Abstract
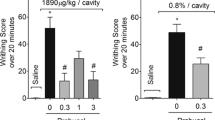
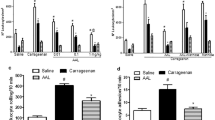
Substance P has been implicated as a mediator of inflammation. The involvement of this neuropeptide in carrageenan-induced hind paw edema in the rat was assessed. Subcutaneous injection of carrageenan into the rat paw caused a significant increase in substance P levels, which preceded the onset of inflammation. While injection of substance P alone caused mild edema, coadministration of submaximal doses of carrageenan and substance P resulted in a synergistic exacerbation in the degree of inflammation. This synergistic response was not detected when the nonamidated precursor of substance P was coinjected with carrageenan. The effects of substance P depletion on inflammation were also evaluated. In animals pretreated with capsaicin followed by injection with carrageenan, no significant increase in either the levels of substance P or the extent of edema was observed when compared to capsaicin-treated controls. These results indicate that substance P may play an important role in the early stages of carrageenan-induced paw edema and that a reduction in the biosynthesis of substance P may lessen the severity of this inflammatory response.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Greaves, M. W. 1988. Inflammation and mediators.Br. J. Dermatol. 119:419–426.
Flower, R. J., E. A. Harvey, andW. P. Kingston. 1976. Inflammatory effects of prostaglandin D2 in rat and human skin.Br. J. Pharmacol. 56:229–233.
Robertson, I., andM. W. Greaves. 1978. Responses of human skin blood vessels to synthetic histamine analogues.Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 5:319–322.
Juhlin, L., andS. Hammarstrom. 1982. Effects of intradermally injected leukotriene C4 and histamine in patients with urticaria, psoriasis and atopic dermatitis.Br. J. Dermatol. 170(Suppl. 23):106–110.
Helme, R. D., P. V. Andrews, andB. A. Watson. 1986. Neurogenic inflammation caused by wool fabric in the rat; Possible mediation by substance P.Neurosci. Lett. 66:333–337.
Tissot, M., P. Pradelles, andJ. P. Giroud. 1988. Substance-P-like levels in inflammatory exudates.Inflammation 12:25–35.
Raychaudhuri, A., C. Colombo, G. Pastor, M. Wong, andA. Y. Jeng, 1991. Effect of capsaicin on carrageenan-induced inflammation in rat pleurisy and exudate substance P. level.Agents Actions 34:251–253.
Levine, J. D., D. H. Collier, A. I. Basbaum, M. A. Moskowitz, andC. A. Helms. 1985. Hypothesis: The nervous system may contribute to the pathophysiology of rheumatoid arthritis.J. Rheumatol. 12:406–411.
Oku, R., M. Satoh, andH. Takagi. 1987. Release of substance P from the spinal dorsal horn is enhanced in polyarthritic rats.Neurosci. Lett. 74:315–319.
Levine, J. D., R. Clark, M. Devor, C. Helms, M. A. Moskowitz, andA. I. Basbaum. 1984. Intraneuronal substance P contributes to the severity of experimental arthritis.Science 226:547–549.
Goetzl, E. J., T. Chernov, F. Renold, andD. G. Payan. 1985. Neuropeptide regulation of the expression of immediate hypersensitivity.J. Immunol. 135(Suppl):802S-805S.
Lotz, M., D. A. Carson, andJ. H. Vaughan. 1987. Substance P activation of rheumatoid synoviocytes: neural pathway in pathogenesis of arthritis.Science 235:893–895.
Lotz, M., J. H. Vaughan, andD. A. Carson, 1988. Effect of neuropeptides on production of inflammatory cytokines by human monocytes.Science 241:1218–1221.
Kimball, E. S., F. J. Persico, andJ. L. Vaught. 1988. Substance P, neurokinin A, and neurokinin B induce generation of IL-1-like activity in P388D1 cells. Possible relevance to arthritic disease.J. Immunol. 141:3564–3569.
Jessell, T. M., L. L. Iversen, andA. C. Cuello. 1978. Capsaicin-induced depletion of substance P from primary sensory neurones.Brain Res. 152:183–188.
Jeng, A. Y., M. Wong, S. J. Lovato, M. D. Erion, andJ. P. Gilligan. 1990. A radioimmunoassay for measuringα-amidating enzyme activity.Anal. Biochem. 185:213–219.
Buck, S. H., andT. F. Burks. 1986. The neuropharmacology of capsaicin: Review of some recent observations.Pharmacol. Rev. 38:179–225.
Jancso, N., A. Jancso-Gabor, andJ. Szolcsanyi. 1967. Direct evidence for neurogenic inflammation and its prevention by denervation and by pretreatment with capsaicin.Br. J. Pharmacol. Chemother. 31:138–151.
Gamse, R., P. Holzer, andF. Lembeck. 1980. Decrease of substance P in primary afferent neurones and impairment of neurogenic plasma extravasation by capsaicin.Br. J. Pharmacol. 68:207–213.
Colpaert, F. C., J. Donnerer, andF. Lembeck. 1983. Effects of capsaicin on inflammation and on the substance P content of nervous tissues in rats with adjuvant arthritis.Life Sci. 32:1827–1834.
Lam, F. Y., andW. R. Ferrell. 1989. Inhibition of carrageenan induced inflammation in the rat knee joint by substance P antagonist.Ann. Rheum. Dis. 48:928–932.
Lembeck, F., J. Donnerer, M. Tsuchiya, andA. Nagahisa. 1992. The nonapeptide tachykinin antagonist, CP-96,345, is a potent inhibitor of neurogenic inflammation.Br. J. Pharmacol. 105:527–530.
Nagahisa, A., Y. Kanai, O. Suga, K. Taniguchi, M. Tsuchiya, J. A. Lowe, III, andH.-J. Hess. 1992. Antiinflammatory and analgesic activity of a nonapeptide substance P receptor antagonist.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 217:191–195.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gilligan, J.P., Lovato, S.J., Erion, M.D. et al. Modulation of carrageenan-induced hind paw edema by substance P. Inflammation 18, 285–292 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01534269
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01534269