Abstract
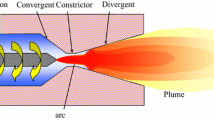
This paper presents a modeling attempt related to low-pressure plasma spraying processes which find increasing applications for materials processing. After a review of the various models for ionization and recombination processes, a two-temperature model for argon plasmas in chemical (ionization) nonequilibrium is established using finite rate chemistry. Results of sample calculations manifest departures from kinetic as well as chemical equilibrium, demonstrating that the conventional models based on the LTE (local thermodynamic equilibrium) assumption cannot provide proper prediction for low-pressure plasma jets.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Mitchner and C. H. Kruger,Partially Ionized Gases, Wiley, New York (1973).
K. Dakeda, K. Hayashi, and T. Ohashi, “Fluid flow and temperature fields of plasma jet in low-pressure spray processes,” Proc. of ISPC-7, Vol. 3 (1985), p. 848.
J. N. Le Toulouzan, G. Gouesbet, R. Darrigo, and A. Berlemont,AIAA J. 25, 30 (1987).
D. Wei, D. Apelian, and B. Farouk, “A critical analysis of proposed plasma jet models to predict temperature and velocity profiles,” MRS Spring Meeting, Paper K.1.6 (1987).
D. Apelian, D. Wei, and M. Paliwal,Thin Solid Films 118, 395 (1984).
T. Honda and A. Kanzawa,AIAA J. 15, 1353 (1977).
G. A. Luk'yanov, V. V. Nazarov, and V. V. Sakhin,Sov. Phys.-Tech. Phys. 23, 744 (1978).
H.-D. Steffens and K.-H. Busse, “Measurements of particle and plasma velocity in a low-pressure plasma jet,” Proc. of ISPC-7, Vol. 2 (1985), p.710.
G. Frind, C. P. Goody, and L. E. Prescott, “Measurement of particle velocity in two low-pressure plasma jets,” Proc. of ISPC-6, Vol. 1 (1983), p. 120.
Y. Arata, A. Kobayashi, and Y. Habara,Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. Part 1, 1697 (1986).
R. Hidaka, T. Ooki, K. Takeda, K. Konda, H. Kanda, K. Chino, Y. Matsuda, K. Muraoka, and M. Akazaki,Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 26, L1724 (1987).
J. W. Bond,Phys. Rev. 105, 1683 (1957).
H. Petschek and S. Byron,Ann. Phys. 1, 270 (1957).
K. N. C. Bray, “Electron-ion recombination in argon flowing through a supersonic nozzle,” inThe High-Temperature Aspects of Hypersonic Flow, W. C. Nelson, ed., Pergamon, New York (1962).
N. D'Angelo,Phys. Rev. 121, 505 (1961).
D. R. Bates and A. E. Kingston,Nature (London) 189, 652 (1961).
E. Hinnov and J. G. Hirschberg,Phys. Rev. 125, 795 (1962).
S. Byron, R. C. Stabler, and P. I. Bortz,Phys. Rev. Lett. 8, 376 (1962).
D. R. Bates, A. E. Kingston, and R. W. P. McWhirter, “Recombination between electrons and atomic ions. I. Optically thin plasmas,”Proc. R. Soc. London A267, 297 (1962).
D. R. Bates, A. E. Kingston, and R. W. P. McWhirter, “Recombination between electrons and atomic Ions. II. Optically thick plasmas,”Proc. R. Soc. London A270, 155 (1962).
M. Gryzinski,Phys. Rev. 115, 374 (1959).
K. E. Harwell and R. G. Jahn,Phys. Fluids 7, 214 (1964);7, 1554 (1964).
E. J. Morgan and R. D. Morrison,Phys. Fluids 8, 1608 (1965).
M. Hoffert and H. Lien,Phys. Fluids 10, 1769 (1967).
C. H. Kruger,Phys. Fluids 13, 1737 (1970).
G. J. Schultz and R. E. Fox,Phys. Rev. 106, 1179 (1957).
L. S. Frost and A. V. Phelps,Phys. Rev. A136, 1538 (1964).
J. F. Shaw, M. Mitchner, and C. H. Kruger,Phys. Fluids 13, 325 (1970).
J. F. Shaw, M. Mitchner, and C. H. Kruger,Phys. Fluids 13, 339 (1970).
C. G. Braun and J. A. Kunc,Phys. Fluids 30, 499 (1987).
T. Holstein,Phys. Rev. 72, 1212 (1947).
T. Holstein,Phys. Rev. 83, 1159 (1951).
J. A. Kunc,Phys. Fluids 27, 2859 (1984).
D. A. Erwin and J. A. Kunc,Phys. Fluids 28, 3349 (1985).
C. J. Chen,Phys. Rev. 177, 245 (1969).
H. N. Olsen,Phys. Fluids 2, 614 (1959).
R. B. Bird, W. E. Stewart, and E. N. Lightfoot,Transport Phenomena, Wiley, New York (1960).
M. Y. Jafirin,Phys. Fluids 8, 606 (1965).
D. Kannapan and T. K. Bose,Phys. Fluids 20, 1668 (1977).
E. J. Miller and S. I. Sandler,Phys. Fluids 16, 491 (1973).
U. Daybelge, “Transport properties of two-temperature partially ionized plasmas,” Ph.D. Thesis, Stanford University (1968).
R. S. Devoto,Phys. Fluids 16, 616 (1973).
U. Daybelge,J. Appl. Phys. 41, 2130 (1970).
R. S. Devoto,Phys. Fluids 10, 2105 (1967).
C. H. Kruger and M. Mitchner,Phys. Fluids 10, 1953 (1967).
R. M. Chmieleski and J. H. Ferziger,Phys. Fluids 10, 364 (1967).
Kun-Chen Hsu, “A self-consistent model for the high-intensity free-burning argon arc,” Ph.D. Thesis, University of Minnesota (1982).
D. B. Spalding,genmix h—A General Computer Program for Two-Dimensional Parabolic Phenomena, Pergamon, Oxford (1977).
Y. C. Lee, “Modeling work in thermal plasma processing,” Ph.D. Thesis, University of Minnesota (1984).
I. K. Jennions, A. S. C. Ma, and D. B. Spalding, “A prediction for 2-dimensional, steady, supersonic flows (thegenmix h computer program),” Imperial College Technical Report HTS/77/24 (1977).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, C.H., Pfender, E. Nonequilibrium modeling of low-pressure argon plasma jets; Part I: Laminar flow. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 10, 473–491 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01447204
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01447204