Summary
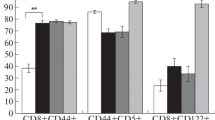
Large numbers of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) could be generated from tumor-draining lymph nodes (DLN) from mice bearing PHS-5 tumor by culturing at low density with autologous tumor cell stimulators and 20 U/ml recombinant interleukin-2 (IL-2). Outgrowth of metastatic tumor cells in culture was prevented by use of this hypoxanthine/aminopterin/thymidine-sensitive mutant of P815, PHS-5. After 9 days in culture, lymphoid cells demonstrated specific cytotoxicity against autologous tumor target cells. Lymph node cells could be expanded continuously in culture with repeated tumor stimulation with up to 7500-fold increase in cell number by 6 weeks; although CTL could be activated from tumor-bearing host spleen cells in short-term culture, they showed no significant growth in long-term cultures. Phenotypically, DLN cells were a mixture of CD8+ and CD4+ cells immediately after harvest but after 2 weeks in culture they were predominantly CD8+ CD4−. CTL could be generated from tumor-bearing mice 10–14 days after i.d. tumor inoculation into the abdominal wall, but the immune response declined both in spleen and DLN by 21 days. Much greater CTL activity could be generated from axillary DLN that contained metastases than from non-draining popliteal nodes that were free of metastatic tumor cells. Some CTL activity could be generated from DLN with the addition of IL-2 alone but was further increased by the addition of more tumor cells as stimulators. When adoptively transferred to a host with 3-day P815 liver metastases, lymphocytes from DLN activated in vitro were able to reduce or eliminate metastases with very little or no IL-2 administered concomitantly. As few as 106 cells were therapeutically effective, and in vivo efficacy was tumor-specific, since L5178Y liver metastases were not affected.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bear HD (1986) Tumor-specific suppressor T-cells which inhibit the in vitro generation of cytolytic T-cells from immune and early tumorbearing host spleens. Cancer Res 46: 1805
Bear HD (1987) Production of tumor-specific suppressor T-cell hybridomas. J Surg Res 42: 369
Berendt MJ, North RJ (1980) T-cell mediated suppression of antitumor immunity. J Exp Med 151: 69
Chou T, Chang AE, Shu S (1988) Generation of therapeutic T lymphocytes from tumor bearing mice by in vitro sensitization. J Immunol 161: 2453
Cozzolino F, Torcia M, Carossino AM, Giordani R, Selli C, Talini G, Reali E, Novelli A, Pistoia V, Ferrarini M (1987) Characterization of invaded lymph nodes in patients with solid tumors. J Exp Med 166: 303
Dye ES, North RJ (1981) T-cell mediated immune suppression as an obstacle to adoptive immunotherapy of the P815 mastocytoma and its metastases. J Exp Med 154: 1033
Lafreniere R, Rosenberg SA (1986) A novel approach to the generation and identification of experimental hepatic metastases in a murine model. J Natl Cancer Inst 76: 309
Rosenberg SA, Spiess P, Lafreniere R (1986) A new approach to the adoptive immunotherapy of cancer with tumor infiltrating lymphocytes. Science 233: 1318
Slingluff CL, Darrow T, Vervaert C, Quinn-Allen MA, Seigler HF (1988) Human cytotoxic T cells specific for autologous melanoma cells: Successful generation from lymph node cells in seven consecutive cases. J Natl Cancer Inst 80: 1016
Ward BA, Shu S, Chon T, Perry-Lalley D, Chang A. E. (1988) Cellular basis of immunologic interactions in adoptive T cell therapy of established metastases from a syngenic murine sarcoma. J Immunol 141: 1047
Wexler H (1966) Accurate identification of experimental pulmonary metastases. J Natl Cancer Inst 36: 641
Zola H, Brooks D (1982) Techniques for the production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies. In: Hurrell JGR (ed) Monoclonal hybridoma antibodies: techniques and applications. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, p 1
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported in part by grants CA42443, CA48075 and T32-CA09210 from the National Cancer Institute, Department of Health and Human Services
Recipient of the Canadian Cancer Society McEachern Fellowship.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McKinnon, J.G., Hoover, S.K., Inge, T.H. et al. Activation and expansion of cytotoxic T lymphocytes from tumor-draining lymph nodes. Cancer Immunol Immunother 32, 38–44 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01741722
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01741722