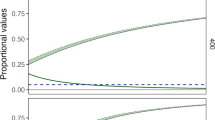
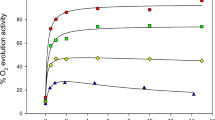
Summary
The influence of the potassium nutritional status upon the photoreduction and photophosphorylation was studied with “broken” chloroplasts ofSpinacia oleracea, Vicia faba andHelianthus annuus. Chloroplasts from plants with a high K supply showed increased rates of photoreduction and photophosphorylation. The latter process was more affected than the photoreduction. Therefore the P/2e− ratio was lower for plants poor in potassium. Additions of potassium chloride (0 to 100 mM) to the incubation medium increased the photophosphorylation and photoreduction rates. But this effect appeared to be independent of the potassium nutrition status, while the rather low rates of photophosphorylation and photoreduction of the chloroplasts poor in potassium could not be overcome by the addition of potassium chloride. It is assumed, that the favorable effect of an adequate potassium nutrition upon photophosphorylation and photoreduction is brought about by enhanced ion fluxes (protons and potassium) through the thylakoid membranes and also by higher activities and efficiencies of enzymes involved
Zusammenfassung
Es wurde der Einfluß des Kaliumernährungszustandes auf die Photoreduktion und auf die Photophosphorylierung an aufgebrochene Chloroplasten vonSpinacia oleracea, Vicia faba undHelianthus annuus untersucht. Chloroplasten von Pflanzen mit hoher K-Versorgung zeigten erhöhte Photoreduktions-und Photophosphorylierungsraten. Hierbei wurde die Phosphorylierung stärker beeinflußt als die Reduktion. Dementsprechend war das P/2e−-Verhältnis kaliumarmer Pflanzen erniedrigt. Zugaben von Kaliumchlorid (0–100 mM KCl) zum Inkubationsmedium erhöhten die Photophosphorylierungs-und die Photoreduktionsrate. Dieser Effekt war jedoch unabhängig vom Kaliumernährungszustand, und die ziemlich niedrigen Phosphorylierungs-und Reduktionsraten Kalium armer Chloroplasten konnten durch Zugaben von Kaliumchlorid nicht auf das Niveau von Chloroplasten mit guter Kaliumversorgung gebracht werden. Es wird angenommen, daß die günstige Wirkung einer guten Kaliumernährung auf Photophosphorylierung und Photoreduktion auf gesteigerte Ionenfluxe (Protonen und Kalium) durch Thylakoidmembranen zurückgeht. Weiterhin dürfte Kalium auch die Aktivität und die Wirksamkeit der beteiligten Enzyme beeinflußst haben.
Similar content being viewed by others
Schrifttum
Arnon, D., Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts: Polyphenoloxidase inBeta vulgaris. Plant Physiol.24, 1–5 (1949).
Avron, M., Photophosphorylation by swiss-chard chloroplasts. Biochim. Biophys. Acta40, 257–272 (1960).
Böger, P., Das Strukturproteid aus Chloroplasten einzelliger Grünalgen und seine Beziehung zum Chlorophyll. Flora154, 174–211 (1964).
Dilley, R. A. und Vernon, L. P., Ion and water transport processes related to light-dependent shrinkage of spinach chloroplasts. Arch. Biochem. Biophys.111, 365–375 (1965).
Jacobi, G., Biochemische Untersuchungen zur Beurteilung der in wäßrigen Medien isolierten Chloroplasten. Z. Naturforsch.18 b, 314–323 (1963).
Jones, L. H., Carbon-14 studies of intermediary metabolism in potassium deficient tomato plants. Canad. J. Bot.44, 297–307 (1966).
Larkum, A. W. D., Ionic relations of chloroplastsin vivo. Nature218, 447–449 (1968).
Latzko, E. und Mechsner, K., Bedeutung der Alkali-Ionen für die Intensität der Lichtphosphorylierung beiChlorella vulgaris. Naturw.45, 247–248 (1958).
Lubin, M. und Ennis, H. C., On the role of intracellular potassium in protein synthesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta82, 614–631 (1964).
Mitchell, P., Coupling of phosphorylation to electron and hydrogen transfer by a chemi-osmotic type of mechanism. Nature191, 144–148 (1961).
Mitchell, P., Chemiosmotic coupling in oxidative and photosynthetic phosphorylation. Biol Rev.41, 445–502 (1966).
Nobel, P. S., Light-induced changes in the ionic content of chloroplasts inPisum sativum. Biochim. Biophys. Acta172, 134–143 (1969).
Peaslee, D. E. und Moss, D. N., Photosynthesis in K- and Mg-deficient maize (Zea mays L.) leaves. Soil Sci, Soc. Am. Proc.30, 220–223 (1966).
Pirson, A., Tichy, C. und Wilhelmi, G., Stoffwechsel und Mineralsalzernährung einzelliger Grünlagen. I. Mitteiling: Vergleichende Untersuchungen an Mangelkulturen von Ankistrodesmus. Planta40, 199–253 (1952).
Strotmann, H. und Berger, S., Adenine nucleotide translocation across the membrane of isolated Acetabularia chloroplasts. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm.35, 20–26 (1969).
Tagawa, K. und Arnon, D. I., Ferredoxins as electron carriers in photosynthesis and the biological production and consumption of hydrogeu gas. Nature195, 537–543 (1963).
Tombesi, L., Calé, M. T. und Tiborne, B., Effects of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizers on the assimilation capacity ofBeta vulgaris chloroplasts. Plant and Soil31, 65–76 (1969).
Walker, D. A., Correlation between photosynthetic activity and membrane integrity in isolated pea chloroplasts. Plant Physiol.40, 1157–1161 (1965).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pflüger, R., Mengel, K. Die photochemische Aktivität von Chloroplasten Aus unterschiedlich mit Kalium ernährten Pflanzen. Plant Soil 36, 417–425 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01373495
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01373495