Summary
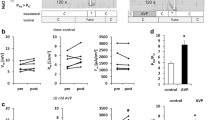
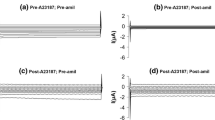
The effect of the K-sparing diuretic amiloride was assessed electrophysiologically in the isolated cortical collecting tubule of the rabbit, a segment which absorbs Na and secretes K. Low concentrations of amiloride in the perfusate caused a rapid, reversible, decrease in the magnitude of the lumen negative transepithelial potential difference,V te, transepithelial conductanceG te, and equivalent short-circuit current,I sc, with an apparentK 1/2 of approximately 7×10−8 m. The effects of a maximum inhibitory concentration of amiloride (10−5 m) were identical to those observed upon Na removal from lumen and bath (Na removal from the bath alone has no effect). Removal of Na in the presence of 10−5 m amiloride had no affect onV te,G te, orI sc, and is consistent with the view that amiloride blocks the Na conductive pathways of the apical cell membrane. Further, in the absence of Na, the subsequent addition of amiloride had no influence. In tubules where active Na absorption was either spontaneously low, or abolished by removal of Na from lumen and bath, the elevation of K from 5 to 155 meq/liter in the perfusate caused a marked change of theV te in the negative direction and an increase in theG te. These effects could be attributed to a high K permeability of the apical cell membrane and not of the tight junctions. Amiloride (10−5 m) had no effect on these responses to K. It is concluded that amiloride selectively blocks the apical cell membrane Na channels but has no effect on the K conductive pathways(s). This selective nature of amiloride may indicate that Na and K are transported across the apical cell membrane via separate conductive pathways.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baer, J.E., Jones, C.B., Spitzer, A.S., Russo, H.F. 1967. The potassium-sparing and natriuretic activity of N-amidino-3, 5-diamino-6-chloropyrazinecarboxamide hydrochloride (amiloride hydrochloride).J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 157:472
Barratt, L.J. 1976. The effect of amiloride on the transepithelial potential difference of the distal tubule of the rat kidney.Pfluegers Arch. 361:251
Bentley, P.J. 1968. Amiloride: A potent inhibitor of sodium transport across the toad bladder.J. Physiol. (London),195:317
Biber, T.U.L. 1971. Effect of changes in transepithelial transport on the uptake of sodium across the outer surface of the frog skin.J. Gen. Physiol. 58:131
Boudry, J.F., Stoner, L.C., Burg, M.B. 1976. Effect of lumen pH on potassium transport in renal cortical collecting tubules.Am. J. Physiol. 230:239
Bull, M.B., Laragh, J.H. 1968. Amiloride: A potassium-sparing natriuretic agent.Circulation 37:45
Burg, M., Grantham, J., Abramow, M., Orloff, J. 1966. Preparation and study of fragments of single rabbit nephrons.Am. J. Physiol. 210:1293
Cuthbert, A.W., Shum, W.K. 1974. Amiloride and the sodium channel.Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 281:261
Cuthbert, A.W., Shum, W.K. 1975. Effects of vasopressin and aldosterone on amiloride binding in toad bladder epithelial cellsProc. R. Soc. London B 189:543
Dörge, A., Nagel, W. 1970. Effect of amiloride on sodium transport in frog skin. II. Sodium transport pool and unidirectional fluxes.Pfluegers Arch. 321:91
Duarte, C.G., Chomety, F., Giebisch, G. 1971. Effect of amiloride, ouabain, and furosemide on distal tubular function in the rat.Am. J. Physiol. 221:632
Ehrlich, E.N., Crabbé, J. 1968. The mechanism of action of amipramizide.Pfluegers Arch. 302:79
Erlij, D., Smith, M.W. 1973. Sodium uptake by frog skin and its modification by inhibitors of transepithelial sodium transport.J. Physiol. (London) 228:221
Frizzell, R.A., Turnheim, K. 1978. Ion transport by rabbit colon. II. Undirectional sodium influx and the effects of amphotericin B and amiloride.J. Membrane Biol. 40:193
Frömter, E., Gebler, B. 1977. Electrical properties of amphibian urinary bladder epithelia. III. The cell membrane resistances and the effect of amiloride Pfluegers Arch.371:99
