Summary
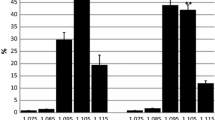
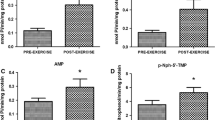
6 patients with AMPD-deficiency and 6 control subjects performed exercise on a bicycle ergometer until heart rate was 200 minus age. During exercise the increase of ammonia plasma concentrations was reduced in AMPD-deficient patients compared with that of control subjects. Plasma concentrations of lactate, pyruvate, inosine, hypoxanthine and xanthine increased during exercise in both groups. The concentrations of lactate, inosine and hypoxanthine were lower in AMPD-deficient patients during exercise, the difference was not significant. In AMPD-deficient patients the ATP-concentrations of red blood cells increased during exercise in contrast to control subjects, whereas the ADP amount did not change significantly.
Our data suggest that in AMPD-deficient-patients AMP is mainly reduced to adenosine during exercise resulting in decreased ammonia concentrations. The increased concentrations of ATP in red blood cells may be the consequence of increased phosphorylation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AMP, ADP, ATP:
-
adenosine-5′-monophosphate, -diphosphate, -triphosphate
- AMPD:
-
AMP deaminase (myoadenylate deaminase)
References
Bontemps F, Van den Berghe G, Hers HG (1986) Pathways of adenine nucleotide catabolism in erythrocytes. J Clin Invest 77:824–839
De Korte D, Haverkort WA, Ross D, Van Gennip AH (1985) Anion exchange high performance liquid chromatography method for the quantitation of nucleotides in human blood cells. Clin Chem Acta 148:185–196
DiMauro S, Miranda AF, Hays AP, Franck WA, Hoffmann GS, Schoenfeldt RS, Singh N (1980) Myoadenylate deaminase deficiency: muscle biopsy and muscle culture in patient with gout. J Neurol Sci 47:191–197
Fishbein WN, Armbrustmacher VW, Griffin JL (1978) Myoadenylate deaminase deficiency: a new disease of muscle. Science 200:545–548
Fishbein WN (1986) Myoadenylate deaminase deficiency. In: Myology. McGraw Hill, New York, pp 1745–1762
Goebel HH, Bardosi A (1987) Myoadenylate deaminase deficiency. Klin Wochenschr 65:1023–1033
Gross M, Reiter S, Zöllner N (1989) Metabolism of D-ribose administered continuously to healthy persons and to patients with myoadenylate deaminase deficiency. Klin Wochenschr 67:1205–1213
Heller SL, Kaiser KK, Planer GJ, Hagberg JM, Brooke MH (1987) McArdle's disease with myoadenylate deaminase deficiency: observations in a combined enzyme deficiency. Neurology 37:1039–1042
Sabina RL, Swain JL, Olanow W, Bradley WG, Fishbein WN, Di Mauro S, Holmes EW (1984) Myoadenylate deaminase deficiency. Functional and metabolic abnormalities associated with disruption of the purine nucleotide cycle. J Clin Invest 73:720–730
Sinkeler SPT, Joosten EMG, Wevers RA, Binkhorst RA, Oerlmans FT, Bennekom CA, Coerwinkel MM, Olei TL (1986) Ischemic exercise test in myoadenylate deaminase deficiency and McArdle's disease: measurement of plasma adenosine, inosine and hypoxanthine. Clin Science 70:399–401
Sinkeler SPT, Wevers RA, Joosten EM, Binkhorst RA, Olei TL, Van't Hof MA, De Haan AF (1986) Improvement of screening in exertional myalgia with standardized ischemic forearm test. Muscle Nerve 9:731–737
Sinkeler SPT, Binkhorst RA, Joosten EMG, Wevers RA, Coerwinkel MM, Olei TL (1987) AMP deaminase deficiency: study of the human skeletal purine metabolism during ischemic isometric exercise. Clin Science 72:475–482
Swain JL, Sabina RL, Holmes EW (1983) Myoadenylate deaminase deficiency. In: Stanbury JB, Wyngaarden JB, Fredrickson DS, Goldstein JL, Brown MS (eds) The metabolism basis of inherited disease, 5th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 1184–1191
Valen PA, Nakayama DA, Veum J, Sulaiman AR, Wortmann RL (1987) Myoadenylate deaminase deficiency and forearm ischemic exercise testing. Arthr Rheumatism 30:661–668
Yoshino M, Murakami K (1985) AMP deaminase reaction as a control system of glycolysis in yeast. J Biol Chem 260:4729–4732
Zöllner N, Reiter S, Gross M, Pongratz D, Reimers CD, Gerbitz K, Paetzke I, Deufel T, Hübner G (1986) Myoadenylate deaminase deficiency: successful symptomatic therapy by high dose oral administration of ribose. Klin Wochenschr 64:1281–1290
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wagner, D.R., Felbel, J., Gresser, U. et al. Muscle metabolism and red cell ATP/ADP concentration during bicycle ergometer in patients with AMPD-deficiency. Klin Wochenschr 69, 251–255 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01666850
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01666850