Summary
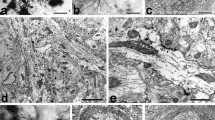
In an extension of our previous light microscopic observations, a type of neuron which shows GABA-like immunoreactivity was identified and described in the ectostriatal core of young domestic chicks, using pre- and postembedding electron microscopic immunocytochemistry. Large GABA immunopositive (GABA+) cells are characterized by an ovoidal or polygonal soma of 12–16 μm diameter, uniformly distributed nuclear chromatin, a prominent Golgi apparatus and an abundance of rough endoplasmic reticulum. In addition to axodendritic terminals, large GABA neurons receive numerous axosomatic synapses of both symmetrical and asymmetrical types covering a substantial part of their perikaryal surface. Axosomatic terminals with symmetrical junctions are usually immunoreactive to GABA whereas the boutons with asymmetrical synaptic specialization are immunonegative. GABA+ boutons also synapse with dendritic spine necks presumably belonging to projection neurons. These terminals usually contain loosely packed synaptic vesicles without any marked accumulation near the synaptic cleft. Large GABA+ terminals with densely packed vesicles were found to synapse with axon hillocks. Based on known descriptions of ectostriatal cytoarchitecture and synaptology, it is suggested that the GABA+ cells of chick ectostriatum represent inhibitory interneurons which may be equivalent to GABAergic non-pyramidal neuronal types of mammalian visual cortex. GABA+ axosomatic synapses afferent to large GABA cells are likely to form the structural basis for a disinhibitory mechanism in the avian ectostriatum.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bagnoli, P., Fontanesi, G., Streit, P., Domenici, L. &Alesci, R. (1989) Changing distribution of GABA-like immunoreactivity in pigeon visual areas during the early posthatching period and effects of retinal removal on tectal GABAergic systems.Visual Neuroscience 3, 491–508.
Bartheld, C. S. Von, Code, R. A. &Rubel, E. W. (1989) GABAergic neurons in brainstem auditory nuclei of the chick: distribution, morphology and connectivity.Journal of Comparative Neurology 287, 470–83.
Benowitz, L. I. (1980) Functional organization of the avian telencephalon. InComparative Neurology of the Telencephalon (edited byEbbesson, S. O. E.) pp. 389–421. New York and London: Plenum.
Benowitz, L. I. &Karten H. J. (1976) Organization of the tectofugal visual pathway in the pigeon: a retrograde transport study.Journal of Comparative Neurology 167, 503–20.
Bilkey, D. K. &Goddard, G. V. (1985) Medial septal facilitation of hippocampal granule cell activity is mediated by inhibition of inhibitory interneurons.Brain Research 361, 99–106.
Cherkin, A. (1969) Kinetics of memory consolidation: role of amnestic treatment parameters.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 63, 1094–101.
Csillag, A., Bourne, R. C., Patel, S. N., Stewart, M. G. &Tömböl, T. (1989) Localization of GABA-like immunoreactivity in the ectostriatum of domestic chicks: GABA immunocytochemistry combined with Golgi impregnation.Journal of Neurocytology 18, 369–79.
Csillag, A., Stewart, M. G., Curtis, E. M. &Rose, S. P. R. (1986) GABAergic structures in the chick forebrain. An autoradiographic study combined with GABA-immunocytochemistry.Society for Neuroscience Abstracts 12, 443.
Csillag, A., Stewart, M. G. &Curtis, E. M. (1987) GABAergic structures in the chick telencephalon: GABA immunocytochemistry combined with light and electron microscope autoradiography, and Golgi impregnation.Brain Research 437, 283–97.
Domenici, L., Waldvogel, H-J., Matute, C. &Streit, P. (1988) Distribution of GABA-like immunoreactivity in the pigeon brain.Neuroscience 25, 931–50.
Freund, T. F. &Antal, M. (1988) GABA-containing neurons in the septum control inhibitory interneurons in the hippocampus.Nature 336, 170–3.
Freund, T. F., Martin, K. A. C., Smith, A. D. &Somogyi, P. (1983) Glutamate decarboxylase-immunoreactive terminals of Golgi impregnated axoaxonic cells and of presumed basket cells in synaptic contact with pyramidal neurons of the cat's visual cortex.Journal of Comparative Neurology 221, 263–78.
Gabbott, P., Somogyi, J., Stewart, M. G. &Hámori, J. (1986) GABA-immunoreactive neurons in the rat cerebellum: a light and electron microscope study.Journal of Comparative Neurology 251, 474–90.
Granda, R. H. &Crossland, W. J. (1989) GABA-like immunoreactivity of neurons in the chicken diencephalon and mesencephalon.Journal of Comparative Neurology 287, 455–69.
