Summary
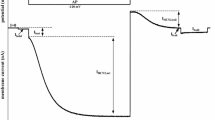
To investigate the voltage dependence of the Na−/K− pump, current-voltage relations were determined in prophasearrested oocytes ofXenopus laevis. All solutions contained 5mm Ba2− and 20mm tetraethylammonium (TEA) to block K− channels. If. in addition, the Na+/K+ pump is blocked by ouabain, K+-sensitive currents no larger than 50 nA/cm2 remain. Reductions in steady-state current (on the order of 700 nA/cm2) produced by 50 μm ouabain or dihydro-ouabain or by K+ removal, therefore, primarily represent current generated by the Na−/K− pump. In Na−-free solution containing 5mm K+, Na+/K+ pump current is relatively voltage independent over the potential range from −160 to +40 mV. If external [K+] is reduced below 0.5mm, negative slopes are observed over this entire voltage range. Similar results are seen in Na+- and Ca2+-free solutions in the presence of 2mm Ni2+, an experimental condition designed to prevent Na+/Ca2+ exchange. The occurrence of a negative slope can be explained by the voltage dependence of the apparent affinity for activation of the Na+/K+ pump by external K+, consistent with the existence of an external ion well for K− binding. In 90mm Na+, 5mm K+ solution, Na+/K+ pump current-voltage curves at negative membrane potentials have a positive slope and can be described by a monotonically increasing sigmoidal function. At an extracellular [K+] of 1.3mm, a negative slope was observed at positive potentials. These findings suggest that in addition to a voltage-dependent step associated with Na+ translocation, a second voltage-dependent step that is dependent on external [K+], possibly external K+ binding, participates in the overall reaction mechanism of the Na+/K+ pump.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apell, H.-J. 1989. Electrogenic properties of the Na, K pump.J. Membrane Biol. 110:103–114
Bahinski, A., Nakao, M., Gadsby, D.C. 1988. Potassium translocation by the Na/K pump is voltage insensitive.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85:3412–3416
Béhé, P., Turin, L. 1984. Arrest and reversal of the electrogenic sodium pump under voltage clamp.8th Int. Biophys. Congr., I. U. P. A. B., Bristol, U.K. p. 304
De Weer, P. 1984. Electrogenic pumps: Theoretical and practical considerations.In: Electrogenic Transport: Fundamental Principles and Physiological Implications. M.P. Blaustein and M. Lieberman, editors, pp. 1–15. Raven, New York
De Weer, P., Gadsby, D.C., Rakowski, R.F. 1988a. Stoichiometry and voltage dependence of the Na/K pump.In: The Na, K-Pump. Part A: Molecular Aspects. J.C. Skou, J.G. Nørby, A.B. Maunsbach, and M. Esmann, editors. pp. 421–434. Alan Liss, New York
De Weer, P., Gadsby, D.C., Rakowski, R.F. 1988b. Voltage dependence of the Na−K pump.Annu. Rev. Physiol. 50:225–241
De Weer, P., Rakowski, R.F., Gadsby, D.C., 1987. Current-voltage relationships of the electrogenic sodium pump of squid giant axon.Biophys. J. 51:385a
Dumont, J.N. 1972. Oogenesis inXenopus laevis (Daudin). I. Stages of oocyte development in laboratory maintained animals.J. Morphol. 136:153–180
Fendler, K., Grell, E., Haubs, M., Bamberg, E. 1985. Pump currents generated by the purified Na−/K− ATPase from kidney on black lipid membranes.EMBO J. 4:3079–3085
Gadsby, D.C., Bahinski, A., Nakao, M. 1989. Voltage dependence of Na/K pump current.Curr. Top. Membr. Transp. 34:269–288
Gadsby, D.C., Nakao, M. 1987. [Na] dependence of the Na/K pump current-voltage relationship in isolated cells from guinea-pig ventricle.J. Physiol. 382:106P
Gadsby, D.C., Nakao, M. 1989. Steady-state current-voltage relationship of the Na/K pump in guinea pig ventricular myocytes.J. Gen. Physiol. 94:511–537
Glynn, I.M. 1984. The electrogenic sodium pump.In: Electrogenic Transport: Fundamental Principles and Physiological Implications. M.P. Blaustein and M. Lieberman, editors. pp. 33–48. Raven, New York
Goldshlegger, R., Karlish, S.J.D., Rephaeli, A., Stein, W.D. 1987. The effect of membrane potential on the mammalian sodium-potassium pump reconstituted into phospholipid vesicles.J. Physiol. 387:331–355
Lafaire, A.V., Schwarz, W. 1985. Voltage-dependent, ouabainsensitive current in the membrane of oocytes ofXenopus laevis.In: The Sodium Pump. I.M. Glynn and C. Ellory, editors. pp. 523–525. Company of Biologists, Cambridge, U.K.
