Summary
Calcium has been shown to enter cholinergic synaptosomes transiently during potassium-induced depolarization, in which ACh and ATP are released together. Because junctional ATP is rapidly hydrolyzed by extracellular ATPases, I studied and compared the roles of ATP, ADP, AMP, and adenosine (Ade) on the control of calcium uptake during depolarization.
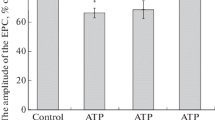
Pure cholinergic synaptosomes of Torpedo fish electric organ were depolarized by high potassium concentrations and the amount of calcium uptake was then measured in the presence of equal concentrations of Ade and its related nucleotides. Calcium uptake was more inhibited when the nucleotide was less phosphorylated. Thus, Ade was the greatest inhibitor.
Because Ade is quickly and actively taken up from the extracellular medium by synaptosomes and converted intracellularly to ATP, I also measured the capacity of Ade, after its initial inhibitory action, to reactivate the calcium uptake. After a short preincubation with Ade, the later uptake of calcium was enhanced. The combined results support a complete role of adenosine and related nucleotides in the control of calcium movement across the presynaptic membrane.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alnaes, E., Rahamimoff, R.: On the role of mitochondria in transmitter release from motor nerve terminals. J. Physiol. (Lond.)248, 285–306 (1975).
Blaustein, M. P.: Effects of potassium, veratridine and scorpion venom on calcium accumulation and transmitter release by nerve terminalsin vitro. J. Physiol. (Lond.)247, 617–655 (1975).
Burnstock, G.: Purinergic nerves. Pharmacol. Rev.24, 509–581 (1972).
Burnstock, G.: Purinergic transmission. In: Handbook of Psychopharmacology, Vol. 5 (Iversen, L. L., Iversen, S. D., Snyder, S. H., eds.), pp. 131–195. New York-London: Plenum Press. 1975.
Dowdall, M. J.: Adenine nucleotides in cholinergic transmission: Presynaptic aspects. In: Nucleotides and Neurotransmission. Conferences on Neurobiologie de Gif. Gif, 1977 (Abst.), pp. 7–8. 1977.
Dowdall, M. J., Boyne, A. F., Whittaker, V. P.: Adenosine triphosphate, a constituent of cholinergic synaptic vesicles. Biochem. J.140, 1–12 (1974).
Hodgkin, A. L., Huxley, A. F.: The components of membrane conductance in the giant axon of Loligo. J. Physiol. (Lond.)116, 473–496 (1952).
Israel, M., Meunier, F. M.: The release of ATP triggered by transmitter action and its possible physiological significance: Retrograde transmission. J. Physiol. (Paris)74, 485–490 (1978).
Israel, M., Lesbats, B., Meunier, F. M., Stinnakre, J.: Postsynaptic release of adenosine triphosphate induced by single impulse transmitter action. Proc. R. Soc. Lond.B 193, 461–468 (1976 a).
Israel, M., Manaranche, R., Mastour-Frachon, P., Morel, N.: Isolation of pure cholinergic nerve endings from the electric organ ofTorpedo marmorata. Biochem. J.160, 113–115 (1976 b).
Israel, M., Lesbats, B., Manaranche, R., Marsal, J., Mastour-Frachon, P., Meunier, F. M.: Related changes in amounts of Ach and ATP in resting and active Torpedo nerve electroplaque synapses. J. Neurochem.28, 1259–1267 (1977).
Israel, M., Lesbats, B., Manaranche, R., Meunier, F. M., Frachon, P.: Retrograde inhibition of transmitter release by ATP. J. Neurochem.34, 923–932 (1980).
Kendrick, N. C., Blaustein, M. P., Fried, R. C., Ratzlaff, R. W.: ATP-dependent calcium storage in presynaptic nerve terminals. Nature265, 246–249 (1977).
Kuroda, Y., McIlwain, H.: Uptake and release of (14C) adenine derivatives at beds of mammalian cortical synaptosomes in a superfusion system. J. Neurochem.22, 691–699 (1974).