Hall, K., Brauth, S. E. &Kitt, C. A. (1984) Retrograde transport of [3H]GABA in the striatotegmental system of the pigeon.Brain Research 310, 157–63.
Hámori, J., Takács, J., Verley, R., Petrusz, P. &Farkas-Bargeton, E. (1990) Plasticity of GABA- and of glutamate-containing terminals in the mouse thalamic ventrobasal complex deprived of vibrissal afferents. An immunogold — electron microscopic study.Journal of Comparative Neurology 302, 739–48.
Hodgson, A. J., Penke, B., Erdei, A., Chubb, I. W. &Somogyi, P. (1985) Antiserum to γ-aminobutyric acid. I. Production and characterisation using a new model system.Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry 33, 229–39.
Hodos, W. &Karten, H. J. (1970) Visual intensity and pattern discrimination deficits after lesions of ectostriatum in pigeons.Journal of Comparative Neurology 140, 53–68.
Horn, G. (1985)Memory, Imprinting and the Brain: An Inquiry into Mechanisms. Oxford: Clarendon.
Hunt, S. P. &Künzle, H. (1976) Selective uptake and transport of label within three identified neuronal systems after injection of3H-GABA into the pigeon optic tectum: an autoradiographic and Golgi study.Journal of Comparative Neurology 170, 173–90.
Jalilian Tehrani, M. H. &Barnes, E. M. Jr. (1986) Ontogeny of the GABA receptor complex in chick brain: studiesin vivo andin vitro.Developmental Brain Research 25, 91–8.
Jong, Y-J., Thampy, K. G. &Barnes, E. M. Jr. (1986) Ontogeny of GABAergic neurons in chick brain: studiesin vivo andin vitro.Developmental Brain Research 25, 83–90.
Kallén, B. (1962) Embryogenesis of brain nuclei in the chick telencephalon.Ergebnisse der Anatomie und Entwicklungsgeschichte 36, 62–82.
Karten, H. J. &Hodos, W. (1970) Telencephalic projections of the nucleus rotundus in the pigeon (Columba livia).Journal of Comparative Neurology 140, 35–52.
Krnjević, K., Ropert, N. &Casullo, J. (1988) Septohippocampal disinhibition.Brain Research 438, 182–92.
Müller, C. M. (1987) γ-aminobutyric acid immunoreactivity in brainstem auditory nuclei of the chicken.Neuroscience Letters 77, 272–6.
Müller, C. M. (1988) Distribution of GABAergic perikarya and terminals in the centres of the higher auditory pathway of the chicken.Cell and Tissue Research 252, 99–106.
Müller, C. M. &Scheich, H. (1987) GABAergic inhibition increases the neuronal selectivity to natural sounds in the avian auditory forebrain.Brain Research 414, 376–80.
Nixdorf, B. E. (1989) Ultrastructural analysis of the development and maturation of synapses and subsynaptic structures in the ectostriatum of the zebra finch.Journal of Comparative Neurology 290, 472–86.
Nixdorf, B. E. &Bischof, H. -J. (1982) Afferent connections of the ectostriatum and visual Wulst in the zebra finch (Taeniopygia guttata castanotis Gould) — an HRP study.Brain Research 248, 9–17.
Rose, S. P. R. (1985) Passive avoidance training in the chick: a model for the analyis of the cell biology of memory storage. InNeural Mechanisms of Conditioning (edited byAlkon, D. L. &Woody, C. D.) pp. 232–48. New York: Plenum.
Somogyi, P. &Hodgson, A. J. (1985) Antiserum to γ-aminobutyric acid. III. Demonstration of GABA in Golgi-impregnated neurons and in conventional electron microscopic sections of cat striate cortex.Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry 33, 249–57.
Somogyi, P., Hodgson, A. J., Chubb, I. W., Penke, B. &Erdei, A. (1985) Antiserum to gamma-aminobutyric acid. II. Immunocytochemical application to the central nervous system.Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry 33, 240–8.
Tömböl, T., Maglóczky, Zs., Stewart, M. G. &Csillag, A. (1988) The structure of chicken ectostriatum. I. Golgi study.Journal für Hirnforschung 29, 525–46.
Watanabe, M., Ito, H. &Ikushima, M. (1985) Cytoarchitecture and ultrastructure of the avian ectostriatum: afferent terminals from the dorsal telencephalon and some nuclei in the thalamus.Journal of Comparative Neurology 236, 241–57.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Csillag, A. Large GABA cells of chick ectostriatum: anatomical evidence suggesting a double GABAergic disinhibitory mechanism. An electron microscopic immunocytochemical study. J Neurocytol 20, 518–528 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01252278
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01252278