Abstract
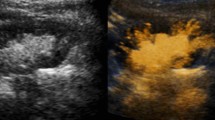
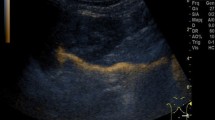
Vesicoureteral reflux (VUR) is common in children with urinary tract infections (UTI) and may result in renal scarring or reflux nephropathy. To date, the primary diagnostic tool has been voiding cystourethrography (VCUG). A new technique for evaluation of grade 1 and 2 VUR is described using color Doppler imaging-mode cystography (CDIMC): 77 children, aged 7 months to 14 years, were examined for VUR by CDIMC and standard VCUG. According to the established reflux sonography (US) using a real-time mode, all patients selected for this study had a normal urinary tract on conventional gray-scale US. We studied 154 ureters, and a total of 31 were found to be refluxing on CDIMC and 30 on VCUG. A positive sonogram was defined as visualization of Doppler signals from the bladder to the ureter during the course of bladder filling. Taking VCUG as the gold standard, we had ten false-positive findings. The false-positive rate of 18.5% may have been due to the shorter observation time of fluoroscopy. Comparison of the two methods shows CDIMC to be 70% sensitive with a specificity of 92% in the detection of VUR grade 1 and 2. To evaluate the incidence of asymptomatic low-grade VUR in a non-infected population, a second series of 38 children (19 males, 19 females) aged 3 to 15 years (mean 8.8 years) with normal urologic status and urine cultures were studied by color Doppler imaging mode (CDIM) for detection of asymptomatic low-grade VUR. Four children were found to have a unilateral refluxing ureter. The incidence of VUR in children with a normal urinary tract and no prior UTI was 10.5%. In conclusion, CDIMC can be used as a possible alternative to standard VCUG for the screening and follow-up of low-grade VUR. In addition, our study indicates that asymptomatic grade 1 and 2 reflux might be a physiological condition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alzen G, Wildberger JE (1995) Sonographische Refluxprfüng mit Luft. Pädiat prax 49: 35–39
Ashcraft KW (1990) Vesicoureteric reflux. In: Ashcraft KW (ed) Pediatric urology. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 151–173
Atala A, Wible HJ, Share JC, Carr MC, Retik AB, Mandell J (1993) Sonography with sonicated albumin in the detection of vesicoureteral reflux. J Urol 150: 756–758
Bailey RR (1984) Long-term follow-up of infants with gross vesicoureteral reflux. Contrib Nephrol 39: 146–151
Blane CE, Dipietro MA, Zerin MJ, Sedman AB, Bloom D (1993) Renal sonography is not a reliable screening examination for vesicoureteral reflux. J Urol 150: 752–755
Burger RH, Smith C (1971) Hereditary and familial vesicoureteral reflux. J Urol 106: 845–848
Chapman SJ, Chantler C, Haycock GB (1988) Radionuclide cystography in vesicoureteric reflux. Arch Dis Child 63: 650–651
Deeg KH, Hahn H, Tröger J (1995) Kommentare zur sonographischen Refluxdiagnostik. Pädiat prax 49: 59–63
Hanbury DC, Coulden RA, Farman P, Sherwood T (1990) Ultrasound cystography in the diagnosis of vesicoureteric reflux. Br J Urol 65: 250–253
Hodson CJ, Cotran RS (1982) Reflux nephropathy. Hospital Practice 17: 133–156
Hofmann V (1981) Ultraschalldiagnostik beim vesico-ureteralen Reflux im Kindesalter. Z Urol Nephrol 74: 249–253
Hofmann V (1995) Stellenwert der sonographischen Refluxdiagnostik. Pädiat prax 49: 41–48
Hofmann V, Beyer HJ (1985) Der diagnostische Stellenwert der Sonographie beim vesico-ureteralen Reflux im Säuglings- und Kindesalter. Mschr Kihderheilk 133: 834–839
Jequier S, Jequier JC (1989) Reliability of voiding cystourethrography to detect reflux. AJR 153: 807–810
Jerkins GR, Noe HN (1982) Familial vesicoureteral reflux: a prospective study. J Urol 128: 774–778
Kangarloo HK, Gold RH, Fine RN (1985) Urinary tract infection in infants and children evaluated by ultrasound. Radiology 154: 367–373
Kessler RM, Altman DH (1982) Real-time sonography detection of vesicoureteral reflux in children AJR 138: 1033–1036
Lebowitz RL, Mandell J (1987) Urinary tract infection in children: putting radiology in its place. Radiology 165: 1–3
Lebowitz RL, Olbing H, Parkkulainen KV, Smellie LM, Tamminen-Möbius TE (1985) International reflux study in children. Pediatr Radiol 15: 105–109
Marshall JL, Johnson ND, De Campo MP (1990) Vesicoureteric reflux in children: prediction with color doppler imaging. Radiology 175: 355–358
Nasrallah PF, Conway JJ, King LR, Belman AB, Weiss S (1978) Quantitative nuclear cystogram: aid in determining spontaneous resolution of vesicoureteral reflux. Urology 12: 654–658
Paltiel HJ, Rupich RC, Kiruluta GH (1992) Enhanced detection of vesicoureteral reflux in infants and children with use of cyclic voiding cystourethrography. Radiology 184: 753–755
Peeden JN, Noe HN (1992) Is it practical to screen for familial vesicoureteral reflux within a private pediatric practice? Pediatrics 89: 758–760
Ransley PG (1978) Vesicoureteral reflux: continuing surgical dilemma. Urology 3: 246–249
Ransley PG, Risdon RA (1981) Reflux nephropathy: effects of antimicrobial therapy in the evolution of the early pyelonephritic scar. Kidney Int 20: 733–742
Report of the International Reflux Commitee (1981) Medical versus surgical treatment of primary vesicoureteral reflux. Pediatrics 67: 392–400
Rohden v. L, Bosse U, Wiemann D (1995) Refluxsonographie bei Kindern mit einem Ultraschallkontrastmittel im Vergleich zur Röntgenmiktionszystourethrographie. Pädiat prax 49: 49–58
Salih M, Baltaci S, Kilic S, Anafarta K, Bedük Y (1994) Color flow Doppler sonography in the diagnosis of vesicoureteric reflux, Eur Urol 26: 93–97
Schneider K, Jablonski C, Kohn M, Fendel H (1984) Screening for vesicoureteral reflux in children using real-time sonography. Pediatr Radiol 14: 400–403
Smellie JM (1980) Childhood urinary infections and their significance. In: Asscher AW (ed) The management of urinary tract infection. Medicine Publishing, Oxford, pp 29–38
Wallace DMA, Rothwell DL, Williams DI (1978) The long-term follow-up of surgically treated vesicoureteric reflux. Br J Urol 50: 479–482
White RHR (1987) Management of urinary tract infection. Arch Dis Child 26: 421–427
Zerin MJ (1993) Impact of contrast medium temperature on bladder capacity and cystographic diagnosis of vesicoureteral reflux in children. Radiology 187: 161–164
Zerin MJ, Chen E, Ritchey ML, Bloom DA (1993) Bladder capacity as measured at voiding; cystourethrography in children: relationship to toilet training and frequency of micturition. Radiology 187: 803–806
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haberlik, A. Detection of low-grade vesicoureteral reflux in children by color Doppler imaging mode. Pediatr Surg Int 12, 38–43 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01194800
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01194800