Abstract
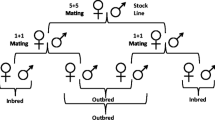
Striking differences in egg structure are exhibited by strains ofDrosophila hydei but do not act as barriers to inter-strain crosses. The structure of eggs of inter-strain hybrid females suggest that the observed differences in egg architecture are of genetic origin. One characteristic, the location of the maturation island, differs in eggs of the reciprocal hybrids. There is some suggestion that the paternal genome may be important in determining the character.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bull, A. L. (1966).Bicaudal, a genetic factor which affects the polarity of the embryo inDrosophila melanogaster.J. Exp. Zool. 161: 221–242.
Carson, H. L. (1961). Rare parthenogenesis inDrosophila robusta.Amer. Nat. 95: 81–86.
Carson, H. L. (1962). Fixed heterozygosity in a parthenogenetic species ofDrosophila.Univ. Texas Publ. 6205: 55–62.
Carson, H. L. (1967). Selection for parthenogenesis inDrosophila mercatorum.Genetics 55: 157–171.
Carson, H. L., M. R. Wheeler &W. B. Heed (1957). A parthenogenetic strain ofDrosophila mangabeirai Malogolowkin.Univ. Texas. Publ. 5721: 115–122.
Counce, S. J. (1961). The analysis of insect embryogenesis.Ann. Rev. Entomol. 6: 295–312.
Counce, S. J. (1963a). Developmental morphology of polar granules inDrosophila J. Morph. 112: 129–146.
Counce, S. J. (1963)b. Fate of sperm tails withinDrosophila eggs.Dros. Info. Service 37: 71.
Counce, S. J. (1966). Whole mounts ofDrosophila embryos.Dros. Info. Service 41: 195–196.
Counce, S. J. &N. M. Hartman (1963). Strain differences in egg structure inDrosophila hydei.Amer. Zool. 3: 503–504.
Dalcq, A. (1951). Le problème de l'évolution est-il près d'être résolu?Ann. Roy. Soc. Zool. Belg. 82: 117–138.
Hildreth, P. E. &J. C. Lucchesi (1963). Fertilization inDrosophila. I. Evidence for the regular occurrence of monospermy.Develop Biol. 6: 262–278.
King, R. C. (1964). Studies on early stages of insect oogenesis.Symp. Roy. Entomol Soc. 2: 13–25.
Krause, G. &K. Sander (1962). Ooplasmic reaction systems in insect embryogenesis.Adv. Morphogenesis 2: 259–303.
Lewis, E. B. (1963). Genes and developmental pathways.Amer. Zool. 3: 33–56.
Mahowald, A. P. (1968). Polar granules ofDrosophila. II. Ultrastructural changes during early embryogenesis.J. Exp. Zool. 167, 237–262.
Mahr, E. (1960a). Normale Entwicklung, Pseudofurchung, und die Bedeutung des Furchungszentrums im Ei des Heimchens (Gryllus domesticus).Zeit. Morph. Ökol. Tiere 49: 263–311.
Mahr, E. (1960b). Struktur und Entwicklungsfunktion des Dotter-Entoplasmasystems im Ei des Heimchens (Gryllus domesticus).Roux' Archiv 152: 263–302.
Murdy, W. H. &H. L. Carson (1959). Parthenogenesis inDrosophila mangabeirai Malog.Amer. Nat. 93: 355–363.
Oppenheimer, J. (1959). Intercellular activities in vertebrate development.Science 130: 686–692.
Patterson, J. T. &W. S. Stone (1952).Evolution in the Genus Drosophila. Macmillan, New York.
Poulson, D. F. (1950). Histogenesis, organogenesis, and differentiation in the embryo ofDrosophila melanogaster Meigen. InBiology of Drosophila ed. byM. Demerec. John Wiley & Sons New York.
Rabinowitz, M. (1941). Studies on the cytology and early embryology of the egg ofDrosophila melanogaster.J. Morph. 69: 1–49.
Seidler, B. (1940). Vergleichend morphologische Untersuchungen der Eistruktur nahe verwandter Käferaten.Zeit. Morphol. Ökol. Tiere 36: 677–744.
Seiler, J. (1960). Untersuchungen über die Entstehung der Parthenogenese beiSolenobia triquetrella F. R.Chromosoma 11: 29–102.
Sonnenblick, B. P. (1950). The early embryology ofDrosophila melanogaster. In:Biology of Drosophila, ed. byM. Demerec. John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Sprackling, L. S. (1960). The chromosome complement of the developing eggs produced byDrosophila parthenogenetica Stalker virgin females.Genetics 45: 243–256.
Stalker, H. D. (1961). Parthenogenesis inDrosophila.Genetics 39: 4–34.
Waddington, C. H. (1951). The evolution of developmental systems.Proc. Australian and New Zealand Assoc. Adv. Sci. 28: 155–159.
Wasserman, M. (1962). Cytological studies of the repleta group of the genusDrosophila. IV. The hydei subgroup.U. Texas. Publ. 6205: 73–83.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Counce, S.J., Ruddle, N.H. Strain differences in egg structure inDrosophila hydei . Genetica 40, 324–338 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01787360
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01787360