Fuchs, W., Larsen, E.H., Lindemann, B. 1977. Current-voltage curve of sodium channels and concentration dependence of sodium permeability in frog skin.J. Physiol. (London) 267:137
Glitzer, M.S., Steelman, S.L. 1966. N-amidino-3, 5-diamino-6-chloropyrazine-carboxamide: An active diuretic in the carboxamide series.Nature (London) 212:191
Grantham, J.J., Burg, M.B., Orloff, J. 1970. The nature of transtubular Na and K transport in isolated rabbit renal collecting tubules.J. Clin. Invest. 49:1815
Gross, J.B., Imai, M., Kokko, J.P. 1975. A functional comparison of the cortical collecting tubule and the distal convoluted tubule.J. Clin. Invest. 55:1284
Helman, S.I., Fisher, R.S. 1977. Microelectrode studies of the active Na transport pathway of frog skin.J. Gen. Physiol. 69:571
Helman, S.I., Grantham, J.J., Burg, M.B. 1971. Effect of vasopressin on electrical resistance of renal cortical collecting tubules.Am. J. Physiol. 220:1825
Helman, S.I., O'Neil, R.G. 1977. A model of active transepithelial Na and K transport of renal collecting tubules.Am. J. Physiol. 2:F559
Helman, S.I., O'Neil, R.G., Fisher, R.S. 1975. Determination of theE Na of frog skin from studies of its current-voltage relationship.Am. J. Physiol. 229:947
Lewis, S.A., Eaton, D.C., Diamond, J.M. 1976. The mechanism of Na+ transport by rabbit urinary bladder.J. Membrane Biol. 28:41
Lewis, S.A., Wills, N.K., Eaton, D.C. 1978. Basolateral membrane potential of a tight epithelium: Ionic diffusion and electrogenic pumps.J. Membrane Biol. 41:117
Lindemann, B., Van Driessche, W. 1977. Sodium-specific membrane channels of frog skin are pores: Current fluctuations reveal high turnover.Science 195:292
Lutz, M.D., Cardinal, J., Burg, M.B. 1973. Electrical resistance of renal proximal tubule perfused in vitro.Am. J. Physiol. 225:729
McKinney, T.D., Burg, M.B. 1978. Bicarbonate absorption by rabbit cortical collecting tubules in vitro.Am. J. Physiol. 234:F141
O'Neil, R.G., Boulpaep, E.L. 1978. Active ion transport properties of rabbit renal collecting tubules: Influence of amiloride and amphotericin B.Fed. Proc. 37:728
O'Neil, R.G., Boulpaep, E.L. 1979. K selectivity of luminal and basolateral cell membranes in renal cortical collecting tubules of rabbit.Fed. Proc. 38:1121
O'Neil, R.G., Helman, S.I. 1977. Transport characteristics of renal collecting tubules: Influence of DOCA and diet.Am. J. Physiol. 3:F544
Reuss, L., Finn, A.L. 1975. Dependence of serosal membrane potential on mucosal membrane potential in toad urinary bladder.Biophys. J. 15:71
Salako, L.A., Smith, A.J. 1970. Changes in sodium pool and kinetics of sodium transport in frog skin produced by amiloride.Br. J. Pharmac. 39:99
Schultz, S.G., Frizzell, R.A., Nellans, H.N. 1977. Active sodium transport and the electrophysiology of rabbit colon.J. Membrane Biol. 33:351
Shareghi, G.R., Stoner, L.C. 1978. Calcium transport across segments of the rabbit distal nephron in vitro.Am. J. Physiol. 235:F367
Stoner, L.C. 1977. Isolated, perfused amphibian renal tubules: The diluting segment.Am. J. Physiol. 2:F438
Stoner, L.C., Burg, M.B., Orloff, J. 1974. Ion transport in cortical collecting tubule: Effect of amiloride.Am. J. Physiol. 227:453
Sudou, K., Hoshi, T. 1977. Mode of action of amiloride in toad urinary bladder: An electrophysiological study of the drug action on sodium permeability of the mucosal border.J. Membrane Biol. 32:115
Thompson, S.M., Dawson, D.C. 1978. Sodium uptake across the apical border of the isolated turtle colon: Confirmation of the two-barrier model.J. Membrane Biol. 42:357
Wills, N.K., Lewis, S.A., Eaton, D.C. 1979. Active and passive properties of rabbit descending colon: A microelectrode and nystatin study.J. Membrane Biol. 45:137
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
O'Neil, R.G., Boulpaep, E.L. Effect of amiloride on the apical cell membrane cation channels of a sodium-absorbing, potassium-secreting renal epithelium. J. Membrain Biol. 50, 365–387 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01868898
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01868898