Summary
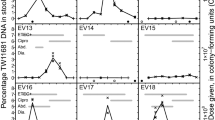
Consecutive serum samples from 61 patients withClostridium difficile diarrhoea were investigated for antibody response toC. difficile toxins A and B in an indirect enzyme immunoassay (ELISA) and in a neutralization assay againstC. difficile cytotoxin. Sera from 64 blood donors, elderly healthy females and patients with other known intestinal enteropathogens served as controls. An immune response was detected by ELISA in approximately half of the patients withC. difficile diarrhoea. The specificity of the ELISA was 94% or 97%, depending on the control material used. Furthermore, a correlation was found between clinical recovery without relapse ofC. difficile diarrhoea and high IgG titers to toxin B in the ELISA, and/or appearance of neutralizing antibodies. It is concluded that the ELISA for detection of serum antibodies toC. difficile toxins may be of diagnostic value in combination with the conventional tissue culture assay for cytotoxin in stool. High ELISA IgG titres to toxin B and/or the appearance of neutralizing antibodies may also be a positive prognostic sign in patients withC. difficile diarrhoea.
Zusammenfassung
Von 61 Patienten mitClostridium difficile-Diarrhoe wurden konsekutive Serumproben mit einem indirekten Enzymimmunassay (ELISA) und einem Neutralisationstest fürC. difficile Cytotoxin auf die Antikörperantwort gegen die Toxine A und B vonC. difficile untersucht. Als Kontrollen wurden Seren von 64 Blutspendern, älteren gesunden Frauen und Patienten, die an Krankheiten durch andere bekannte enteropathogene Erreger litten, verwendet. Bei annähernd der Hälfte der Patienten mitC. difficile-Diarrhoe wurde mittels ELISA eine Immunantwort entdeckt. In Abhängigkeit vom Kontrollmaterial ergab sich für den ELISA-Test eine Spezifität von 94% oder 97%. Bei Patienten, die sich ohne Rezidiv von derC. difficile-Diarrhoe erholten, bestand eine Korrelation zu hohen IgG-Titern gegen Toxin B im ELISA-Test und/oder Auftreten von neutralisierenden Antikörpern. Daraus läßt sich schließen, daß die Bestimmung der Antikörper gegenC. difficile-Toxine im Serum mit ELISA in Kombination mit dem herkömmlichen Gewebekultur-Test auf Cytotoxin von diagnostischem Wert ist. Hohe ELISA IgG-Titer gegen Toxin B und/oder das Auftreten neutralisierender Antikörper im Serum können bei Patienten mitC. difficile-Diarrhoe als positives prognostisches Zeichen gewertet werden.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature
George, R. H., Symonds, J., Dimock, F., Brown, J. D., Arabi, Y., Shinagawa, N., Keighley, M. R. B., Alexander-Williams, J., Burdon, D. W. Identification ofClostridium difficile as cause of pseudo-membranous colitis. Br. Med. J. 1 (1978) 695.
Bartlett, J. G. Antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1 (1979) 530–539.
Bartlett, J. G., Tedesco, F. J., Shull, S., Lowe, B., Chang, T.-W. Symptomatic relapse after oral vancomycin therapy of antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis. Gastroenterology 78 (1980) 431–434.
George, W. L., Rolfe, R. D., Harding, G. K. M., Klein, R., Putnam, C. W., Finegold, S. M. Clostridium difficile and cytotoxin in feces of patients with antimicrobial agent-associated pseudomembranous colitis. Infection 10 (1982) 205–207.
Sack, D. A. Immune and other defense factors of significance for diarrhoeal diseases: In:Holme, T., Holmgren, J., Merson, M. H., Möllby, R. (eds.): Acute enteric infections in children. Elsevier, Holland 1981, pp. 261–271.
Aronsson, B., Granström, M., Möllby, R., Nord, C. E. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for antibodies toClostridium difficile toxins in patients with pseudomembranous colitis and anti-biotic-associated diarrhoea. J. Immunol. Methods 60 (1983) 341–350.
Ekwall, E., Haeggmann, S., Kalin, M., Svenungsson, B., Lindberg, A. A. Antibody response toShigella sonnei infection determined by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2 (1983) 200–205.
Aronsson, B., Möllby, R., Nord, C. E. Occurrence of toxin producingClostridium difficile in antibiotic-associated diarrhoea in Sweden. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 170 (1981) 27–35.
Libby, J. M., Wilkins, T. D. Production of antitoxins to two toxins ofClostridium difficile and immunological comparison of the toxins by cross-neutralization studies. Infect. Immun. 35 (1982) 374–376.
Aronsson, B., Möllby, R., Nord, C. E. Clostridium difficile and antibiotic-associated diarrhoea in Sweden. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. Suppl. 35 (1982) 53–58.
Granström, M., Julander, I., Hedström, S. A., Möllby, R. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for antibodies against teichoic acid in patients with staphylococcal infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 17 (1983) 640–646.
Cremer, N. E. Antibody formation and the immune response. In:Freeman, B. A. (ed.): Burrows textbook of microbiology. 21st ed. The WB Saunders Co., Philadelphia 1979, p. 362.
Viscidi, R., Laughon, B. E., Yolken, R., Bo-Linn, R., Moench, T., Ryder, R. W., Bartlett, J. G. Serum antibody response to toxins A and B ofClostridium difficile. J. Infect. Dis. 148 (1983) 93–100.
George, R. H., Hartley, S. Antibodies toClostridium difficile cytotoxin in a pediatric population. Am. J. Dis. Child. 137 (1983) 1024.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aronsson, B., Granström, M., Möllby, R. et al. Serum antibody response to clostridium difficile toxins in patients with clostridium difficile diarrhoea. Infection 13, 97–101 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01642866
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01642866