Abstract
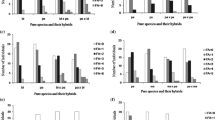
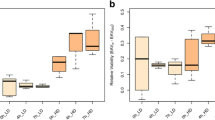
Phenotypic divergence of eggshells between D. melanogaster and D. simulans strains, was compared, using SEM, for analyzing fitness related eco-physiological traits of the eggshells in the two sibling species. The variations of eggshell traits between strains within species, between species and asymmetry in hybrids of two species have been calculated for understanding the demographic success of the two species. The present results revealed that variation of traits between strains within species was not always same which suggest that many traits are not strongly constrained within species. The main findings show that following eco-physiological traits of eggshells are mostly diverged between two species: (i) dorsal appendages (DA) length, (ii) insertion position of DA in main body of eggshell, (iii) the number and size of respiratory pores in dorsal and ventral side of DA, (iv) average length and volume of eggshells and (v) the thickness of chorionic hexagonal ridges. Examination of interspecific hybrids showed that the traits have undergone considerable genetic changes during evolutionary divergence of the two species. The authors propose that divergent ovipositional preference of the females of two species, may be the driving force in establishing species specific life history parameters for avoiding competition at pre-adult stages and demographic success.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lachaise D, Silvain JF (2004) How two Afrotropical endemics made two cosmopolitan human commensals: the Drosophila melanogaster—D. simulans paleogeographic riddle. Genetica 120:17–39
Tsacas L, Lachaise D (1974) Quatrenouvelles especes de laCote-d’Ivoire du genre Drosophila, groupe melanogaster, et discussionde l’origine du sous-groupe melanogaster (Diptera: Drosophilidae). Ann Univ Abidjan E Ecol 7:193–211
Veuille M, Baudry E, Cobb M, Derome N, Gravot E (2004) Historicity and the population genetics of Drosophila melanogaster and D. simulans. Genetica 120:61–70
Pool JE, Aquadra CF (2006) History and structure of sub-Saharan populations of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 174:915–929
Lachaise D, Carious ML, David JR, Lemeunier F, Tsacas L et al (1988) Historical biogeography of the Drosophila melanogaster species subgroup. Evol Biol 22:159–225
Dean MD, Ballard JWO (2004) Linking phylogenetics with population genetics to reconstruct the geographic origin of a species. Mol Phylogenet Evol 32:998–1009
Caracristi G, Schlotterer C (2003) Genetic differentiation between American and European Drosophila melanogaster populations could be attributed to admixture of African alleles. Mol Biol Evol 20:792–799
Nunes MDS, Neumeier H, Schlotterer C (2008) Contrasting patterns of natural variation in global Drosophila melanogaster populations. Mol Ecol 17:4470–4479
Gupta JP (2005) A monograph on Indian Drosophilidae. J Sci Res 51:1–252
David JR, Allemand R, Capy P, Chakir M, Gibert P, Petavy G, Moreteau B (2004) Comparative life histories and ecophysiology of Drosophila melanogaster and D. simulans. Genetica 120:151–163
Obbard DJ, Jiggins FM, Halligan DL, Little TJ (2006) Natural selection drives extremely rapid evolution in antiviral RNAi genes. Curr Biol 16:580–585
Andolfatto P (2001) Contrasting patterns of X linked and autosomal nucleotide variation in Drosophila melanogaster and Drosophila simulans. Mol Biol Evol 18:279–290
Nolte V, Schlotterer C (2008) African Drosophila melanogaster and D. simulans populations have similar levels of sequence variability, suggesting comparable effective population size. Genetics 178:405–412
Begun DJ, Aquadro CF (1993) African and North American populations of Drosophila melanogaster are very different at the DNA level. Nature 356:519–520
Emerson JJ, Cardoso-Moreira M, Borevitz JO, Long M (2008) Natural selection shapes genome-wide patterns of copy number polymorphism in Drosophila melanogaster. Science 320:1629–1631
Pool JE, Corbett-Detig RB, Sugino RP, Stevens KA, Cardeno CM, Crepeau MW, Duchen P, Emerson JJ, Saelao P, Begun DJ, Langley CH (2012) Population genomics of sub-Saharan Drosophila melanogaster: African diversity and non-African admixture. PLoS Genet 8:e1003080. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1003080
Langley CH, Stevens K, Cardeno C, Lee YCG, Schrider DR, Pool JE, Langley SA, Suarez C, Corbett-Detig RB, Kolaczkowski B, Fang S, Nista PM, Holloway AK, Kern AD, Dewey CN, Song YS, Hahn MW, Begun DJ (2012) Genomic variation in natural populations of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 192:533–598
Aquadro CF, Lado KM, Noon WA (1988) The rosy region of Drosophila melanogaster and Drosophila simulans. I. Contrasting levels of naturally occurring DNA restriction map variation and divergence. Genetics 119:875–888
Andolfatto P, Wong KM, Bachtrog D (2011) Effective population size and the efficacy of selection on the X chromosomes of two closely related Drosophila species. Genome Biol Evol 3:114–128
Hoffmann AA, Parsons PA (1993) Direct and correlated responses to selection for desiccation resistance: a comparison of Drosophila melanogaster and D. simulans. J Evol Biol 6:643–657
