Summary
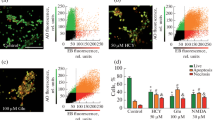
The effect of MPP+, a dopaminergic neurotoxin, in mitochondrial membrane potential was investigated in dissociated cerebellar granule cells using rhodamine 123 and flow cytometry. MPP+ (1 mM) decreased the mitochondrial membrane potential by 30%. Antagonists of the NMDA receptor complex, such as MK-801 (IC50 value of 20.92 ± 0.02 nM), 5,7-dichlorokynurenic acid (IC50 value of 6.46 ± 1.06 μM) and D-AP5 (IC50 value of 8.29 ± 0.63 μM), inhibited the action of MPP+. Neither NBQX, nor riluzole, nor desipramine modified the action of MPP+. Dibucaine restored the basal values of mitochondrial membrane potential altered by MPP+. Since, in the presence of NMDA, MPP+ antagonized the effect of this total agonist, it can be concluded that, in this preparation, MPP+ interacts with the NMDA receptor complex as a partial agonist. This interaction could be the result of an allosteric modulation of the NMDA receptor complex by MPP+. The decrease of mitochondrial membrane potential induced by MPP+ is antagonized by dibucaine, suggesting that this effect is mediated by an activation of phospholipase A2.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JD, Odunze IN (1991) Biochemical mechanisms of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine toxicity: could oxidative stress be involved in the brain? Biochem Pharmacol 41: 1099–1105
Akaneya Y, Takahashi M, Hatanaka H (1995a) Involvement of free radicals in MPP+ neurotoxicity against rat dopaminergic neurons in culture. Neurosci Lett 193: 53–56
Akaneya Y, Takahashi M, Hatanaka H (1995b) Survival of and 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+) neurotoxicity against dopaminergic neurons in coculture of rat mesencephalon with their target and non-target regions. Neurosci Res 23: 53–66
Brouillet E, Beal MF (1993) NMDA antagonists partially protect against MPTP induced neurotoxicity in mice. Neurochemistry 4: 387–390
Cadet JL, Ali SF, Rothman RB, Epstein CJ (1995) Neurotoxicity, drugs abuse and the CuZn-superoxide dismutase transgenic mice. Mol Neurobiol 11: 155–163
Carboni S, Melis F, Pani L, Hadjiconstantinou M, Rossetti ZL (1990) The non-competitive NMDA-receptor antagonist MK-801 prevents the massive release of glutamate and aspartate from rat straitum induced by 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+). Neurosci Lett 117: 129–133
Chan P, DeLanney LE, Irwin I, Langston JM, DiMonte D (1991) Rapid ATP loss caused by 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine in mouse brain. J Neurochem 57: 348–351
Clarke PBS, Reuben M (1995) Inhibition by dizocilpine (MK-801) of striatal dopamine release induced by MPTP and MPP+: possible action at the dopamine transporter. Br J Pharmacol 114: 315–322
Cleeter MWJ, Cooper JM, Schapira AHV (1992) Irreversible inhibition of mitochondrial complex I by 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium: evidence for free radical involvement. J Neurochem 58: 786–792
Hantraye P, Brouillet E, Ferrante R, Palfi S, Dolan R, Matthews RT, Beal MF (1996) Inhibition of neuronal nitric oxide synthase prevents MPTP-induced parkinsonism in baboons. Nature Med 2: 1017–1021
Hsu KS, Huang CC, Gean PW (1995) Voltage and use dependent block by 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion (MPP+) on N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) activated currents in rat hippocampal neurons. Neurosci Lett 189: 17–20
Javitch JA, D'Amato RJ, Stritmatter SM, Snyder SH (1985) Parkinsonism-inducing neurotoxin. N-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine: uptake of the metabolite N-methyl-4-phenylpyridine by dopamine neurons explains selective toxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82: 2173–2177
Marini AM, Paul SM (1992) N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-mediated neuroprotection in cerebellar granule cells requires new RNA and protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 6555–6559
Markey SP, Johannessen JN, Chiueh CC, Burns RS, Herkenham MA (1984) Intraneuronal generation of a pyridinium metabolite may cause drug-induced parkinsonism. Nature 311: 464–467
Michel PP, Agid Y (1992) The glutamate antagonist, MK-801, does not prevent dopaminergic cell death induced by the 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion (MPP+) in rat dissociated mesencephalic cultures. Brain Res 597: 233–240
Poirier J, Donaldson J, Barbeau A (1985) The specific vulnerability of the substantia nigra to MPTP is related to the presence of transition metals. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 128: 25–33
Reinhard JF, Daniels AJ, Painter GR (1990) Carrier-independent entry of 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+) into adrenal chromaffin cells as a consequence of charge delocalization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 168: 1143–1148
Reynolds IJ, Miller RJ (1988) Tricyclic antidepressants block N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors: similarities to the action of Zn. Br J Pharmacol 95: 95–102
Russ H, Staudt K, Martel F, Gliese M, Schömig E (1996) The extraneuronal transporter for monoamine transmitters exists in cells derived from human central nervous system glia. Eur J Neurosci 8: 1256–1264
Santiago M, Venero JL, Machado A, Cano J (1992) In vivo protection of striatum from MPP+ neurotoxicity by N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist. Brain Res 586: 203–207
Sonsalla PK, Zeevalk GD, Manzino L, Giovanni A, Nicklas WJ (1992) MK-801 fails to protect against the dopaminergic neuropathology produced by systemic 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine in mice or intranigral 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium in rats. J Neurochem 58: 1972–1989
Starr MS (1995) Antiparkinsonian actions of glutamate antagonists-alone and with L- DOPA: a review of evidence and suggestions for possible mechanisms. J Neural Transm [P-D Sect] 10: 141–185
Storey E, Hyman BT, Jenkins B, Brouillet E, Miller JM, Rosen BR, Beal MF (1992) 1-Methyl-4-phenylpyridinium produces excitotoxic lesions in rat striatum as a result of impairment of oxidative metabolism. J Neurochem 58: 1975–1978
Sundstrom E, Mo LL (1995) Effects of 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium on radioligand binding to the NMDA receptor complex. Res Commun Mol Pathol Pharmacol 88: 131–136
Sureda FX, Camins A, Trullas R, Camarasa J, Escubedo E (1996a) A flow cytometric study of N-methyl-D-aspartate effects on dissociated cerebellar cells. Brain Res 723: 110–114
Sureda FX, Viu E, Zapata A, Capdevila JL, Camins A, Escubedo E, Camarasa J, Trullas R (1996b) Modulation of NMDA-induced cytosolic calcium levels by ACPC in cultured cerebellar granule cells. Neuroreport 7: 1824–1828
Sureda FX, Escubedo E, Gabriel C, Camarasa J, Camins A (1996c) Effect of glutamate receptor ligands on mitochondrial membrane potential in rat dissociated cerebellar cells. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 354: 420–423
Turski L, Bressler K, Retting KJ, Löschman PA, Wachtel H (1991) Protection of substantia nigra from MPP+ neurotoxicity by N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonists. Nature 349: 414–418
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Camins, A., Sureda, F.X., Gabriel, C. et al. Effect of 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+) on mitochondrial membrane potential in cerebellar neurons: Interaction with the NMDA receptor. J. Neural Transmission 104, 569–577 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01291876
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01291876