Summary
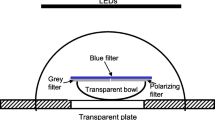
The desert antCataglyphis bicolor is able to use the pattern of polarized light in the sky as compass. By confronting the ant to single spots of artificially and naturally polarized light it is shown howCataglyphis uses the polarization pattern.
When exposed to a horizontal e-vector,Cataglyphis was always oriented correctly. Orientation errors occurred, however, when other e-vector directions were presented. This indicates that the e-vector positions assumed by the ant do not coincide with the e-vector positions actually realized in the sky. From this it is concluded thatCataglyphis has no detailed knowledge of the actual azimuthal positions of the e-vectors. Instead, it is relying on a simplified celestial map of the polarization patterns in the sky (Fig. 7).
Usually, the ant did not confuse celestial spots with identical e-vector directions. Even at sunset when the polarization pattern is completely ambiguous, correct orientation occurred. This suggests that the ant uses additional celestial cues such as the degree of polarization, the color or the intensity to find its way home when the sun is obscured.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batschelet E (1965) Statistical methods for the analysis in animal orientation and certain biological rhythms. Am Inst Biol Sciences, Washington DC
Batschelet E (1981) Circular statistics in biology. Academic Press, London New York
Brines ML (1978) Skylight polarization patterns as cues for honey bee orientation: Physical measurements and behavioral experiments. PhD thesis, Rockefeller University New York
Brines ML, Gould JL (1979) Bees have rules. Science 206:571–573
Coulson KL, Dave JV, Sekera Z (1960) Tables related to radiation emerging from planetary atmosphere with Rayleigh scattering. University of California Press, Berkeley Los Angeles
Duelli P (1975) A fovea for e-vector orientation in the eye ofCataglyphis bicolor (Formicidae, Hymenoptera). J Comp Physiol 102:43–56
Duelli P, Wehner R (1973) The spectral sensitivity of polarized light orientation inCataglyphis bicolor (Formicidae, Hymenoptera). J Comp Physiol 86:37–53
Fent K (1985) Himmelsorientierung bei der WüstenameiseCataglyphis bicolor: Bedeutung von Komplexaugen und Ocellen. PhD thesis, University of Zürich
Fent K, Wehner R (1985) Ocelli: A celestial compass in the desert antCataglyphis. Science 228:192–194
Gould JL, Dyer FC, Towne WF (1985) Recent progress in the study of the dance language. In: Hölldobler B, Lindauer M (eds) Exp Behav Ecol. Fortschr Zool 31:141–161
Heiversen O von, Edrich W (1974) Der Polarisationsempfänger im Bienenauge: ein Ultraviolettrezeptor. J Comp Physiol 94:33–47
Kirschfeld K, Lindauer M, Martin H (1975) Problems of menotactic orientation according to the polarized light of the sky. Z Naturforsch 30c:88–90
Lanfranconi B (1982) Kompassorientierung nach dem rotierenden Himmelsmuster bei der WüstenameiseCataglyphis bicolor. PhD thesis, University of Zürich
Räber F (1979) Retinatopographie und Sehfeldtopologie des Komplexauges vonCataglyphis bicolor (Formicidae, Hymenoptera) und einiger verwandter Formiciden-Arten. PhD thesis, University of Zürich
Rössel S, Wehner R (1982) The bee's map of the e-vector pattern in the sky. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:4451–4455
Rössel S, Wehner R (1984) How bees analyse the polarization pattern in the sky. Experiments and model. J Comp Physiol A 154:607–615
Rössel S, Wehner R, Lindauer M (1978) E-vector orientation in bees. J Comp Physiol 125:1–12
Sekera Z (1957) Polarization of skylight. In: Flügge S (ed) Handbuch der Physik, vol 48. Springer, Berlin Göttingen Heidelberg
Waterman TH (1981) Polarization sensitivity. In: Autrum H (ed) Vision in invertebrates. (Handbook of sensory physiology, vol. VII/6B). Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 281–469
Wehner R (1982) Himmelsnavigation bei Insekten. Neurophysiologie und Verhalten. Neujahrsbl Naturforsch Ges Zürich 184:1–132
Wehner R, Lanfranconi B (1981) What do the ants know about the rotation of the sky? Nature 293:731–733
Wehner R, Rossel S (1985) The bee's celestial compass — A case study in behavioural neurobiology. In: Hölldobler B, Lindauer M (eds) Exp Behav Ecol. Fortschr Zool 31:11–53
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fent, K. Polarized skylight orientation in the desert antCataglyphis . J. Comp. Physiol. 158, 145–150 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01338557
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01338557