Summary
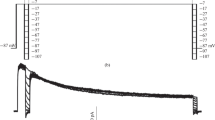
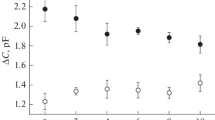
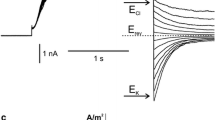
The potential difference across the membrane ofHydrodictyon africanum was controlled by voltage clamping and positive and negative steps in the PD were applied. For positive steps in the PD to values less negative than a threshold value, there is a PD and time-dependent increase in the outward current which has an S-shaped time course. Following the cessation of these steps, the current reverses instantaneously and declines with a simple time course. These currents show a strong K+ dependence and are blocked by tetraethylammonium (TEA) and nonyltriethylammonium (C9) ions, suggesting that they arise from the opening and then the closing of K+ channels. There is also a PD and time-dependent increase in the inward currents in response to negative steps in the membrane PD. The membrane properties have been described by three current-voltage curves, for the instantaneous current, for the steady-state current and for the current flow when the K+ channels are open. The response of the unclamped or free-running membrane PD to steps of constant current can be accounted for by the observed kinetics of the opening and closing of the K+ channels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong, C.M. 1971. Interaction of tetraethylammonium ion derivatives with the potassium channels of giant axons.J. Gen. Physiol. 58:413–437
Armstrong, C.M. 1975. Ionic pores, gates and gating currents.Q. Rev. Biophys. 7:179–210
Bielby, M.J., Coster, H.G.L. 1979. The action potential inChara corallina. II. Two activation-inactivation transients in voltage clamps of the plasmalemma.Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 6:323–335
Conti, F., Neher, E. 1980. Single channel recordings of K+ currents in squid axons.Nature (London) 285:140–143
Findlay, G.P. 1982. Electrogenic and diffusive components of the membrane ofHydrodictyon africanum.J. Membrane Biol. 68:179–189
Findlay, G.P., Hope, A.B. 1964. Ionic relations of cells ofChara australis. VII. The separate electrical characteristics of the plasmalemma and tonoplast.Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 17:62–77
Findlay, G.P., Hope, A.B. 1976. Electrical properties of plant cells: Methods and findings.In: Encyclopedia of Plant Physiology, New Series, Vol. 2. Part A, Transport in Plants II. pp. 53–92. U. Lüttge and M.G. Pitman, editors. Springer-Verlag, Berlin-Heidelberg-New York
Hill, S.A., Osterhout, W.J.V. 1938. Calculations of bioelectric potentials. II. The concentration potential of KCl inNitella.J. Gen. Physiol. 21:541–556
Hodgkin, A.L., Huxley, A.F. 1952. Currents carried by sodium and potassium ions through the membrane of the giant axon ofLoligo.J. Physiol. (London) 116:449–472
Keifer, D.W., Lucas, W.J. 1982. Potassium channels inChara corallina. Control and interaction with the electrogenic H+ pump.Plant Physiol. 69:781–788
Muller, R.U., Anderson, O.S. 1982. Monazomycin induced single channels. II. Origin of the voltage dependence of the macroscopic conductance.J. Gen. Physiol. 80:427–449
Muller, R.U., Finkelstein, A. 1972. Voltage-dependent conductance induced in thin lipid membranes by monazomycin.J. Gen. Physiol. 60:263–284
Osterhout, W.J.V. 1930. Calculations of bioelectric potentials. I. Effects of KCl and NaCl onNitella.J. Gen. Physiol. 13:715–732
Smith, P.T., Walker, N.A. 1981. Studies on the perfused plasmalemma ofChara corallina. I. Current-voltage curves: ATP and potassium dependence.J. Membrane Biol. 60:223–236
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Findlay, G.P., Coleman, H.A. Potassium channels in the membrane ofHydrodictyon africanum . J. Membrain Biol. 75, 241–251 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01871955
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01871955