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., Randall, R. J.: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem.193, 265–275 (1951).
Meunier, F. M., Morel, N.: Adenosine uptake by cholinergic synaptosomes from Torpedo electric organ. J. Neurochem.31, 845–851 (1978).
Meunier, F. M., Israel, M., Lesbats, B.: Release of ATP from stimulated nerve electroplaque junctions. Nature257, 407–408 (1975).
Nagy, A., Baker, R. R., Morris, S. J., Whittaker, V. P.: The preparation and characterization of synaptic vesicles of high purity. Brain Res.109, 285–309 (1976).
Nagy, A., Shuster, T. A., Rosenberg, M. D.: Adenosine triphosphatase activity at the external surface of chicken brain synaptosomes. J. Neurochem.40, 226–234 (1983).
Ribeiro, J. A., Walker, J.: The effects of ATP and ADP on transmission at the rat and frog neuromuscular junctions. Br. J. Pharmacol.54, 213–218 (1975).
Ribeiro, J. A., Sa-Almeida, A. M., Namorado, J. M.: Adenosine and adenosine triphosphate decrease45Ca uptake by synaptosomes stimulated by potassium. Biochem. Pharmacol.28, 1297–1300 (1979).
Rosenblatt, D. E., Lauter, C. J., Trams, E. G.: Deficiency of a Ca2+-ATPase in brains of seizure prone mice. J. Neurochem.27, 1299–1304 (1976).
Satchell, D. D., Lynch, A., Burke, P. M., Burnstock, G.: Potentiation of the effects of exogenously applied ATP and purinergic nerve stimulation on the guinea pig taenia coli by dipyridamole and hexobenzidine. Eur. J. Pharmacol.19, 343–350 (1972).
Sawynok, J., Jhamandas, K. H.: Inhibition of acetylcholine release from cholinergic nerves by adenosine, adenosine nucleotides, and morphine: Antagonism by theophylline. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.197, 379–390 (1976).
Shubert, P., Lee, K., Kreutzberg, G. W.: Formation and function of adenosine in the CNS. I. Release and modulatory action. Proc. Int. Soc. Neurochem. Nottingham 1981, pp. 111. 1981.
Shillinsky, E. M.: On the association between transmitter secretion and the release of adenine nucleotides from mammalian motor nerve terminals. J. Physiol. (Lond.)247, 145–162 (1975).
Vizi, E. S., Knoll, J.: The inhibitory effect of adenosine and related nucleotides on the release of acetylcholine. Neuroscience1, 391–398 (1976).
Weller, M., Morgan, I. G.: A possible role of the phosphorylation of synaptic membrane proteins in the control of calcium ion permeability. Biochem. Biophys. Acta465, 527–534 (1977).
White, T. D.: Release of ATP from a synaptosomal preparation by elevated extracellular K+ and by veratridine. J. Neurochem30, 329–336 (1978).
White, T. D., Potter, P., Wonnacott, S.: Depolarization-induced release of ATP from cortical synaptosomes is not associated with acetylcholine release. J. Neurochem.34, 1109–1112 (1980).
Whittaker, V. P., Essman, W. E., Dowe, G. H. C.: The isolation of pure cholinergic synaptic vesicles from the electric organs of Elasmobranch fish of the familyTorpedinidae. Biochem. J.128, 833–846 (1972).
Zimmermann, H.: Turnover of adenine nucleotides in cholinergic synaptic vesicles of the Torpedo electric organ. Neuroscience3, 827–836 (1978).
Zimmermann, H., Dowdall, M. J., Lane, D. A.: Purine salvage at the cholinergic nerve endings of the Torpedo electric organ: The central role of adenosine. Neuroscience4, 979–993 (1979).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Quintana, J. Adenosine and related nucleotides alter calcium uptake in depolarized synaptosomes of torpedo electric organ. J. Neural Transmission 64, 271–284 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01256472
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01256472