Abstract
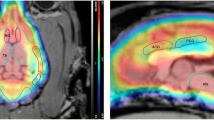
The benzodiazepine receptor ligand iomazenil was labelled with carbon-11 to allow a direct positron emission tomography/single-photon emission tomography (PET/SPET) comparison with the well-known iodine-123 labelled compound. Imaging showed the same regional distribution for both modalities. Blood sample activity was corrected for metabolites by extraction with chloroform and high-performance liquid chromatographic analysis. Metabolism is very fast: 5 min after application more than 85% of the plasma activity is present as hydrophilic metabolites. Kinetic methods were used to obtain regional estimates of transport rate constants and receptor concentrations. A three-compartment model was employed which gave transport rate constants for brain uptake (K 1) and the distribution volume for the specifically receptor bound compartment (DV s).K 1 varied from 0.32 to 0.50 ml/min per gram for the cortical regions, cerebellum, thalamus and striatum for PET and SPET. MeanDV s-PET andDV s-SPET values were, respectively, 23±5 and 31±5 ml/g for the occipital cortex, 11±3 and 15±2 ml/g for the cerebellum, 7±2 and 11±3 ml/g for the thalamus, 5±3 and 10±3 ml/g for the striatum, and 3±2 and 3±1 ml/g for the pons. These values correlated very well individually. The coefficient of variation of the SPET parameters was quite comparable to that of the PET parameters, especially after 180 min (PET 90 min) study duration. Thus quantitative benzodiazepine receptor information can be obtained from dynamic SPET imaging in the same way as with PET.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Möhler H, Okada T. Demonstration of benzodiazepine receptors in the central nervous system.Science 1977; 198: 849–851.
Squires RF, Braestrup C. Benzodiazepine receptors in rat brain.Nature 1977; 266: 732–734.
Haefely W, Polc P. Physiology of GABA enhancement by benzodiazepines and barbiturates. In: Olsen RW, Venter JC, eds.Benzodiazepine-GABA receptors and chloride channels: structure and function properties. New York: Alan R Liss; 1986: 81–108.
Hunkeler W, Möhler H, Pieri L, et al. Selective antagonists of benzodiazepines.Nature 1985; 290: 514–516.
Geller E, Thomson D, eds. Proceedings of the international symposium on flumazenil — the first benzodiazepine antagonist.Eur J Anaesthesiol 1988; Suppl 2: 1–132.
Mazière M, Prenant C, Sastre J, et al.11C-RO 15 1788 et11C-flunitrazepam, deux coordinats pour l'étude par tomographie par positons des sites de liaison des benzodiazepines.CR Acad Sci (Paris) 1983; 296: 871–876.
Hantraye P, Brouillet E, Fukada H, et al. Benzodiazepine receptors studied in living primates by positron emission tomography: antagonist interactions.Eur J Pharmacol 1988; 153: 25–32.
Shinotoh H, Yamasaki T, Inoue O, et al. Visualization of specific binding sites of benzodiazepine in human brain.J Nucl Med 1986; 27: 1593–1599.
Frey KA, Holthoff VA, Koeppe RA, Jewett DM, Kilbourn MR, Kuhl DE. Parametric in vivo imaging of benzodiazepine receptor distribution in human brain.Ann Neurol 1991; 30: 663–672.
Price JC, Mayberg HS, Dannals RF, et al. Measurement of benzodiazepine receptor number and affinity in humans using tracer kinetic modeling, positron emission tomography, and [11C]flumazenil.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1993; 13:656–667.
Beer H-F, Bläuenstein PA, Hasler PH, Schubiger PA. Iomazenil: pharmacological and animal data. In: Schubiger PA, Hasler PH, eds.Iomazenil and other brain receptor tracers for SPECT. Basel: Editiones Roche; 1990: 9–29.
Beer H-F, Bläuenstein PA, Hasler PH, et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of iodine-123 Ro 16-0154: a new imaging agent for SPECT investigations of benzodiazepine receptors.J Nucl Med 1990; 31: 1007–1014.