Lafaire, A.V., Schwarz, W. 1986. The voltage dependence of the rheogenic Na+/K+ ATPase in the membrane of oocytes ofXenopus laevis.J. Membrane Biol. 91:43–51
LaTona, J. 1990. Ion concentration and voltage dependence of Na/K pump current inXenopus laevis oocytes. Ph.D. Thesis. The University of Health Sciences/The Chicago Medical School, North Chicago, IL, University Microfilms, Ann Arbor, MI
Läuger, P., Apell, H.-J. 1986. A microscopic model for the current-voltage behavior of the Na,K pump.Eur. Biophys. J. 13:309–321
Nagel, G., Fendler, K., Grell, E., Bamberg, E. 1987. Na− currents generated by the purified (Na++K+)-ATPase on planar lipid membranes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 901:239–249
Nakao, M., Gadsby, D.C. 1986. Voltage dependence of Na translocation by the Na/K pump.Nature 323:628–630
Nakao, M., Gadsby, D.C. 1989. [Na] and [K] dependence of the Na/K pump current-voltage relationship in guinea pig ventricular myocytes.J. Gen. Physiol. 94:539–565
Passow, H. 1986. Dependence of the sodium pump on membrane potential: Introductory remarks.Prog. Zool. 33:383–386
Rakowski, R.F., Gadsby, D.C., De Weer, P. 1989a. Stoichiometry and voltage dependence of the sodium pump in voltage-clamped, internally dialyzed squid giant axon.J. Gen. Physiol. 93:903–941
Rakowski, R.F., Paxson, C.L. 1988. Voltage dependence of Na/K pump current inXenopus oocytes.J. Membrane Biol. 106:173–182
Rakowski, R.F., Paxson, C.L., LaTona, J. 1989b. Current-voltage relationships of the electrogenic Na/K pump inXenopus oocytes.FASEB J. 3:A873
Rakowski, R.F., Vasilets, L.A., Schwarz, W. 1990. Conditions for a negative slope in the current-voltage relationship of the Na/K pump inXenopus oocytes.Biophys. J. 57:182a
Rephaeli, A., Richards, D.E., Karlish, S.J.D. 1986. Conformational transitions in fluorescein-labeled (Na,K)ATPase reconstituted into phospholipid vesicles.J. Biol. Chem. 261:6248–6254
Schwarz, W., Gu, Q. 1988. Characteristics of the Na+/K+-ATPase fromTorpedo californica expressed inXenopus oocytes: A combination of tracer flux measurements with electrophysiological measurements.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 945:167–174
Schwarz, W., Vasilets, L.A. 1990. Variations in the negative slope of the current-voltage (I–V) relationship fo the Na+/K+ pump inXenopus oocytes.J. Gen. Physiol. 96:11a
Schweigert, B., Lafaire, A.V., Schwarz, W. 1988. Voltage dependence of the Na−K ATPase: Measurements of ouabain-dependent membrane current and ouabain binding in oocytes ofXenopus laevis.Pfluegers Arch. 412:579–588
Stürmer, W., Apell, H.-J., Wuddel, I., Läuger, P. 1989. Conformational transitions and charge translocation by the Na,K pump: Comparison of optical and electrical transients elicited by ATP-concentration jumps.J. Membrane Biol. 110:67–86
Stürmer, W., Bühler, R., Apell, H.-J., Läuger, P. 1990. Charge translocation by the Na/K pump: Kinetics of local field changes studied by time0resolved fluorescence measurements.J. Gen. Physiol. 96:75a
Vasilets, L.A., Schmalzing, G., Mädefessel, K., Haase, W., Schwarz, W. 1990. Activation of protein kinase C by phorbol ester induces down regulation of the Na+/K+-ATPase in oocytes ofXenopus laevis.J. Membrane Biol. 118:131–142
Wu, M.W., Civan, M.M. 1990. Voltage dependence of the Na/K-pump current ofRana oocytes.Biophys. J. 57:353a
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rakowski, R.F., Vasilets, L.A., LaTona, J. et al. A negative slope in the current-voltage relationship of the Na+/K+ pump inXenopus oocytes produced by reduction of external [K+]. J. Membrain Biol. 121, 177–187 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01870531
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01870531