Summary
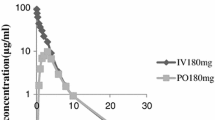
The pharmacokinetics of cefotaxime (HR 756) were investigated in two groups of patients (Groups I and II) with creatinine clearances of ≥60 and <60 ml/min per 1.73 m2 respectively. Each of the 24 patients included in the study received 0.5 g or 1.0 g cefotaxime intravenously as a bolus injection. The decline of serum concentrations was biphasic in all patients, and the data were fitted to the pharmacokinetic two-compartment model. The mean distribution and elimination half-lives of cefotaxime in individuals in Group I were 0.2 and 1.2 hours respectively. In the uremic individuals, the pharmacokinetic parameters did not differ markedly from those in normal subjects, except when renal function was markedly reduced. In severe renal impairment, the elimination half-life increased to 8.3 hours. Cumulative 24-hour urinary excretion accounted for a mean of 59% of the dose in normal individuals, and from 0.3 to 36% of the dose in uremic individuals. Incomplete recovery of intact drug in urine of normal individuals reflects excretion by an extrarenal pathway, possibly as desacetyl cefotaxime. Urine levels were greater than the minimum inhibitory concentrations for susceptible organisms for at least eight hours after dosing in all individuals who produced urine. Because of the relatively small effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of cefotaxime, dose reduction is necessary only in cases of severe renal impairment.
Zusammenfassung
Die Pharmakokinetik von Cefotaxim (HR 756) wurde bei zwei Gruppen von Patienten (Gruppe I und II) mit Kreatinin Clearance von jeweils ≥60 und <60 ml/min pro 1,73 m2 untersucht. Die 24 in die Studie aufgenommenen Patienten erhielten entweder 0,5 g oder 1,0 g Cefotaxim intravenös als Bolus-Injektion. Der Abfall der Serumkonzentrationen war bei allen Patienten biphasisch und die Werte paßten zum pharmakokinetischen Zwei-Kompartimenten-Modell. Die mittlere Verteilungs- und Eliminationshalbwertszeiten von Cefotaxim bei Personen von Gruppe I betrugen 0,2 bzw. 1,2 Stunden. Bei den urämischen Patienten unterschieden sich die pharmakokinetischen Parameter nicht wesentlich von denen der normalen Probanden, ausgenommen bei schwerer Beeinträchtigung der Nierenfunktion. Bei schwerer Nierenfunktionsstörung stieg die Eliminationshalbwertszeit auf 8,3 Stunden an. Die kumulative 24-Stunden-Ausscheidung im Urin machte bei den Normalpersonen im Mittel 59% der Dosis aus und lag bei den urämischen Patienten zwischen 0,3 bis 36% der Dosis. Die unvollständige Recovery der unveränderten Substanz im Urin von Normalpersonen spricht für die Ausscheidung über einen extrarenalen Weg, möglicherweise als Desacetylcefotaxim. Die Urinspiegel lagen mindestens acht Stunden lang nach der Dosierung bei allen Patienten, die Urin ausschieden, über den minimalen Hemmkonzentrationen für empfindliche Keime. Da eine gestörte Nierenfunktion die Pharmakokinetik von Cefotaxim nur relativ gering beeinflußt. ist eine Verminderung der Dosis nur bei Fällen von schwerer Nierenfunktionsstörung nötig.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature
Neu, H. C., Aswapokee, N., Aswapokee, P., Fu, K. P. HR 756, a new cephalosporin active against gram-positive and gram-negative aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 15 (1979) 273–281.
Heymès, R., Luta, A., Schinner, E. Experimental evaluation of HR 756, a new cephalosporin derivative: Pre-clinical study. Infection 5 (1977) 259–260.
Counts, G. W., Turck, W. Antibacterial activity of a new parental cephalosporin-HR 756: Comparison with cefamandole and ceforanide. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 16 (1979) 64–68.
Wise, R., Rollason, T., Logan, M., Andrews, J. M., Beford, K. A. HR 756, a highly active cephalosporin: Comparison with cefazolin and carbenicillin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 14 (1978) 807–811.
Chabbert, Y. A., Lutz, A. J. HR 756, thesyn isomer of a new methoxyimino cephalosporin with unusual activity. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 14 (1978) 749–754.
Fu, K. P., Neu, H. C. Beta-lactamase stability of HR 756, a novel cephalosporin, compared to that of cefuroxime and cefoxitin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 14 (1978) 322–326.
Lüthy, R., Münch, R., Blaser, J., Bhend, H., Siegenthaler, W. Human pharmacology of cefotaxime (HR 756), a new cephalosporin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 16 (1979) 127–133.
Methodology for determining HR 756 in serum and urine. Hoechst-Roussel Pharmaceutical Inc., Sommerville, N. J., USA.
MACC nonlinear regression routines. Academic Computer Center, University of Wisconsin, Madison 1972.
Foord, R. D. Cefuroxime: Human pharmacokinetics. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 9 (1976) 741–747.
Brogard, J. M., Comte, F., Pinget, M. Pharmacokinetics of cephalosporin antibiotics. Antibiot. Chemother. 25 (1978) 123–162.
Wise, R., Willis, P. J., Andrews, J. M., Bedford, K. A. Activity of the cefotaxime (HR 756) desacetyl metabolite compared with those of cefotaxime and other cephalosporins. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 17 (1980) 84–86.
Nielsen, O. S., Naber, K. G., Madsen, P. O.: Konzentration von Cefotaxim im Urogenitaltract. Infection (1980) in press.
Welling, P. G., Craig, W. A., Kunin, C. M. Prediction of drug dosage in patients with renal failure using data derived from normal subjects. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 18 (1975) 45–52.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nielsen, O.S., Bundtzen, R.W., Craig, W.A. et al. Cefotaxime pharmacokinetics following a single intravenous dose to patients with varying renal function. Infection 8 (Suppl 3), S305–S309 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01639601
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01639601