Chess KF, Ringo JM (1985) Ovipositional site selection by Drosophila melanogaster and D. simulans. Evolution 39:869–877
Capy P, Pla E, David JR (1993) Phenotypic and genetic variability of morphometrical traits in natural populations of Drosophila melanogaster and D. simulans. I. Geographic variations. Genet Sel Evol 25:517–536
Chakir M, David JR, Pla E, Capy P (1995) Genetic basis of some morphological differences between temperate and equatorial populations of Drosophila melanogaster. Experientia 51:744–748
Gibert P, Capy P, Imasheva A, Moreteau B, Morin JP, Petavy G, David JR (2004) Comparative analysis of morphological traits among Drosophila melanogaster and D. simulans: genetic variability, clines and phenotypic plasticity. Genetica 120:165–179
Jagadeeshan S, Singh RS (2007) Rapid evolution of outer egg membrane proteins in Drosophila melanogaster subgroup: a case of ecologically driven evolution of female reproductive traits. Mol Biol Evol 24:929–938
Kambysellis MP (1975) Ultrastructure of the chorion proteins in very closely related Drosophila species endemic to Hawaii. Syst Zool 23:507–512
Kambysellis MP (1993) Ultrastructural diversity in the egg chorion of Hawaiian Drosophila and Scaptomyza: ecological and phylogenetic consideration. Int J Insect Morphol Embryol 22:417–446
Kambysellis MP, Ho KF, Craddock EM, Piano F, Parisi M, Cohen J (1995) Pattern of ecological status in the diversification of Hawaiian Drosophila inferred from a molecular phylogeny. Curr Biol 5:1129–1139
Margaritis LH, Kafatos FC, Petri WH (1980) The eggshell of Drosophila melanogaster. I. Fine structure of the layers and regions of the wild type eggshell. J Cell Sci 43:1–35
Spradling AC (1993) Developmental genetics of oogenesis. In: Bate M, Martinez-Avias A (eds) The development of Drosophila melanogaster, I. Cold Spring Harbor press, New York, pp 1–70
Waring GL (2000) Morphogenesis of the eggshell in Drosophila. Int Rev Cytol 198:67–108
Margaritis LH (1985) Structure and physiology of eggshell. In: Kerkut GA, Gilbert LI (eds) Comprehensive insect physiology, biochemistry, vol 1. Pergaman press, New York, pp 153–173
Yakoby N, Lembong J, Schüpbach T, Shvartsman SY (2008) Drosophila eggshell is patterned by sequential action of feed forward and feedback loops. Development 135:343–351
Tootle TL, Williams D, Hubb A, Frederick R, Spradling A (2011) Drosophila eggshell production: identification of new genes and coordination by Pxt. PLoS One 6:e19934
Kalantzi-Makri MC, Trougakos IP, Tafas TP, Sourdis J, Margaritis LH (1999) Phylogenetic and taxonomical relationships of the eight species in the melanogaster subgroup of the genus Drosophila (Sophophora) based on the electrophoretic mobility of the major chorion proteins and the eggshell ultrastructure. J Zool (Lond) 249:295–306
Lindsley DL, Zimm G (1992) The genome of Drosophila melanogaster. Academic Press, San Diego
Fly Base Consortium (2003) The Fly Base data base of the Drosophila genome projects and community literature. Nucleic Acids Res 31:172–175
Ashburner M (1989) Drosophila: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Lab Press, New York
Chatterjee RN, Chatterjee P, Pal A, Pal-Bhadra M (2007) Drosoiphila simulans Lethal hybrid rescue mutation (Lhr) rescues inviable hybrids by restoring X chromosomal dosage compensation and causes fluctuating asymmetry of development. J Genet 86:203–215
Schwarzkopf L, Blows MW, Caley MJ (1999) Life history consequences of divergent selection of egg size in Drosophila melanogaster. Am Nat 154:333–340
Barbash DA, Ashburner M (2003) A noval system of fertility rescue in Drosophila hybrids reveals a link between hybrid lethality and female sterility. Genetics 163:217–226
Sainz A, Wilder JA, Wolf M, Hollocher H (2003) Drosophila melanogaster and D. simulans rescue strains produce fit offspring, despite divergent centromere-specific histone alleles. Heredity 91:28–35
Lachaise D, Tsacas L (1983) Breeding sites in tropical African drosophilids, vol 22. Academic Press, London, pp 1–332
Sanchez L, Santamaria P (1997) Reproductive isolation and morphogenetic evolution in Drosophila analyzed by breakage of ethological barriers. Genetics 147:231–242
Acknowledgments
The authors are also thankful to Dr. Masayoshi Watada, Ehime University, Japan for generously sending the Drosophila stocks. They are thankful to Dr. D. Barbash, Cornell University, USA for facilitating Lhr and In(1)AB, w stocks. The work has been supported by WB DST research Grants [Sanction No. 289 (Sanc.) ST/P/ST/2G-30/2011 dt.19.07.2012] to RNC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
They further declared that there is no conflict of interest among authors in publication of the paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chatterjee, R.N., Kuthe, S. & Chatterjee, P. Eggshells of Drosophila melanogaster and D. simulans: Ultrastructure, Measurement and Analyses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., India, Sect. B Biol. Sci. 87, 733–746 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-015-0647-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-015-0647-1