Zoghbi SS, Baldwin RM, Seibyl JP, et al. Pharmacokinetics of the SPECT benzodiazepine receptor radioligand [123I]iomazenil in human and non-human primates.Nucl Med Biol, Int J Appl Instrum Part B 1992; 19: 881–888.
Laruelle M, Abi-Dargham A, al-Tikriti MS, et al. SPECT quantification of [123I]iomazenil binding to benzodiazepine receptors in nonhuman primates. II. Equilibrium analysis of constant infusion experiments and correlation with in vitro parameters.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1994; 14: 453–465.
Schubiger PA, Hasler PH, Beer-Wohlfahrt H, et al. Evaluation of a multicentre study with iomazenil — a benzodiazepine receptor ligand.Nucl Med Commun 1991; 12: 569–582.
Cordes M, Henkes H, Ferstl F, et al. Evaluation of focal epilepsy: a SPECT scanning comparison of 123-I-iomazenil vs. HM-PAO.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1992; 13: 249–253.
Johnson EW, de Lanerolle NC, Kim JH, et al. “Central” and “peripheral” benzodiazepine receptors: opposite changes in human epileptogenic tissue.Neurology 1992; 42: 811–815.
Van Isselt JW, Van Huffelen AC, Van Rijk PP. The value of I-123-iomazenil SPECT in the presurgical work-up of patients with medically intractable focal epilepsy.J Nucl Med 1993; 34: 22P, No. 80.
Schröder J, Bubeck B, Roelcke U, Jauss M, Schubiger PA, Sauer P. A new methodical approach for the imaging of cerebral benzodiazepine receptors in schizophrenia: preliminary results of a single photon emission tomography study with [123I]-iomazenil. In: Maurer K, ed.Imaging of the brain in psychiatry and related fields. Berlin Heidelberg New York: Springer; 1993: 97–103.
Schlegel S, Steinert H, Bockisch A, Hahn K, Schloesser R, Benkert O. Decreased benzodiazepine receptor binding in panic disorder measured by iomazenil SPECT.Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 1994; 244: 49–51.
Buchali K. Results of displacement studies of benzodiazepine receptors (123I-iomazenil and flumazenil).Nucl Med 1992; 31: 29–31.
Verhoeff NP, Erbas B, Kapucu O, et al. Quantification of central benzodiazepine receptor binding potential in the brain with 123I-iomazenil SPECT: technical and interobserver variability.Nucl Med Commun 1993; 14: 634–643.
Laruelle M, Baldwin RM, Rattner Z, et al. SPECT quantification of [123I]iomazenil binding to benzodiazepine receptors in non-human primates. I. Kinetic modeling of single bolus experiments.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1994; 14: 439–452.
Abi-Dargham A, Laruelle M, Seibyl J, et al. SPECT measurements of benzodiazepine receptors in human brain with iodine-123-iomazenil: kinetic and equilibrium paradigms.J Nucl Med 1994; 35: 228–238.
Westera G, Eberle I, Hunkeler W, Ametamey S, Schubiger PA. The production of11C-Iomazenil.J Labeled Compounds Radiopharm 1993; 32: 169–170.
Barre L, Debruyne D, Abadie P, Moulin M, Baron J. A comparison of methods for the separation of [11C]Ro 15-1788 (flumazenil) from its metabolites in the blood of rabbits, baboons and humans.Appl Radiat Isot, Int J Radiat Appl Instrum Part A 1991; 42:435–439.
Chang LT. A method for attenuation correction in radionuclide computed tomography.IEEE NS 1978; 25: 638–639.
Press WH, Teukolky SA, Vetterling WT, Flannery BP. In:Numerical recipes in C, the art of scientific computing, 2nd edn. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 1992: 412–420.
Gandelman MS, Baldwin RM, Zoghbi SS, Zea-Ponce Y, Innis RB. Evaluation of ultrafiltration for the free-fraction determination of single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) radiotracers. β-CIT, IBF and iomazenil.J Pharm Sci 1994; 83: 1014–1019.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Westera, G., Buck, A., Burger, C. et al. Carbon-11 and iodine-123 labelled iomazenil: a direct PET-SPET comparison. Eur J Nucl Med 23, 5–12 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01736983
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01736983