hoffman, J.F., Yingst, D.R., Goldinger, J.M., Blum, R.M., Knauf, P.A. 1980. On the mechanism of Ca-dependent K transport in human red blood cells.In: Membrane transport in Erythrocytes. Alfred Benzon Symposium XIV. U.V. Lassen, H.H. Ussing and J.O. Wieth, editors. pp. 178–192. Munksgaard, Copenhagen
Hoffmann, E.K. 1978. Regulation of cell volume by selective changes in the leak permeabilities of Ehrlich ascites tumor cells.In: Osmotic and Volume Regulation. Alfred Benzon Symposium XI. C.B. Jørgensen and E. Skadhauge, editors. pp. 397–417. Munksgaard, Copenhagen
Hoffmann, E.K. 1980. Cell volume regulation in mammalian cells.In: Animals and Environmental Fitness. R. Gilles, editor. pp. 43–59. Pergamon, Oxford and New York
Hoffmann, E.K. 1982. Anion exchange and anion-cation cotransport systems in mammalian cells.Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London B. 299:519–535
Hoffmann, E.K. 1983. Volume regulation by animal cells.In: Cellular Acclimatization to Environmental Change. Soc. Exptl. Biol. Seminar Series 18. A.R. Cossins and P.G. Shetterline, editors. pp. 55–80. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Hoffmann, E.K., Lambert, I.H. 1983. Amino acid transport and cell volume regulation in Ehrlich ascites tumour cells.J. Physiol. (London) 338:613–625
Hoffmann, E.K., Simonsen, L.O., Sjøholm, C. 1979. Membrane potential, chloride exchange, and chloride conductance in Ehrlich mouse ascites tumour cells.J. Physiol. (London) 296:61–84
Hoffmann, E.K., Sjøholm, C., Simonsen, L.O. 1983. Na+, Cl− cotransport in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells activated during volume regulation (regulatory volume increase).J. Membrane Biol. 76:269–280
Hyttel, J. 1978. Effects of neuroleptics on3H-haloperidol and3H-cis(2)-flupenthixol binding and on adenylate cyclase activity in vitro.Life Sci. 23:551–556
Knauf, P.A., Fuhrmann, G.F., Rothstein, S., Rothstein, A. 1977. The relationship between anion exchange and net anion flow across the human red blood cell membrane.J. Gen. Physiol. 69:363–386
Kregenow, F.M. 1971. The response of duck erythrocytes to nonhemolytic hypotonic media. Evidence for a volume-controlling mechanism.J. Gen. Physiol. 58:372–395
Kregenow, F.M. 1981. Osmoregulatory salt transporting mechanisms: Control of cell volume in anisotonic media.Annu. Rev. Physiol. 43:493–505
Lackington, I., Orrego, F. 1981. Inhibition of calcium-activated potassium conductance of human erythrocytes by calmodulin inhibitory drugs.FEBS Lett. 133:103–106
Lassen, U.V., Lew, V.L., Pape, L., Simonsen, L.O. 1977. Transient increase in the K permeability of intact human andAmphiuma red cells induced by external Ca at alkaline pH.J. Physiol. (London) 266:72P-73P
Lassen, U.V., Pape, L., Vestergaard-Bogind, B. 1980. Calcium related transient changes in membrane potential of red cells.In: Membrane Transport in Erythrocytes. Alfred Benzon Symposium XIV. U.V. Lassen, H.H. Ussing and J.O. Wieth, editors. pp. 255–268. Munksgaard, Copenhagen
Lauf, P.K. 1982. Evidence for chloride dependent potassium and water transport induced by hyposmotic stress in erythrocytes of the marine teleost,Opsanus tau.J. Comp. Physiol. 146:9–16
Lauf, P.K., Theg, B.E. 1980. A chloride dependent K+ flux induced by N-ethylmaleimide in genetically low K+ sheep and goat erythrocytes.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 92:1422–1428
Levinson, C. 1978. Chloride and sulphate transport in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells: Evidence for a common mechanism.J. Cell. Physiol. 95:23–32
Lew, V.L., Ferreira, H.G. 1978. Calcium transport and the properties of a calcium-activated potassium channel in red cell membranes.In: Current Topics in Membranes and Transport. F. Bronner and A. Kleinzeller, editors. Vol. 10, pp. 217–277. Academic, London
Lew, V.L., Muallem, S., Seymour, C.A. 1982. Properties of the Ca2+-activated K+ channel in one-step inside-out vesicles from human red cell membranes.Nature (London) 296:742–744
MacKnight, A.D.C., Leaf, A. 1977. Regulation of cellular volume.Physiol. Rev. 57:510–573
Pape, L. 1982. Effect of extracellular Ca2+, K+ and OH− on erythrocyte membrane potential as monitored by the fluorescent probe 3,3′-dipropylthiodicarbocyanine.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 686:225–232
Parker, J.C. 1983. Hemolytic action of potassium salts on dog red blood cells.Am. J. Physiol. 244:C313-C317
Parker, J.C., Hoffman, J.F. 1976. Influences of cell volume and adrenalectomy on cation flux in dog red blood cells.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 433:404–408
Plishker, G.A., Appel, S.H., Dedman, J.R., Means, A.R. 1980. Phenothiazine inhibition of calmodulin stimulates Ca-dependent K-efflux in human red blood cells.Fed. Proc. 39:1713
Ponder, E. 1948. Hemolysis and Related Phenomena. pp. 83–92. Grune & Stratton, New York
Poznansky, M., Solomon, A.K. 1972. Effect of cell volume on potassium transport in human red cells.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 274:111–118
Reichstein, E., Rothstein, A. 1981. Effects of quinine on Ca2+-induced K+ efflux from human red blood cells.J. Membrane Biol. 59:57–63
Rorive, G., Gilles, R. 1979. Intracellular inorganic osmotic effectors.In: Mechanisms of Osmoregulation in Animals. R. Gilles, editor. pp. 83–109. John Wiley & Sons, New York
Roti-Roti, L.W., Rothstein, A. 1973. Adaptation of mouse leukemic cells (L5178Y) to anisotonic media. I. Cell volume regulation.Exp. Cell Res. 79:295–310
Sigler, K., Janacek, K. 1971. The effect of non-electrolyte osmolarity on frog oocytes. II. Intracellular potential.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 241:539–546
Simonsen, L.O., Hoffmann, E.K., Sjøholm, C. 1976. Chloride conductance of the Ehrlich ascites tumor cell membrane.FEBS-Smp. Biochem. Memb. Transp. p. 225
Sjøholm, C., Hoffmann, E.K. 1984. Characterization of the Cl− transport site of Ehrlich cells by a kinetic analysis of the inhibitory effects of DIDS and pyridoxal phosphate.J. Membrane Biol. (Submitted)
Valdeolmillos, M., Garcia-Sancho, J., Herreros, B. 1982. Ca2+-dependent K+ transport in the Ehrlich ascites tumor cell.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 685:273–278
Weiss, B., Prozialeck, W., Cimino, M., Barnette, M.S., Wallace, T.L. 1980. Pharmacological regulation of calmodulin.In: Calmodulin and Cell Functions. D.M. Watterson and F.F. Vincenzi, editors.Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 356:319–345
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoffmann, E.K., Simonsen, L.O. & Lambert, I.H. Volume-induced increase of K+ and Cl− permeabilities in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Role of internal Ca2+ . J. Membrain Biol. 78, 211–222 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01925969
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01925969